【视觉SLAM十四讲】建图
本文介绍了从稀疏路标点到稠密地图构建的关键技术。针对单目相机无法直接获取深度信息的问题,提出通过极线搜索和块匹配实现稠密重建。具体采用SAD、SSD和NCC三种相似度度量方法进行像素块匹配,并利用深度滤波器将观测信息融合到高斯分布中,逐步优化深度估计。通过推导几何不确定性模型,设定收敛阈值判断深度数据稳定性。最后给出基于OpenCV和Sophus的代码实现框架,包括极线搜索、深度滤波更新等核心功能
在此之前,我们主要关注的是定位,即稀疏路标点主要用于计算相机位姿,但是仅有稀疏特征点显然是不够的,机器人无法得知哪里是桌子、哪里是墙,无法进行导航和避障。因此在这一讲,主要目标是构建稠密地图
单目稠密重建
极线搜索与块匹配
回顾一下视觉里程计 1 中对极几何的内容,极线搜索其实和三角测量的思路很像
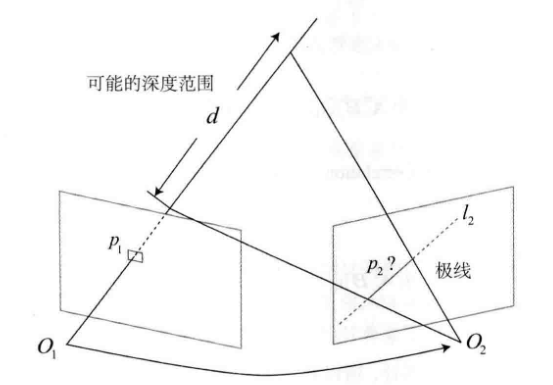
极线搜索
假设我们在第一帧看到一个特征点 p 1 p_{1} p1,由于此时我们并不知道其深度,所以它对应的空间点 P P P 可能在一条射线的任意一点上
在第二帧中,这条射线的投影就是一条线,即极线。那么第二帧中的匹配点,必然落在极线上,只需在极线上搜索就能找到 p 2 p_{2} p2
必须知道相机之间的运动,否则无法确定极线
块匹配
现在问题来到了如何快速确定 p 2 p_{2} p2 ,由于单个像素的灰度值可区分度太低了,我们可以在 p 1 p_{1} p1 周围取一个像素块,并在极线上取一个同样大小的像素块滑动,寻找最相似的方块。需要注意的是,只有假设整个小块的灰度值不变,比较才有意义
相似度衡量指标:
- SAD:绝对差之和。计算简单,速度快
S ( A , B ) S A D = ∑ i , j ∣ A ( i , j ) − B ( i , j ) ∣ S(A,B)_{SAD}=\sum_{i,j}|A(i,j)-B(i,j)| S(A,B)SAD=i,j∑∣A(i,j)−B(i,j)∣ - SSD:平方差之和。对大误差敏感
S ( A , B ) S S D = ∑ i , j ( A ( i , j ) − B ( i , j ) ) 2 S(A,B)_{SSD}=\sum_{i,j}(A(i,j)-B(i,j))^2 S(A,B)SSD=i,j∑(A(i,j)−B(i,j))2 - NCC:归一化互相关。计算复杂,但是鲁棒性强(相似度,接近 1 表示相似)
S ( A , B ) N C C = ∑ i , j A ( i , j ) B ( i , j ) ∑ i , j A ( i , j ) 2 ∑ i , j B ( i , j ) 2 S(A,B)_{NCC}=\frac{\sum_{i,j}A(i,j)B(i,j)}{\sqrt{ \sum_{i,j}A(i,j)^2\sum_{i,j}B(i,j)^2 }} S(A,B)NCC=∑i,jA(i,j)2∑i,jB(i,j)2∑i,jA(i,j)B(i,j)
假设现在使用 NCC 进行相似性度量,可以得到类似数据
![[NCC.png]]
该分布存在多个峰值,所以一般倾向于使用概率分布而非单一数值描述深度
深度滤波器
假设深度的分布服从高斯分布
P ( d ) ∼ N ( μ , σ 2 ) P(d)\sim N(\mu,\sigma^2) P(d)∼N(μ,σ2)
- μ \mu μ(均值):要估计的深度值
- σ 2 \sigma^2 σ2(方差):深度值的不程度
接下来我们要解决的问题是一个信息融合问题,假设新观测的信息也满足高斯分布,随着相机的不断移动,我们不断把新的观测融合到现有的高斯分布中,使其向收敛靠近
已知两个高斯分布的乘积仍为高斯分布,有
μ f u s e = σ o b s 2 μ + σ 2 μ o b s σ 2 + σ o b s 2 , σ f u s e 2 = σ 2 σ o b s 2 σ 2 + σ o b s 2 \mu_{fuse}=\frac{\sigma^2_{obs}\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma^2+\sigma^2_{obs}},\quad\sigma^2_{fuse}=\frac{\sigma^2\sigma^2_{obs}}{\sigma^2+\sigma^2_{obs}} μfuse=σ2+σobs2σobs2μ+σ2μobs,σfuse2=σ2+σobs2σ2σobs2
仅考虑几何不确定性,已知 p 1 p_{1} p1 和 p 2 p_{2} p2 对应,由此观测到 p 1 p_{1} p1 的深度值,求得对应的三维点 P P P 。现在假设极线 l 2 l_{2} l2 存在一个像素的误差,那么最终求得的三维点 P P P ,误差会有多大呢?
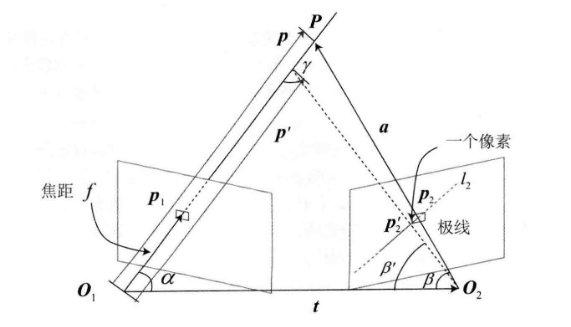
推导的过程就略掉了,直接给出答案
∣ ∣ p ′ ∣ ∣ = ∣ ∣ t ∣ ∣ sin β ′ sin γ ′ ||p'||=||t|| \frac{\sin \beta'}{\sin \gamma'} ∣∣p′∣∣=∣∣t∣∣sinγ′sinβ′
此时可以设
σ o b s = ∣ ∣ p ∣ ∣ − ∣ ∣ p ′ ∣ ∣ \sigma_{obs}=||p||-||p'|| σobs=∣∣p∣∣−∣∣p′∣∣
当不确定性小于某个阈值时,则可以认为深度数据已经收敛
单目稠密建图代码实现
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <fstream>
// parameters
const int boarder = 20; // 边缘宽度
const int width = 640; // 图像宽度
const int height = 480; // 图像高度
const double fx = 481.2f;
const double fy = -480.0f;
const double cx = 319.5f;
