vue3—— 9. computed计算属性
<p>原始值: {{ count }}</p><p>计算后的值: {{ doubledCount }}</p><button @click="increment">增加</button>
·
Vue3 computed计算属性
Vue3 computed计算属性
一、computed计算属性基本概念
1.1 什么是computed计算属性?
computed计算属性是Vue3提供的用于声明式地依赖响应式状态的派生值的API。它允许你定义一个依赖于其他响应式数据的属性,当依赖的数据变化时,计算属性会自动更新。
核心特点:
- 响应式依赖:自动追踪其依赖的响应式数据
- 缓存机制:只有当依赖变化时才会重新计算
- 声明式语法:以声明式方式描述派生值,更简洁易读
- 只读默认:默认情况下是只读的,可配置为可写
生活比喻:计算属性就像一个自动更新的公式。例如,当你计算"总分=语文+数学+英语"时,只要任何一门成绩变化,总分会自动更新,而不需要每次手动计算。
核心区别总结:
| 特性 | computed计算属性 | 方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 执行时机 | 依赖变化时自动执行 | 每次调用时执行 |
| 缓存 | 有缓存,依赖不变不重新计算 | 无缓存,每次调用都执行 |
| 调用方式 | 作为属性访问(无括号) | 作为方法调用(有括号) |
| 参数 | 不能接收参数 | 可以接收参数 |
| 适用场景 | 依赖固定的响应式数据派生值 | 需要参数或频繁变化的计算 |
1.3 computed计算属性的基本使用
<template>
<div class="computed-basic">
<h2>计算属性基本使用</h2>
<div class="input-section">
<label>
姓: <input v-model="firstName" placeholder="请输入姓">
</label>
<label>
名: <input v-model="lastName" placeholder="请输入名">
</label>
</div>
<div class="result-section">
<p><strong>全名:</strong> {{ fullName }}</p>
<p><strong>全名(大写):</strong> {{ fullNameUpperCase }}</p>
<p><strong>姓名长度:</strong> {{ nameLength }} 个字符</p>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
// 基本响应式数据
const firstName = ref('');
const lastName = ref('');
// 计算属性 - 全名
const fullName = computed(() => {
// 当firstName或lastName变化时,会重新计算
return `${firstName.value} ${lastName.value}`.trim() || '请输入姓名';
});
// 计算属性 - 全名大写
const fullNameUpperCase = computed(() => {
// 依赖于fullName计算属性
return fullName.value.toUpperCase();
});
// 计算属性 - 姓名长度
const nameLength = computed(() => {
// 依赖于fullName计算属性
return fullName.value.length;
});
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
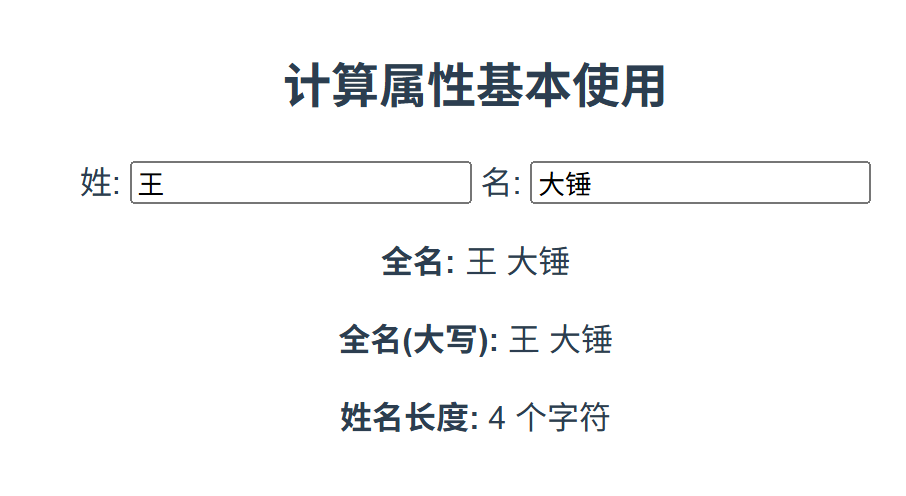
运行结果:
- 在姓和名输入框中输入内容,全名会实时更新
- 全名大写和姓名长度也会自动更新
- 如果未输入内容,显示"请输入姓名"
代码解析:
- 使用
computed()函数创建计算属性,参数是一个 getter 函数 - 计算属性的值基于 getter 函数的返回值
- 计算属性可以依赖其他计算属性(如
fullNameUpperCase依赖fullName) - 计算属性会自动追踪其依赖的响应式数据,当依赖变化时重新计算
二、computed计算属性的高级特性
2.1 可写计算属性
默认情况下,计算属性是只读的。但可以通过提供一个getter和setter函数,创建可写的计算属性。
<template>
<div class="writable-computed">
<h2>可写计算属性</h2>
