AD9361,数据接口
CMOSLVDS
CMOS



OSERDESE2为 DDR模式,修改模式为4:1 DDR模式,CLK与CLKDIV为2倍关系。
LVDS



Xilinx原语IBUFDS、OBUFDS
IBUFDS、和OBUFDS都是差分信号缓冲器,用于不同电平接口之间的缓冲和转换。IBUFDS 用于差分输入,OBUFDS用于差分输出。
IBUFDS

https://docs.amd.com/r/en-US/ug953-vivado-7series-libraries/IBUFDS
// IBUFDS : In order to incorporate this function into the design,
// Verilog : the following instance declaration needs to be placed
// instance : in the body of the design code. The instance name
// declaration : (IBUFDS_inst) and/or the port declarations within the
// code : parenthesis may be changed to properly reference and
// : connect this function to the design. All inputs
// : and outputs must be connected.
// <-----Cut code below this line---->
// IBUFDS: Differential Input Buffer
// Kintex-7
// Xilinx HDL Language Template, version 2019.1
IBUFDS #(
.DIFF_TERM("FALSE"), // Differential Termination
.IBUF_LOW_PWR("TRUE"), // Low power="TRUE", Highest performance="FALSE"
.IOSTANDARD("DEFAULT") // Specify the input I/O standard
) IBUFDS_inst (
.O(O), // Buffer output
.I(I), // Diff_p buffer input (connect directly to top-level port)
.IB(IB) // Diff_n buffer input (connect directly to top-level port)
);
// End of IBUFDS_inst instantiation
OBUFDS

https://docs.amd.com/r/en-US/ug953-vivado-7series-libraries/OBUFDS
// OBUFDS : In order to incorporate this function into the design,
// Verilog : the following instance declaration needs to be placed
// instance : in the body of the design code. The instance name
// declaration : (OBUFDS_inst) and/or the port declarations within the
// code : parenthesis may be changed to properly reference and
// : connect this function to the design. Delete or comment
// : out inputs/outs that are not necessary.
// <-----Cut code below this line---->
// OBUFDS: Differential Output Buffer
// Kintex-7
// Xilinx HDL Language Template, version 2019.1
OBUFDS #(
.IOSTANDARD("DEFAULT"), // Specify the output I/O standard
.SLEW("SLOW") // Specify the output slew rate
) OBUFDS_inst (
.O(O), // Diff_p output (connect directly to top-level port)
.OB(OB), // Diff_n output (connect directly to top-level port)
.I(I) // Buffer input
);
// End of OBUFDS_inst instantiation
拓展 : IOBUFDS
// IOBUFDS : In order to incorporate this function into the design,
// Verilog : the following instance declaration needs to be placed
// instance : in the body of the design code. The instance name
// declaration : (IOBUFDS_inst) and/or the port declarations within the
// code : parenthesis may be changed to properly reference and
// : connect this function to the design. Delete or comment
// : out inputs/outs that are not necessary.
// <-----Cut code below this line---->
// IOBUFDS: Differential Bi-directional Buffer
// Kintex-7
// Xilinx HDL Language Template, version 2019.1
IOBUFDS #(
.DIFF_TERM("FALSE"), // Differential Termination ("TRUE"/"FALSE")
.IBUF_LOW_PWR("TRUE"), // Low Power - "TRUE", High Performance = "FALSE"
.IOSTANDARD("BLVDS_25"), // Specify the I/O standard
.SLEW("SLOW") // Specify the output slew rate
) IOBUFDS_inst (
.O(O), // Buffer output
.IO(IO), // Diff_p inout (connect directly to top-level port)
.IOB(IOB), // Diff_n inout (connect directly to top-level port)
.I(I), // Buffer input
.T(T) // 3-state enable input, high=input, low=output
);
// End of IOBUFDS_inst instantiation
Xilinx原语 IBUF, OBUF
IBUF
https://docs.amd.com/r/en-US/ug1344-versal-architecture-libraries/IBUF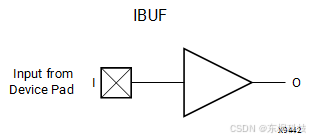
// IBUF: Input Buffer
// Versal Prime series
// Xilinx HDL Language Template, version 2024.1
IBUF IBUF_inst (
.O(O), // 1-bit output: Buffer output
.I(I) // 1-bit input: Buffer input
);
// End of IBUF_inst instantiation
OBUF
https://docs.amd.com/r/en-US/ug1344-versal-architecture-libraries/OBUF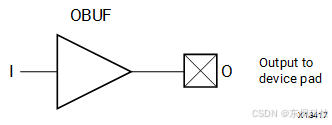
// OBUF: Output Buffer
// Versal Prime series
// Xilinx HDL Language Template, version 2024.1
OBUF OBUF_inst (
.O(O), // 1-bit output: Buffer output (connect directly to top-level port)
.I(I) // 1-bit input: Buffer input
);
// End of OBUF_inst instantiation
Xilinx原语 IBUFG
IBUFG 通过外部引脚驱动全局时钟网络。
BUFG 通过内部信号驱动全局时钟网络。
Xilinx原语 BUFG,BUFIO,BUFR
BUFG
https://docs.amd.com/r/en-US/ug953-vivado-7series-libraries/BUFG
全局缓冲, BUFG 的输出到达 FPGA 内部的 IOB、 CLB、块 RAM 的时钟延迟和抖动最小.