const double cy = 239.5f;
const int ncc_windows_size = 3; // NCC窗口半宽度
const int ncc_area = (2 * ncc_windows_size + 1) * (2 * ncc_windows_size + 1); // NCC窗口面积
const double min_cov = 0.1; // 最小方差
const double max_cov = 10; // 最大方差
/**
@brief 使用新图像更新深度图
@param ref 参考图像
@param curr 当前图像
@param T 从参考图像到当前图像的位姿变换
@param depth 深度图
@param depth_cov 深度协方差图
@return 是否更新成功
*/
bool update(const cv::Mat& ref, const cv::Mat& curr, const Sophus::SE3d& T, cv::Mat& depth, cv::Mat& depth_cov2);
/**
* @brief 进行极线搜索
* @param ref 参考图像
* @param curr 当前图像
* @param T 从参考图像到当前图像的位姿变换
* @param pt_ref 参考图像中的点
* @param depth_mu 深度均值
* @param depth_cov 深度协方差
* @param pt_curr 当前图像中的点
* @param epipolar_direaction 极线方向
*/
bool epipolarSearch(const cv::Mat& ref, const cv::Mat& curr, const Sophus::SE3d& T, const Eigen::Vector2d& pt_ref, const double& depth_mu, const double& depth_cov, Eigen::Vector2d& pt_curr, Eigen::Vector2d& epipolar_direaction);
/**
* @brief 更新深度滤波器
* @param pt_ref 参考图像中的点
* @param pt_curr 当前图像中的点
* @param T 从参考图像到当前图像的位姿变换
* @param epipolar_direction 极线方向
* @param depth 深度均值
* @param depth_cov2 深度方差
* @return 是否更新成功
*/
bool updateDepthFilter(const Eigen::Vector2d& pt_ref, const Eigen::Vector2d& pt_curr, const Sophus::SE3d& T, const Eigen::Vector2d& epipolar_direction, cv::Mat& depth, cv::Mat& depth_cov2);
/**
* @brief 计算 NCC
* @param ref 参考图像
* @param curr 当前图像
* @param pt_ref 参考图像中的点
* @param pt_curr 当前图像中的点
* @return NCC值
*/
double NCC(const cv::Mat& ref, const cv::Mat& curr, const Eigen::Vector2d& pt_ref, const Eigen::Vector2d& pt_curr);
// 双线性灰度插值
inline double getBilinearInterpolatedValue(const cv::Mat& img, const Eigen::Vector2d& pt)
{
const uchar* data = &img.data[int(pt(1, 0)) * img.step + int(pt(0, 0))];
double xx = pt(0, 0) - floor(pt(0, 0));
double yy = pt(1, 0) - floor(pt(1, 0));
return ((1 - xx) * (1 - yy) * double(data[0]) + xx * (1 - yy) * double(data[1]) +
(1 - xx) * yy * double(data[img.step]) + xx * yy * double(data[img.step + 1])) / 255.0;
}
// ============================
// 显示估计的深度图
void plotDepth(const cv::Mat& depth_truth, const cv::Mat& depth_estimate);
// 像素转相机坐标系
inline Eigen::Vector3d px2cam(const Eigen::Vector2d px)
{
return Eigen::Vector3d((px(0, 0) - cx) / fx, (px(1, 0) - cy) / fy, 1);
}
// 相机坐标系转像素
inline Eigen::Vector2d cam2px(const Eigen::Vector3d p_cam)
{
return Eigen::Vector2d(p_cam(0, 0) * fx / p_cam(2, 0) + cx, p_cam(1, 0) * fy / p_cam(2, 0) + cy);
}
// 判断像素点是否在图像内
inline bool inside(const Eigen::Vector2d& px)
{
return px(0, 0) >= boarder && px(0, 0) < width - boarder && px(1, 0) >= boarder && px(1, 0) < height - boarder;
}