<div class="input-group">
<label>姓: <input v-model="firstName"></label>
</div>
<div class="input-group">
<label>名: <input v-model="lastName"></label>
</div>
<div class="input-group">
<label>全名: <input v-model="fullName"></label>
</div>
<div class="log-section">
<h3>操作日志:</h3>
<ul>
<li v-for="(log, index) in logs" :key="index" :class="{ recent: index === logs.length - 1 }">
{{ log }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
// 基本数据
const firstName = ref('张');
const lastName = ref('三');
const logs = ref([]);
// 添加日志
const addLog = (message) => {
logs.value.push(`[${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}] ${message}`);
// 只保留最近10条日志
if (logs.value.length > 10) {
logs.value.shift();
}
};
// 可写计算属性
const fullName = computed({
// getter - 读取时调用
get() {
const name = `${firstName.value} ${lastName.value}`.trim();
addLog('读取全名: ' + name);
return name;
},
// setter - 修改时调用
set(newValue) {
addLog('修改全名: ' + newValue);
// 将新值拆分为名和姓
const names = newValue.split(' ');
if (names.length >= 2) {
firstName.value = names[0];
lastName.value = names.slice(1).join(' ');
} else if (names.length === 1) {
firstName.value = names[0];
lastName.value = '';
} else {
firstName.value = '';
lastName.value = '';
}
}
});
// 初始日志
addLog('组件初始化');
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
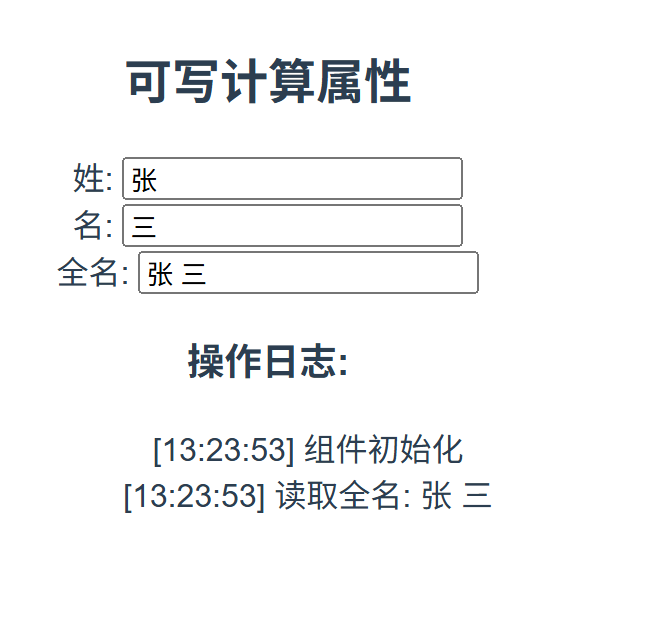
运行结果:
- 修改姓或名输入框,全名输入框会自动更新
- 修改全名输入框,姓和名输入框会自动拆分更新
- 操作日志会记录所有读取和修改操作
代码解析:
- 可写计算属性通过传递一个包含
get和set方法的对象创建 get方法:读取计算属性时调用,返回计算后的值set方法:修改计算属性时调用,接收新值,可以反向更新依赖的响应式数据- 可写计算属性适用于需要双向绑定的派生值场景
2.4 计算属性与watch的区别
计算属性和watch都可以响应数据变化,但它们的适用场景不同。
<template>
<div class="computed-vs-watch">
<h2>计算属性 vs watch</h2>
<div class="input-section">
<label>
输入: <input v-model="inputValue" placeholder="输入一些文本">
</label>
</div>
<div class="results">
<div class="result-item">
<h3>计算属性结果</h3>
<p>字符数: {{ charCount }}</p>
<p>单词数: {{ wordCount }}</p>
<p>大写转换: {{ upperCaseText }}</p>
</div>
<div class="result-item">
<h3>watch结果</h3>
<p>最后修改时间: {{ lastUpdated }}</p>
<p>历史字符数: {{ historyCharCounts.join(', ') }}</p>