// BUFG: Global Clock Simple Buffer
// 7 Series
// Xilinx HDL Language Template, version 2024.1
BUFG BUFG_inst (
.O(O), // 1-bit output: Clock output
.I(I) // 1-bit input: Clock input
);
// End of BUFG_inst instantiation
BUFIO
https://docs.amd.com/r/en-US/ug953-vivado-7series-libraries/BUFIO
BUFIO 是 IO 时钟网络,其独立于全局时钟资源,适合采集源同步数据。它只能驱动 IO Block里面的逻辑,不能驱动 CLB 里面的 LUT, REG 等逻辑。
BUFIO 在采集源同步 IO 数据时,提供非常小的延时。但是不能驱动FPGA的内部逻辑,需要BUFIO和BUFG搭配起来使用以实现最佳的性能。
// BUFIO: Local Clock Buffer for I/O
// 7 Series
// Xilinx HDL Language Template, version 2024.1
BUFIO BUFIO_inst (
.O(O), // 1-bit output: Clock output (connect to I/O clock loads).
.I(I) // 1-bit input: Clock input (connect to an IBUF or BUFMR).
);
// End of BUFIO_inst instantiation
BUFR
BUFR 是 regional 时钟网络,它的驱动范围只能局限在一个 clock region 的逻辑。 BUFR 相比 BUFG 的最大优势是偏斜和功耗都比较小。
https://docs.amd.com/r/en-US/ug953-vivado-7series-libraries/BUFR
// BUFR: Regional Clock Buffer for I/O and Logic Resources within a Clock Region
// 7 Series
// Xilinx HDL Language Template, version 2024.1
BUFR #(
.BUFR_DIVIDE("BYPASS"), // Values: "BYPASS, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8"
.SIM_DEVICE("7SERIES") // Must be set to "7SERIES"
)
BUFR_inst (
.O(O), // 1-bit output: Clock output port
.CE(CE), // 1-bit input: Active high, clock enable (Divided modes only)
.CLR(CLR), // 1-bit input: Active high, asynchronous clear (Divided modes only)
.I(I) // 1-bit input: Clock buffer input driven by an IBUF, MMCM or local interconnect
);
// End of BUFR_inst instantiation
Xilinx原语 ISERDESE2,OSERDESE2
ISERDESE2
Primitive: Input SERial/DESerializer with Bitslip
// ISERDESE2: Input SERial/DESerializer with Bitslip
// 7 Series
// Xilinx HDL Language Template, version 2024.1
ISERDESE2 #(
.DATA_RATE("DDR"), // DDR, SDR
.DATA_WIDTH(4), // Parallel data width (2-8,10,14)
.DYN_CLKDIV_INV_EN("FALSE"), // Enable DYNCLKDIVINVSEL inversion (FALSE, TRUE)
.DYN_CLK_INV_EN("FALSE"), // Enable DYNCLKINVSEL inversion (FALSE, TRUE)
// INIT_Q1 - INIT_Q4: Initial value on the Q outputs (0/1)
.INIT_Q1(1'b0),
.INIT_Q2(1'b0),
.INIT_Q3(1'b0),
.INIT_Q4(1'b0),
.INTERFACE_TYPE("MEMORY"), // MEMORY, MEMORY_DDR3, MEMORY_QDR, NETWORKING, OVERSAMPLE
.IOBDELAY("NONE"), // NONE, BOTH, IBUF, IFD
.NUM_CE(2), // Number of clock enables (1,2)
.OFB_USED("FALSE"), // Select OFB path (FALSE, TRUE)
.SERDES_MODE("MASTER"), // MASTER, SLAVE
// SRVAL_Q1 - SRVAL_Q4: Q output values when SR is used (0/1)
.SRVAL_Q1(1'b0),
.SRVAL_Q2(1'b0),
.SRVAL_Q3(1'b0),
.SRVAL_Q4(1'b0)
)
ISERDESE2_inst (
.O(O), // 1-bit output: Combinatorial output
// Q1 - Q8: 1-bit (each) output: Registered data outputs
.Q1(Q1),
.Q2(Q2),
.Q3(Q3),
.Q4(Q4),
.Q5(Q5),
.Q6(Q6),
.Q7(Q7),
.Q8(Q8),
// SHIFTOUT1, SHIFTOUT2: 1-bit (each) output: Data width expansion output ports
.SHIFTOUT1(SHIFTOUT1),
.SHIFTOUT2(SHIFTOUT2),
.BITSLIP(BITSLIP), // 1-bit input: The BITSLIP pin performs a Bitslip operation synchronous to
// CLKDIV when asserted (active High). Subsequently, the data seen on the Q1
// to Q8 output ports will shift, as in a barrel-shifter operation, one