// 显示极线匹配
void showEpipolarMatch(const cv::Mat& ref, const cv::Mat& curr, const Eigen::Vector2d& px_ref, const Eigen::Vector2d& px_curr);
// 显示极线
void showEpipolarLine(const cv::Mat& ref, const cv::Mat& curr, const Eigen::Vector2d& px_ref, const Eigen::Vector2d& px_min_curr, const Eigen::Vector2d& px_max_curr);
// 评测深度估计
void evaluateDepth(const cv::Mat& depth_truth, const cv::Mat& depth_estimate);
// ============================
bool update(const cv::Mat& ref, const cv::Mat& curr, const Sophus::SE3d& T, cv::Mat& depth, cv::Mat& depth_cov2)
{
// 从边缘开始遍历每个像素
for (int x = boarder; x < width - boarder; x++)
{
for (int y = boarder; y < height - boarder; y++)
{
// 深度收敛或发散
if (depth_cov2.ptr<double>(y)[x] < min_cov || depth_cov2.ptr<double>(y)[x] > max_cov)
continue;
Eigen::Vector2d pt_curr;
Eigen::Vector2d epipolar_direction;
bool ret = epipolarSearch(ref, curr, T, Eigen::Vector2d(x, y), depth.ptr<double>(y)[x], sqrt(depth_cov2.ptr<double>(y)[x]), pt_curr, epipolar_direction);
if (ret == false)
continue;
// showEpipolarMatch(ref, curr, Eigen::Vector2d(x, y), pt_curr);
updateDepthFilter(Eigen::Vector2d(x, y), pt_curr, T, epipolar_direction, depth, depth_cov2);
}
}
return true;
}
bool epipolarSearch(const cv::Mat& ref, const cv::Mat& curr, const Sophus::SE3d& T, const Eigen::Vector2d& pt_ref, const double& depth_mu, const double& depth_cov, Eigen::Vector2d& pt_curr, Eigen::Vector2d& epipolar_direaction)
{
Eigen::Vector3d f_ref = px2cam(pt_ref);
f_ref.normalize();
Eigen::Vector3d P_ref = f_ref * depth_mu; // 3d 点在参考帧下的坐标
Eigen::Vector2d px_mean_curr = cam2px(T * P_ref); // 3d 点在当前帧下的像素坐标
double d_min = depth_mu - 3 * depth_cov, d_max = depth_mu + 3 * depth_cov; // 深度范围在mu±3sigma内
if (d_min < 0.1)
d_min = 0.1;
Eigen::Vector2d px_min_curr = cam2px(T * (f_ref * d_min));
Eigen::Vector2d px_max_curr = cam2px(T * (f_ref * d_max));
Eigen::Vector2d epipolar_line = px_max_curr - px_min_curr; // 极线
epipolar_direaction = epipolar_line; // 极线方向
epipolar_direaction.normalize();
double half_length = 0.5 * epipolar_line.norm();
if (half_length > 100)
half_length = 100;
// showEpipolarLine(ref, curr, pt_ref, px_min_curr, px_max_curr);
// 在极线上搜索最佳匹配点
double best_ncc = -1.0;
Eigen::Vector2d best_px_curr;
for (double l = -half_length; l <= half_length; l += 0.7)
{
Eigen::Vector2d px_curr = px_mean_curr + l * epipolar_direaction; // 待匹配点
if (!inside(px_curr))
continue;
double ncc = NCC(ref, curr, pt_ref, px_curr);
if (ncc > best_ncc)
{
best_ncc = ncc;
best_px_curr = px_curr;
}
}
if (best_ncc < 0.85f)
return false;
pt_curr = best_px_curr;
return true;
}