<p>变化次数: {{ changeCount }}</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, computed, watch } from 'vue';
// 基本数据
const inputValue = ref('');
const lastUpdated = ref('');
const historyCharCounts = ref([]);
const changeCount = ref(0);
// 计算属性 - 适合派生值
const charCount = computed(() => {
return inputValue.value.length;
});
const wordCount = computed(() => {
if (!inputValue.value.trim()) return 0;
return inputValue.value.trim().split(/\s+/).length;
});
const upperCaseText = computed(() => {
return inputValue.value.toUpperCase();
});
// watch - 适合执行副作用
watch(inputValue, (newValue, oldValue) => {
// 记录最后修改时间
lastUpdated.value = new Date().toLocaleTimeString();
// 记录历史字符数
historyCharCounts.value.push(newValue.length);
// 限制历史记录长度
if (historyCharCounts.value.length > 5) {
historyCharCounts.value.shift();
}
// 增加变化次数
changeCount.value++;
});
</script>
<style scoped>
.computed-vs-watch {
max-width: 800px;
margin: 20px auto;
padding: 20px;
border: 1px solid #e0e0e0;
border-radius: 6px;
}
.input-section {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
input {
padding: 8px;
width: 300px;
}
.results {
display: flex;
gap: 20px;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.result-item {
flex: 1;
min-width: 300px;
padding: 15px;
border: 1px solid #e0e0e0;
border-radius: 4px;
}
</style>
运行结果:
- 在输入框中输入文本:
- 计算属性实时更新字符数、单词数和大写转换结果
- watch记录最后修改时间、历史字符数和变化次数
核心区别总结:
| 特性 | computed计算属性 | watch |
|---|---|---|
| 用途 | 声明式地派生值 | 执行响应数据变化的副作用 |
| 语法 | 函数式,返回计算值 | 命令式,执行函数 |
| 缓存 | 有缓存 | 无缓存 |
| 返回值 | 必须有返回值 | 不需要返回值 |
| 适用场景 | 数据转换、过滤、组合 | 数据变化后的异步操作、复杂逻辑 |
| 依赖 | 自动追踪响应式依赖 | 需要显式指定依赖 |
三、computed计算属性的实际应用场景
3.1 数据转换和格式化
计算属性非常适合对原始数据进行转换和格式化,如日期格式化、货币格式化等。
<template>
<div class="data-formatting">
<h2>数据转换和格式化</h2>
<div class="data-input">
<label>
原始价格: <input v-model.number="price" type="number" step="0.01" min="0">
</label>
<label>
原始日期: <input v-model="rawDate" type="date">
</label>
</div>
<div class="formatted-results">
<p><strong>格式化价格:</strong> {{ formattedPrice }}</p>
<p><strong>带符号价格:</strong> {{ priceWithSymbol }}</p>
<p><strong>格式化日期:</strong> {{ formattedDate }}</p>