// position every time Bitslip is invoked (DDR operation is different from
// SDR).
// CE1, CE2: 1-bit (each) input: Data register clock enable inputs
.CE1(CE1),
.CE2(CE2),
.CLKDIVP(CLKDIVP), // 1-bit input: TBD
// Clocks: 1-bit (each) input: ISERDESE2 clock input ports
.CLK(CLK), // 1-bit input: High-speed clock
.CLKB(CLKB), // 1-bit input: High-speed secondary clock
.CLKDIV(CLKDIV), // 1-bit input: Divided clock
.OCLK(OCLK), // 1-bit input: High speed output clock used when INTERFACE_TYPE="MEMORY"
// Dynamic Clock Inversions: 1-bit (each) input: Dynamic clock inversion pins to switch clock polarity
.DYNCLKDIVSEL(DYNCLKDIVSEL), // 1-bit input: Dynamic CLKDIV inversion
.DYNCLKSEL(DYNCLKSEL), // 1-bit input: Dynamic CLK/CLKB inversion
// Input Data: 1-bit (each) input: ISERDESE2 data input ports
.D(D), // 1-bit input: Data input
.DDLY(DDLY), // 1-bit input: Serial data from IDELAYE2
.OFB(OFB), // 1-bit input: Data feedback from OSERDESE2
.OCLKB(OCLKB), // 1-bit input: High speed negative edge output clock
.RST(RST), // 1-bit input: Active high asynchronous reset
// SHIFTIN1, SHIFTIN2: 1-bit (each) input: Data width expansion input ports
.SHIFTIN1(SHIFTIN1),
.SHIFTIN2(SHIFTIN2)
);
// End of ISERDESE2_inst instantiation
OSERDESE2
7系列FPGA器件中的专用并串转换器。
Primitive: Output SERial/DESerializer with bitslip

// OSERDESE2: Output SERial/DESerializer with bitslip
// 7 Series
// Xilinx HDL Language Template, version 2024.1
OSERDESE2 #(
.DATA_RATE_OQ("DDR"), // DDR, SDR
.DATA_RATE_TQ("DDR"), // DDR, BUF, SDR
.DATA_WIDTH(4), // Parallel data width (2-8,10,14)
.INIT_OQ(1'b0), // Initial value of OQ output (1'b0,1'b1)
.INIT_TQ(1'b0), // Initial value of TQ output (1'b0,1'b1)
.SERDES_MODE("MASTER"), // MASTER, SLAVE
.SRVAL_OQ(1'b0), // OQ output value when SR is used (1'b0,1'b1)
.SRVAL_TQ(1'b0), // TQ output value when SR is used (1'b0,1'b1)
.TBYTE_CTL("FALSE"), // Enable tristate byte operation (FALSE, TRUE)
.TBYTE_SRC("FALSE"), // Tristate byte source (FALSE, TRUE)
.TRISTATE_WIDTH(4) // 3-state converter width (1,4)
)
OSERDESE2_inst (
.OFB(OFB), // 1-bit output: Feedback path for data
.OQ(OQ), // 1-bit output: Data path output
// SHIFTOUT1 / SHIFTOUT2: 1-bit (each) output: Data output expansion (1-bit each)
.SHIFTOUT1(SHIFTOUT1),
.SHIFTOUT2(SHIFTOUT2),
.TBYTEOUT(TBYTEOUT), // 1-bit output: Byte group tristate
.TFB(TFB), // 1-bit output: 3-state control
.TQ(TQ), // 1-bit output: 3-state control
.CLK(CLK), // 1-bit input: High speed clock
.CLKDIV(CLKDIV), // 1-bit input: Divided clock
// D1 - D8: 1-bit (each) input: Parallel data inputs (1-bit each)
.D1(D1),
.D2(D2),
.D3(D3),
.D4(D4),
.D5(D5),
.D6(D6),
.D7(D7),
.D8(D8),
.OCE(OCE), // 1-bit input: Output data clock enable
.RST(RST), // 1-bit input: Reset
// SHIFTIN1 / SHIFTIN2: 1-bit (each) input: Data input expansion (1-bit each)
.SHIFTIN1(SHIFTIN1),
.SHIFTIN2(SHIFTIN2),
// T1 - T4: 1-bit (each) input: Parallel 3-state inputs
.T1(T1),
.T2(T2),
.T3(T3),
.T4(T4),
.TBYTEIN(TBYTEIN), // 1-bit input: Byte group tristate
.TCE(TCE) // 1-bit input: 3-state clock enable
);
// End of OSERDESE2_inst instantiation