double NCC(const cv::Mat& ref, const cv::Mat& curr, const Eigen::Vector2d& pt_ref, const Eigen::Vector2d& px_curr)
{
double mean_ref = 0, mean_curr = 0;
std::vector<double> values_ref, values_curr;
for (int x = -ncc_windows_size; x <= ncc_windows_size; x++)
{
for (int y = -ncc_windows_size; y <= ncc_windows_size; y++)
{
double value_ref = double(ref.ptr<uchar>(int(y + pt_ref(1, 0)))[int(x + pt_ref(0, 0))]) / 255.0;
mean_ref += value_ref;
double value_curr = getBilinearInterpolatedValue(curr, Eigen::Vector2d(px_curr(0, 0) + x, px_curr(1, 0) + y));
mean_curr += value_curr;
values_ref.push_back(value_ref);
values_curr.push_back(value_curr);
}
}
mean_ref /= ncc_area;
mean_curr /= ncc_area;
// 计算 NCC
double numerator = 0, demoninator1 = 0, denominator2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < values_ref.size(); i++)
{
double n = (values_ref[i] - mean_ref) * (values_curr[i] - mean_curr);
numerator += n;
demoninator1 += (values_ref[i] - mean_ref) * (values_ref[i] - mean_ref);
denominator2 += (values_curr[i] - mean_curr) * (values_curr[i] - mean_curr);
}
return numerator / sqrt(demoninator1 * denominator2 + 1e-10);
}
bool updateDepthFilter(const Eigen::Vector2d& px_ref, const Eigen::Vector2d& px_curr, const Sophus::SE3d& T, const Eigen::Vector2d& epipolar_direction, cv::Mat& depth, cv::Mat& depth_cov2)
{
// 三角化计算深度
// 这里的 T 是参考帧 -> 当前帧的变换, 需要取逆
Sophus::SE3d T_inv = T.inverse();
Eigen::Vector3d f_ref = px2cam(px_ref);
f_ref.normalize();
Eigen::Vector3d f_curr = px2cam(px_curr);
f_curr.normalize();
// d_ref * f_ref = d_curr * (R * f_curr) + t
// Rf = R * f_curr
// 构建误差 e = d_ref * f_ref - d_curr * RF - t
// 令误差最小,构建方程
// [f_ref^T - f_ref^T * Rf][d_ref] = [f_ref^T * t]
// [Rf^T * f_ref, -Rf^T * Rf][d_curr] [Rf^T * t]
Eigen::Vector3d t = T_inv.translation();
Eigen::Vector3d Rf = T_inv.so3() * f_curr;
Eigen::Vector2d b = Eigen::Vector2d(t.dot(f_ref), t.dot(Rf));
Eigen::Matrix2d A;
A(0, 0) = f_ref.dot(f_ref);
A(0, 1) = -f_ref.dot(Rf);
A(1, 0) = -A(0, 1);
A(1, 1) = -Rf.dot(Rf);
Eigen::Vector2d ans = A.inverse() * b;
Eigen::Vector3d x1 = ans[0] * f_ref; // 参考帧下的3d点
Eigen::Vector3d x2 = t + ans[1] * Rf; // 当前帧下的3d点
Eigen::Vector3d min_pt = (x1 + x2) / 2.0;
double depth_estimate = min_pt.norm();
// 计算深度不确定性
Eigen::Vector3d p = f_ref * depth_estimate;
Eigen::Vector3d a = p - t;
double t_norm = t.norm();
double a_norm = a.norm();
double alpha = acos(f_ref.dot(t) / t_norm);
double beta = acos(-a.dot(t) / (a_norm * t_norm));
Eigen::Vector3d f_curr_prime = px2cam(px_curr + epipolar_direction);
f_curr_prime.normalize();
double beta_prime = acos(f_curr_prime.dot(-t) / t_norm);