<p><strong>相对日期:</strong> {{ relativeDate }}</p>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
// 原始数据
const price = ref(1234.56);
const rawDate = ref('2023-01-15');
// 格式化价格
const formattedPrice = computed(() => {
return new Intl.NumberFormat('zh-CN', {
minimumFractionDigits: 2,
maximumFractionDigits: 2
}).format(price.value);
});
// 带符号价格
const priceWithSymbol = computed(() => {
return new Intl.NumberFormat('zh-CN', {
style: 'currency',
currency: 'CNY'
}).format(price.value);
});
// 格式化日期
const formattedDate = computed(() => {
if (!rawDate.value) return '';
return new Intl.DateTimeFormat('zh-CN', {
year: 'numeric',
month: 'long',
day: 'numeric',
weekday: 'long'
}).format(new Date(rawDate.value));
});
// 相对日期(如"3天前")
const relativeDate = computed(() => {
if (!rawDate.value) return '';
const today = new Date();
const inputDate = new Date(rawDate.value);
const diffTime = today - inputDate;
const diffDays = Math.floor(diffTime / (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24));
if (diffDays === 0) return '今天';
if (diffDays === 1) return '昨天';
if (diffDays === -1) return '明天';
if (diffDays > 0) return `${diffDays}天前`;
return `${Math.abs(diffDays)}天后`;
});
</script>
<style scoped>
.data-formatting {
max-width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
padding: 20px;
border: 1px solid #e0e0e0;
border-radius: 6px;
}
.data-input {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
gap: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
input {
padding: 8px;
width: 250px;
}
.formatted-results {
padding: 15px;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
border-radius: 4px;
}
p {
margin: 8px 0;
}
</style>
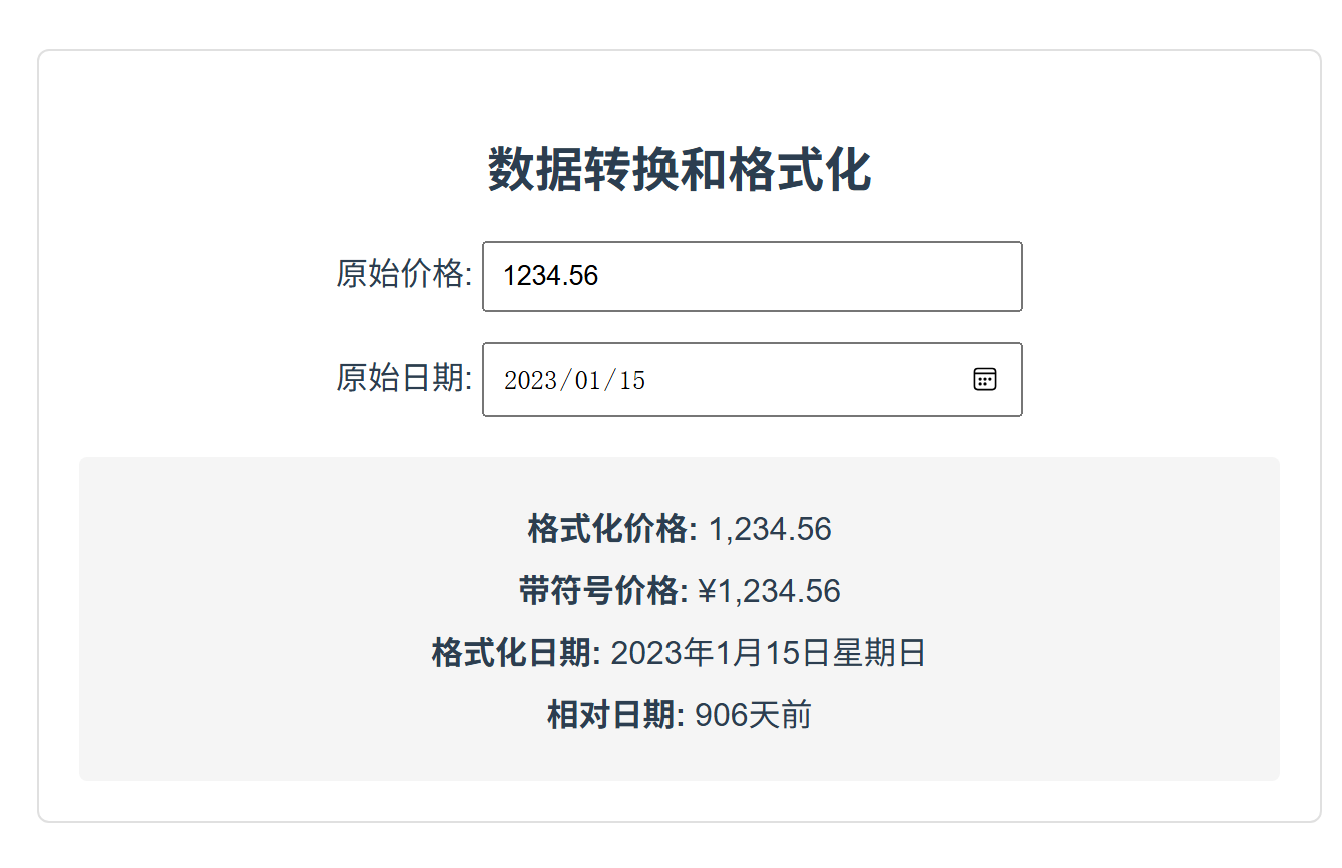
运行结果:
- 价格输入框输入1234.56,显示:
- 格式化价格: 1,234.56
- 带符号价格: ¥1,234.56
- 日期选择2023-01-15,显示:
- 格式化日期: 2023年1月15日 星期日
- 相对日期: 根据当前日期计算的相对天数
代码解析:
- 使用计算属性对价格和日期进行格式化
- 利用浏览器内置的Intl对象进行国际化格式化
- 计算属性使数据转换逻辑与模板分离,更易于维护
- 当原始数据变化时,格式化结果会自动更新
3.2 数据过滤和搜索
计算属性非常适合实现数据过滤和搜索功能,尤其是当数据量不大时。
<template>
<div class="data-filtering">
<h2>数据过滤和搜索</h2>
<div class="search-controls">
<input
v-model="searchQuery"
placeholder="搜索产品..."