ad_data_clk
// ***************************************************************************
// ***************************************************************************
// Copyright 2014 - 2017 (c) Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
//
// In this HDL repository, there are many different and unique modules, consisting
// of various HDL (Verilog or VHDL) components. The individual modules are
// developed independently, and may be accompanied by separate and unique license
// terms.
//
// The user should read each of these license terms, and understand the
// freedoms and responsibilities that he or she has by using this source/core.
//
// This core is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY
// WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
//
// Redistribution and use of source or resulting binaries, with or without modification
// of this file, are permitted under one of the following two license terms:
//
// 1. The GNU General Public License version 2 as published by the
// Free Software Foundation, which can be found in the top level directory
// of this repository (LICENSE_GPL2), and also online at:
// <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/old-licenses/gpl-2.0.html>
//
// OR
//
// 2. An ADI specific BSD license, which can be found in the top level directory
// of this repository (LICENSE_ADIBSD), and also on-line at:
// https://github.com/analogdevicesinc/hdl/blob/master/LICENSE_ADIBSD
// This will allow to generate bit files and not release the source code,
// as long as it attaches to an ADI device.
//
// ***************************************************************************
// ***************************************************************************
`timescale 1ns/100ps
module ad_data_clk #(
parameter SINGLE_ENDED = 0) (
input rst,
output locked,
input clk_in_p,
input clk_in_n,
output clk);
// internal signals
wire clk_ibuf_s;
// defaults
assign locked = 1'b1;
// instantiations
generate
if (SINGLE_ENDED == 1) begin
IBUFG i_rx_clk_ibuf (
.I (clk_in_p),
.O (clk_ibuf_s));
end else begin
IBUFGDS i_rx_clk_ibuf (
.I (clk_in_p),
.IB (clk_in_n),
.O (clk_ibuf_s));
end
endgenerate
BUFG i_clk_gbuf (
.I (clk_ibuf_s),
.O (clk));
endmodule
// ***************************************************************************
// ***************************************************************************
ad_data_in
// ***************************************************************************
// ***************************************************************************
// Copyright 2014 - 2017 (c) Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
//
// In this HDL repository, there are many different and unique modules, consisting
// of various HDL (Verilog or VHDL) components. The individual modules are
// developed independently, and may be accompanied by separate and unique license
// terms.
//
// The user should read each of these license terms, and understand the
// freedoms and responsibilities that he or she has by using this source/core.