double gamma = M_PI - alpha - beta_prime;
double p_prime = t_norm * sin(beta_prime) / sin(gamma);
double d_cov = p_prime - depth_estimate;
double d_cov2 = d_cov * d_cov;
// 高斯融合
double mu = depth.ptr<double>(int(px_ref(1, 0)))[int(px_ref(0, 0))];
double sigma2 = depth_cov2.ptr<double>(int(px_ref(1, 0)))[int(px_ref(0, 0))];
double mu_fuse = (d_cov2 * mu + sigma2 * depth_estimate) / (sigma2 + d_cov2);
double sigma2_fuse = (sigma2 * d_cov2) / (sigma2 + d_cov2);
depth.ptr<double>(int(px_ref(1, 0)))[int(px_ref(0, 0))] = mu_fuse;
depth_cov2.ptr<double>(int(px_ref(1, 0)))[int(px_ref(0, 0))] = sigma2_fuse;
return true;
}
bool readDatasetFiles(const std::string& path, std::vector<std::string>& color_image_files, std::vector<Sophus::SE3d>& poses, cv::Mat& ref_depth)
{
std::ifstream fin(path + "/first_200_frames_traj_over_table_input_sequence.txt");
if (!fin)
{
std::cerr << "cannot find the pose file!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
while (!fin.eof())
{
std::string image;
fin >> image;
double data[7];
for (double& d : data)
fin >> d;
color_image_files.push_back(path + "/images/" + image);
poses.emplace_back(Sophus::SE3d(Eigen::Quaterniond(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]), Eigen::Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2])));
if (!fin.good())
break;
}
fin.close();
// load reference depth
fin.open(path + "/depthmaps/scene_000.depth");
ref_depth = cv::Mat(height, width, CV_64F);
if (!fin)
return false;
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
{
double depth = 0;
fin >> depth;
ref_depth.ptr<double>(y)[x] = depth / 100.0;
}
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
std::vector<std::string> color_image_files;
std::vector<Sophus::SE3d> poses;
cv::Mat ref_depth;
bool ret = readDatasetFiles("../data/test_data", color_image_files, poses, ref_depth);
if (ret == false)
return -1;
cv::Mat ref = cv::imread(color_image_files[0], cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
Sophus::SE3d pose_ref = poses[0];
double init_depth = 3.0;
double init_cov2 = 3.0;
cv::Mat depth = cv::Mat(height, width, CV_64F, init_depth); // 初始深度均值
cv::Mat depth_cov2 = cv::Mat(height, width, CV_64F, init_cov2); // 初始深度方差
for (int idx = 1; idx < color_image_files.size(); idx++)
{
std::cout << "==== loop ==== " << idx << std::endl;
cv::Mat curr = cv::imread(color_image_files[idx], cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (curr.data == nullptr)
continue;
Sophus::SE3d pose_curr = poses[idx];
Sophus::SE3d T_curr_ref = pose_curr.inverse() * pose_ref;
update(ref, curr, T_curr_ref, depth, depth_cov2);
evaluateDepth(ref_depth, depth);
plotDepth(ref_depth, depth);
cv::imshow("current", curr);
cv::waitKey(1);
}
std::cout << "estimation finished." << std::endl;
cv::imwrite("depth_estimate.png", depth * 100);
return 0;
}
void evaluateDepth(const cv::Mat &depth_truth, const cv::Mat &depth_estimate)
{
double ave_depth_error = 0; // 平均误差
double ave_depth_error_sq = 0; // 平方误差
int cnt_depth_data = 0;
for (int y = boarder; y < depth_truth.rows - boarder; y++)
{
for (int x = boarder; x < depth_truth.cols - boarder; x++)
{
double error = depth_truth.ptr<double>(y)[x] - depth_estimate.ptr<double>(y)[x];
ave_depth_error += error;
ave_depth_error_sq += error * error;
cnt_depth_data++;
}
}
ave_depth_error /= cnt_depth_data;
ave_depth_error_sq /= cnt_depth_data;
std::cout << "Average squared error = " << ave_depth_error_sq << ", average error: " << ave_depth_error << std::endl;
}
像素梯度
这里其实可以很直观的看到纯视觉信息的弊端:依赖于纹理信息。对于诸如杂志,花纹等纹理丰富的目标,视觉信息往往可以推理出较为准确的深度信息;但是对于墙壁等梯度不明显的像素,在块匹配时没有区分性,很容易出现误匹配。
同时,像素梯度也和极线方向相关,当像素梯度和极线方向平行时,沿着加息那做块匹配时,我们可以很明显地判断出匹配度最高点在何处,反而当像素梯度与极线方向平行时,处处的匹配度都是相等的,因此无法得到有效匹配
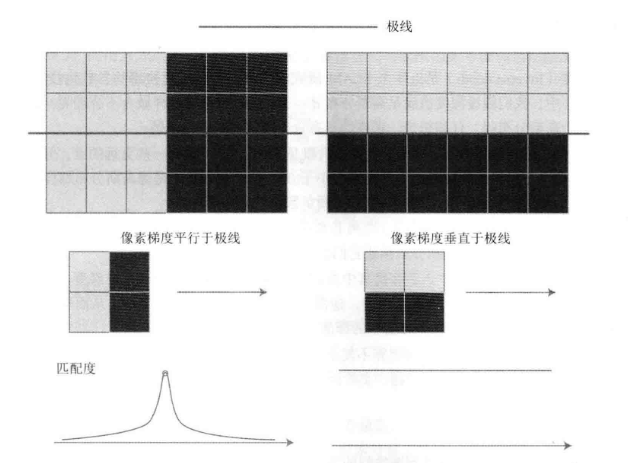
当然,现实往往极线和像素深度的关系不会如此极端,而是偏向于交叉,但是二者关系确切也可做一个算法参考方向
逆深度
既然像素深度无法确定,那么我们是否可以假设其为高斯分布呢?从参数化的角度看,对于三维世界点,我们常用 x , y , z x,y,z x,y,z 三个量来描述,但在 SLAM 系统中,通常使用像素坐标 u , v u,v u,v 和深度值 d d d 来描述三维点。虽然描述的是同一个量,但是前者三个变量的误差是高度耦合的,反映到协方差矩阵中会表现处非对角线元素不为零;而如果使用 u , v , d u,v,d u,v,d ,最起码 u , v u,v u,v 和 d d d 之间是独立的,而且 u , v u,v u,v 通常是确定的,这就可以讲问题简化为一个一维更新问题
此时假设深度值满足高斯分布 d ∼ N ( μ , σ 2 ) d\sim N(\mu,\sigma^2) d∼N(μ,σ2) ,那么问题又来了,如果在室外场景,可能存在距离非常远乃至无穷远处的点,高斯分布难以涵盖这些点。因此,逆深度的用处就彰显出来了,通过对深度取倒数, 原本无穷远处的点将被近似于0,此时深度值可以用高斯分布表示
图像间的变换
做块匹配时,我们假设图像小块在相机运动时保持不变,这个假设在相机平移时是成立的,但当相机发生明显旋转的时候,相关性就会立刻跑偏
因此,在块匹配之前通常要进行一些预处理操作。根据相机模型,如果已知参考帧的一个像素 P R P_R PR ,对应的真实三维点世界坐标 P W P_{W} PW 及其深度 d R d_{R} dR ,那么
d R P R = K ( R R W P W + t R W ) d_{R}P_{R}=K(R_{RW}P_{W}+t_{RW}) dRPR=K(RRWPW+tRW)
在当前帧,也有着同样的变换,故 d c P c = d R K R C W R R W T K − 1 P R + K t C W − K R C W R R W T K t R W d_{c}P_{c}=d_{R}KR_{CW}R_{RW}^TK^{-1}P_{R}+Kt_{CW}-KR_{CW}R_{RW}^TKt_{RW} dcPc=dRKRCWRRWTK−1PR+KtCW−KRCWRRWTKtRW当 d R , P R d_{R},P_{R} dR,PR 已知时,可以计算出 P C P_{C} PC 的投影位置,此时可以通过增量构建仿射变换
[ d u c d u c ] = [ d u c d u d u c d v d v c d u d v c d v ] [ d u d v ] \begin{bmatrix}du_{c}\\d_{uc}\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} \frac{du_{c}}{du}& \frac{du_{c}}{dv}\\ \frac{dv_{c}}{du}& \frac{dv_{c}}{dv} \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}du\\dv\end{bmatrix} [ducduc]=[duducdudvcdvducdvdvc][dudv]
RGBD 点云地图实现
相较于单目和双目相机进行稠密重建,RGB-D 相机的建图显然简单很多,RGB-D 相机可以通过硬件测量深度而无需消耗大量的计算资源来估计;并且,面对缺少纹理的物体,RGB-D 相机也可以测得深度。