//
// This core is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY
// WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
//
// Redistribution and use of source or resulting binaries, with or without modification
// of this file, are permitted under one of the following two license terms:
//
// 1. The GNU General Public License version 2 as published by the
// Free Software Foundation, which can be found in the top level directory
// of this repository (LICENSE_GPL2), and also online at:
// <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/old-licenses/gpl-2.0.html>
//
// OR
//
// 2. An ADI specific BSD license, which can be found in the top level directory
// of this repository (LICENSE_ADIBSD), and also on-line at:
// https://github.com/analogdevicesinc/hdl/blob/master/LICENSE_ADIBSD
// This will allow to generate bit files and not release the source code,
// as long as it attaches to an ADI device.
//
// ***************************************************************************
// ***************************************************************************
`timescale 1ns/100ps
module ad_data_in #(
// parameters
parameter SINGLE_ENDED = 0,
parameter FPGA_TECHNOLOGY = 0,
parameter IODELAY_ENABLE = 1,
parameter IODELAY_CTRL = 0,
parameter IODELAY_GROUP = "dev_if_delay_group",
parameter REFCLK_FREQUENCY = 200) (
// data interface
input rx_clk,
input rx_data_in_p,
input rx_data_in_n,
output rx_data_p,
output rx_data_n,
// delay-data interface
input up_clk,
input up_dld,
input [ 4:0] up_dwdata,
output [ 4:0] up_drdata,
// delay-cntrl interface
input delay_clk,
input delay_rst,
output delay_locked);
// internal parameters
localparam NONE = -1;
localparam SEVEN_SERIES = 1;
localparam ULTRASCALE = 2;
localparam ULTRASCALE_PLUS = 3;
localparam IODELAY_CTRL_ENABLED = (IODELAY_ENABLE == 1) ? IODELAY_CTRL : 0;
localparam IODELAY_CTRL_SIM_DEVICE = (FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE_PLUS) ? "ULTRASCALE" :
(FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE) ? "ULTRASCALE" : "7SERIES";
localparam IODELAY_FPGA_TECHNOLOGY = (IODELAY_ENABLE == 1) ? FPGA_TECHNOLOGY : NONE;
localparam IODELAY_SIM_DEVICE = (FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE_PLUS) ? "ULTRASCALE_PLUS" :
(FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE) ? "ULTRASCALE" : "7SERIES";
// internal signals
wire rx_data_ibuf_s;
wire rx_data_idelay_s;
wire [ 8:0] up_drdata_s;
// delay controller
generate
if (IODELAY_CTRL_ENABLED == 0) begin
assign delay_locked = 1'b1;
end else begin
(* IODELAY_GROUP = IODELAY_GROUP *)
IDELAYCTRL #(.SIM_DEVICE (IODELAY_CTRL_SIM_DEVICE)) i_delay_ctrl (
.RST (delay_rst),
.REFCLK (delay_clk),
.RDY (delay_locked));
end
endgenerate
// receive data interface, ibuf -> idelay -> iddr
generate
if (SINGLE_ENDED == 1) begin
IBUF i_rx_data_ibuf (
.I (rx_data_in_p),
.O (rx_data_ibuf_s));
end else begin
IBUFDS i_rx_data_ibuf (
.I (rx_data_in_p),
.IB (rx_data_in_n),
.O (rx_data_ibuf_s));
end
endgenerate
// idelay
generate
if (IODELAY_FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == SEVEN_SERIES) begin
(* IODELAY_GROUP = IODELAY_GROUP *)
IDELAYE2 #(
.CINVCTRL_SEL ("FALSE"),
.DELAY_SRC ("IDATAIN"),
.HIGH_PERFORMANCE_MODE ("FALSE"),
.IDELAY_TYPE ("VAR_LOAD"),
.IDELAY_VALUE (0),
.REFCLK_FREQUENCY (REFCLK_FREQUENCY),
.PIPE_SEL ("FALSE"),
.SIGNAL_PATTERN ("DATA"))
i_rx_data_idelay (
.CE (1'b0),
.INC (1'b0),
.DATAIN (1'b0),