最简单、最直接的建图形式就是估算相机位姿,将 RGB-D 数据转化为点云,然后进行拼接得到由离散点组成的点云地图,同时为了更好的视觉效果,也可以融入 rgb 的彩色信息,抑或是使用三角网络(Mesh)、面片(Surfel)进行建图;如果希望知道地图的障碍物信息并在地图上导航,也可以通过体素(Voxel)占据网格地图
点云稠密建图
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <opencv4/opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv4/opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Core>
#include <boost/format.hpp>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/filters/statistical_outlier_removal.h>
int main()
{
std::vector<cv::Mat> colorImg, depthImg;
std::vector<Eigen::Isometry3d> poses;
std::ifstream fin("../data/RGBD_data/pose.txt");
if (!fin)
{
std::cerr << "cannot find pose file!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
boost::format fmt("../data/RGBD_data/%s/%d.%s"); // 图像文件格式
colorImg.push_back(cv::imread((fmt % "color" % (i + 1) % "png").str()));
depthImg.push_back(cv::imread((fmt % "depth" % (i + 1) % "png").str(), -1));
double data[7] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
{
fin >> data[i];
}
Eigen::Quaterniond q(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]);
Eigen::Isometry3d T(q);
T.pretranslate(Eigen::Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2]));
poses.push_back(T);
}
// 计算点云并拼接
// 相机内参
double cx = 319.5;
double cy = 239.5;
double fx = 481.2;
double fy = -480.0;
double depthScale = 5000.0;
typedef pcl::PointXYZRGB PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloud;
PointCloud::Ptr pointCloud(new PointCloud);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
PointCloud::Ptr current(new PointCloud);
cv::Mat color = colorImg[i];
cv::Mat depth = depthImg[i];
Eigen::Isometry3d T = poses[i];
for (int v = 0; v < color.rows; v++)
{
for (int u = 0; u < color.cols; u++)
{
unsigned int d = depth.ptr<unsigned short>(v)[u]; // 深度值
if (d == 0)
continue; // 为0表示没有测量到
Eigen::Vector3d point;
point[2] = double(d) / depthScale;
point[0] = (u - cx) * point[2] / fx;
point[1] = (v - cy) * point[2] / fy;
Eigen::Vector3d pointWorld = T * point;
PointT p;
const cv::Vec3b bgr = color.at<cv::Vec3b>(v, u);
p.x = pointWorld[0];
p.y = pointWorld[1];
p.z = pointWorld[2];
p.b = bgr[0];
p.g = bgr[1];
p.r = bgr[2];
current->points.push_back(p);
}
}
PointCloud::Ptr tmp(new PointCloud);
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval<PointT> statistical_filter; // 统计离群点滤波器,剔除离群点
statistical_filter.setMeanK(50);
statistical_filter.setStddevMulThresh(1.0);
statistical_filter.setInputCloud(current);
statistical_filter.filter(*tmp);
*pointCloud += *tmp;
}
pointCloud->is_dense = false;
std::cout << "点云共有" << pointCloud->size() << "个点。" << std::endl;
pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT> voxel; // 体素格滤波器,降采样
double resolution = 0.03;
voxel.setLeafSize(resolution, resolution, resolution);
PointCloud::Ptr tmp(new PointCloud);
voxel.setInputCloud(pointCloud);
voxel.filter(*tmp);
tmp->swap(*pointCloud);
std::cout << "滤波后,点云共有" << pointCloud->size() << "个点。" << std::endl;
pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary("../data/map/map.pcd", *pointCloud); // 保存点云
}
八叉树地图建图
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <opencv4/opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv4/opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <octomap/octomap.h>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Core>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Geometry>
#include <boost/format.hpp>
int main()
{
std::vector<cv::Mat> colorImg, depthImg;
std::vector<Eigen::Isometry3d> poses;
std::ifstream fin("../data/RGBD_data/pose.txt");
if (!fin)
{
std::cerr << "cannot find pose file!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
boost::format fmt("../data/RGBD_data/%s/%d.%s"); // 图像文件格式
colorImg.push_back(cv::imread((fmt % "color" % (i + 1) % "png").str()));
depthImg.push_back(cv::imread((fmt % "depth" % (i + 1) % "png").str(), -1));
double data[7] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
{
fin >>data[i];
}
Eigen::Quaterniond q(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]);
Eigen::Isometry3d T(q);
T.pretranslate(Eigen::Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2]));
poses.push_back(T);
}
double cx = 319.5;
double cy = 239.5;
double fx = 481.2;
double fy = -480.0;
double depthScale = 5000.0;
octomap::OcTree tree(0.01);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cv::Mat color = colorImg[i];
cv::Mat depth = depthImg[i];
Eigen::Isometry3d T = poses[i];
octomap::Pointcloud pointcloud;
for (int u = 0; u < color.rows; u++)
{
for (int v = 0; v < color.cols; v++)
{
unsigned int d = depth.at<unsigned short>(u, v);
if (d == 0)
continue;
Eigen::Vector3d point;
point[2] = double(d) / depthScale;
point[0] = (v - cx) * point[2] / fx;
point[1] = (u - cy) * point[2] / fy;
Eigen::Vector3d pointWorld = T * point;
pointcloud.push_back(pointWorld[0], pointWorld[1], pointWorld[2]);
}
}
// 将点云存入八叉树地图,给定原点,这样可以计算投射线
tree.insertPointCloud(pointcloud, octomap::point3d(T(0, 3), T(1, 3), T(2, 3)));
}
tree.updateInnerOccupancy();
tree.writeBinary("../data/map/octomap.bt");
}

DAMO开发者矩阵,由阿里巴巴达摩院和中国互联网协会联合发起,致力于探讨最前沿的技术趋势与应用成果,搭建高质量的交流与分享平台,推动技术创新与产业应用链接,围绕“人工智能与新型计算”构建开放共享的开发者生态。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容





所有评论(0)