.LDPIPEEN (1'b0),
.CINVCTRL (1'b0),
.REGRST (1'b0),
.C (up_clk),
.IDATAIN (rx_data_ibuf_s),
.DATAOUT (rx_data_idelay_s),
.LD (up_dld),
.CNTVALUEIN (up_dwdata),
.CNTVALUEOUT (up_drdata));
end
endgenerate
generate
if ((IODELAY_FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE) || (IODELAY_FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE_PLUS)) begin
assign up_drdata = up_drdata_s[8:4];
(* IODELAY_GROUP = IODELAY_GROUP *)
IDELAYE3 #(
.SIM_DEVICE (IODELAY_SIM_DEVICE),
.DELAY_SRC ("IDATAIN"),
.DELAY_TYPE ("VAR_LOAD"),
.REFCLK_FREQUENCY (REFCLK_FREQUENCY),
.DELAY_FORMAT ("COUNT"))
i_rx_data_idelay (
.CASC_RETURN (1'b0),
.CASC_IN (1'b0),
.CASC_OUT (),
.CE (1'b0),
.CLK (up_clk),
.INC (1'b0),
.LOAD (up_dld),
.CNTVALUEIN ({up_dwdata, 4'd0}),
.CNTVALUEOUT (up_drdata_s),
.DATAIN (1'b0),
.IDATAIN (rx_data_ibuf_s),
.DATAOUT (rx_data_idelay_s),
.RST (1'b0),
.EN_VTC (~up_dld));
end
endgenerate
generate
if (IODELAY_FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == NONE) begin
assign rx_data_idelay_s = rx_data_ibuf_s;
assign up_drdata = 5'd0;
end
endgenerate
// iddr
generate
if ((FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE) || (FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE_PLUS)) begin
IDDRE1 #(.DDR_CLK_EDGE ("SAME_EDGE")) i_rx_data_iddr (
.R (1'b0),
.C (rx_clk),
.CB (~rx_clk),
.D (rx_data_idelay_s),
.Q1 (rx_data_p),
.Q2 (rx_data_n));
end
endgenerate
generate
if (FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == SEVEN_SERIES) begin
IDDR #(.DDR_CLK_EDGE ("SAME_EDGE")) i_rx_data_iddr (
.CE (1'b1),
.R (1'b0),
.S (1'b0),
.C (rx_clk),
.D (rx_data_idelay_s),
.Q1 (rx_data_p),
.Q2 (rx_data_n));
end
endgenerate
endmodule
// ***************************************************************************
// ***************************************************************************
ad_data_out
// ***************************************************************************
// ***************************************************************************
// Copyright 2014 - 2017 (c) Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
//
// In this HDL repository, there are many different and unique modules, consisting
// of various HDL (Verilog or VHDL) components. The individual modules are
// developed independently, and may be accompanied by separate and unique license
// terms.
//
// The user should read each of these license terms, and understand the
// freedoms and responsibilities that he or she has by using this source/core.
//
// This core is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY
// WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
//
// Redistribution and use of source or resulting binaries, with or without modification
// of this file, are permitted under one of the following two license terms:
//
// 1. The GNU General Public License version 2 as published by the
// Free Software Foundation, which can be found in the top level directory
// of this repository (LICENSE_GPL2), and also online at:
// <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/old-licenses/gpl-2.0.html>
//
// OR
//
// 2. An ADI specific BSD license, which can be found in the top level directory
// of this repository (LICENSE_ADIBSD), and also on-line at:
// https://github.com/analogdevicesinc/hdl/blob/master/LICENSE_ADIBSD
// This will allow to generate bit files and not release the source code,
// as long as it attaches to an ADI device.
//
// ***************************************************************************
// ***************************************************************************
`timescale 1ns/100ps
module ad_data_out #(
parameter FPGA_TECHNOLOGY = 0,
parameter SINGLE_ENDED = 0,
parameter IODELAY_ENABLE = 0,
parameter IODELAY_CTRL = 0,
parameter IODELAY_GROUP = "dev_if_delay_group",
parameter REFCLK_FREQUENCY = 200) (
// data interface
input tx_clk,
input tx_data_p,
input tx_data_n,
output tx_data_out_p,
output tx_data_out_n,
// delay-data interface
input up_clk,
input up_dld,
input [ 4:0] up_dwdata,
output [ 4:0] up_drdata,
// delay-cntrl interface
input delay_clk,
input delay_rst,
output delay_locked);
localparam NONE = -1;
localparam SEVEN_SERIES = 1;
localparam ULTRASCALE = 2;
localparam ULTRASCALE_PLUS = 3;
localparam IODELAY_CTRL_ENABLED = (IODELAY_ENABLE == 1) ? IODELAY_CTRL : 0;
localparam IODELAY_CTRL_SIM_DEVICE = (FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE_PLUS) ? "ULTRASCALE" :
(FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE) ? "ULTRASCALE" : "7SERIES";
localparam IODELAY_FPGA_TECHNOLOGY = (IODELAY_ENABLE == 1) ? FPGA_TECHNOLOGY : NONE;
localparam IODELAY_SIM_DEVICE = (FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE_PLUS) ? "ULTRASCALE_PLUS_ES1" :
(FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE) ? "ULTRASCALE" : "7SERIES";
// internal signals
wire tx_data_oddr_s;
wire tx_data_odelay_s;
// delay controller
generate
if (IODELAY_CTRL_ENABLED == 0) begin
assign delay_locked = 1'b1;
end else begin
(* IODELAY_GROUP = IODELAY_GROUP *)
IDELAYCTRL #(.SIM_DEVICE (IODELAY_CTRL_SIM_DEVICE)) i_delay_ctrl (
.RST (delay_rst),
.REFCLK (delay_clk),
.RDY (delay_locked));
end
endgenerate
// transmit data interface, oddr -> odelay -> obuf
generate
if ((FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE) || (FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == ULTRASCALE_PLUS)) begin
ODDRE1 i_tx_data_oddr (
.SR (1'b0),
.C (tx_clk),
.D1 (tx_data_n),
.D2 (tx_data_p),
.Q (tx_data_oddr_s));
end
endgenerate
generate
if (FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == SEVEN_SERIES) begin
ODDR #(.DDR_CLK_EDGE ("SAME_EDGE")) i_tx_data_oddr (
.CE (1'b1),
.R (1'b0),
.S (1'b0),
.C (tx_clk),
.D1 (tx_data_n),
.D2 (tx_data_p),
.Q (tx_data_oddr_s));
end
endgenerate
// odelay
generate
if (IODELAY_FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == SEVEN_SERIES) begin
(* IODELAY_GROUP = IODELAY_GROUP *)
ODELAYE2 #(
.CINVCTRL_SEL ("FALSE"),
.DELAY_SRC ("ODATAIN"),
.HIGH_PERFORMANCE_MODE ("FALSE"),
.ODELAY_TYPE ("VAR_LOAD"),
.ODELAY_VALUE (0),
.REFCLK_FREQUENCY (REFCLK_FREQUENCY),
.PIPE_SEL ("FALSE"),
.SIGNAL_PATTERN ("DATA"))
i_tx_data_odelay (
.CE (1'b0),
.CLKIN (1'b0),
.INC (1'b0),
.LDPIPEEN (1'b0),
.CINVCTRL (1'b0),
.REGRST (1'b0),
.C (up_clk),
.ODATAIN (tx_data_oddr_s),
.DATAOUT (tx_data_odelay_s),
.LD (up_dld),
.CNTVALUEIN (up_dwdata),
.CNTVALUEOUT (up_drdata));
end
endgenerate
generate
if (IODELAY_FPGA_TECHNOLOGY == NONE) begin
assign up_drdata = 5'd0;
assign tx_data_odelay_s = tx_data_oddr_s;
end
endgenerate
// obuf
generate
if (SINGLE_ENDED == 1) begin
assign tx_data_out_n = 1'b0;
OBUF i_tx_data_obuf (
.I (tx_data_odelay_s),
.O (tx_data_out_p));
end else begin
OBUFDS i_tx_data_obuf (
.I (tx_data_odelay_s),
.O (tx_data_out_p),
.OB (tx_data_out_n));
end
endgenerate
endmodule
// ***************************************************************************
// ***************************************************************************

DAMO开发者矩阵,由阿里巴巴达摩院和中国互联网协会联合发起,致力于探讨最前沿的技术趋势与应用成果,搭建高质量的交流与分享平台,推动技术创新与产业应用链接,围绕“人工智能与新型计算”构建开放共享的开发者生态。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献11条内容
已为社区贡献11条内容








所有评论(0)