class="search-input"
>
<div class="filter-options">
<label>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="inStockOnly"> 仅显示有货
</label>
<select v-model="sortBy" class="sort-select">
<option value="name">按名称排序</option>
<option value="priceAsc">价格从低到高</option>
<option value="priceDesc">价格从高到低</option>
</select>
</div>
</div>
<div class="product-list">
<div v-if="filteredProducts.length === 0" class="no-results">
没有找到匹配的产品
</div>
<div v-for="product in filteredProducts" :key="product.id" class="product-card">
<h3>{{ product.name }}</h3>
<p class="price">¥{{ product.price.toFixed(2) }}</p>
<p class="stock" :class="{ outOfStock: !product.inStock }">
{{ product.inStock ? '有货' : '缺货' }}
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
// 原始产品数据
const products = ref([
{ id: 1, name: 'Vue3实战教程', price: 89.00, inStock: true },
{ id: 2, name: 'JavaScript高级程序设计', price: 129.00, inStock: true },
{ id: 3, name: 'TypeScript完全指南', price: 79.00, inStock: false },
{ id: 4, name: '前端工程化实践', price: 69.00, inStock: true },
{ id: 5, name: 'React设计模式与最佳实践', price: 99.00, inStock: false },
{ id: 6, name: 'CSS揭秘', price: 59.00, inStock: true }
]);
// 搜索和过滤条件
const searchQuery = ref('');
const inStockOnly = ref(false);
const sortBy = ref('name');
// 过滤和排序产品的计算属性
const filteredProducts = computed(() => {
// 1. 过滤产品
let result = [...products.value];
// 搜索过滤
if (searchQuery.value) {
const query = searchQuery.value.toLowerCase();
result = result.filter(product =>
product.name.toLowerCase().includes(query)
);
}
// 库存过滤
if (inStockOnly.value) {
result = result.filter(product => product.inStock);
}
// 2. 排序产品
switch (sortBy.value) {
case 'priceAsc':
result.sort((a, b) => a.price - b.price);
break;
case 'priceDesc':
result.sort((a, b) => b.price - a.price);
break;
case 'name':
default:
result.sort((a, b) => a.name.localeCompare(b.name));
}
return result;
});
</script>
<style scoped>
.data-filtering {
max-width: 1000px;
margin: 20px auto;
padding: 20px;
border: 1px solid #e0e0e0;
border-radius: 6px;
}
.search-controls {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.search-input {
padding: 8px;
width: 300px;
margin-right: 20px;
}
.filter-options {
display: inline-block;
margin-left: 20px;
}
.filter-options label {
margin-right: 20px;
}
.sort-select {
padding: 6px;
}
.product-list {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(auto-fill, minmax(200px, 1fr));
gap: 20px;
}
.product-card {
padding: 15px;
border: 1px solid #e0e0e0;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.price {
color: #e53935;
font-weight: bold;
}
.stock {
color: #43a047;
}
.outOfStock {
color: #f44336;
}
.no-results {
grid-column: 1 / -1;
text-align: center;
padding: 40px;
color: #757575;
}
</style>
运行结果:
- 在搜索框输入"vue",只显示包含"vue"的产品
- 勾选"仅显示有货",只显示有库存的产品
- 选择不同的排序选项,产品会按相应方式排序
代码解析:
- 使用一个计算属性整合过滤和排序逻辑
- 计算属性依赖于搜索关键词、库存过滤条件和排序选项
- 当任何过滤条件变化时,计算属性会重新计算并返回过滤后的结果
- 这种方式使模板非常简洁,所有逻辑集中在计算属性中
3.3 表单验证
计算属性可以用于实时表单验证,提供即时反馈。
<template>
<div class="form-validation">
<h2>表单验证</h2>
<form @submit.prevent="handleSubmit">
<div class="form-group">
<label>用户名:</label>
<input
v-model="username"
placeholder="请输入用户名"
:class="{ invalid: !usernameValid }"
>
<span v-if="!usernameValid" class="error-message">{{ usernameError }}</span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>邮箱:</label>
<input
v-model="email"
type="email"
placeholder="请输入邮箱"
:class="{ invalid: !emailValid }"
>
<span v-if="!emailValid" class="error-message">{{ emailError }}</span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>密码:</label>
<input
v-model="password"
type="password"
placeholder="请输入密码"
:class="{ invalid: !passwordValid }"
>
<span v-if="!passwordValid" class="error-message">{{ passwordError }}</span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>确认密码:</label>
<input
v-model="confirmPassword"
type="password"
placeholder="请确认密码"
:class="{ invalid: !confirmPasswordValid }"
>
<span v-if="!confirmPasswordValid" class="error-message">{{ confirmPasswordError }}</span>
</div>
<button type="submit" :disabled="!formValid">提交</button>
</form>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';
// 表单数据
const username = ref('');
const email = ref('');
const password = ref('');
const confirmPassword = ref('');
// 用户名验证
const usernameValid = computed(() => {
return username.value.length >= 3 && username.value.length <= 20;
});
const usernameError = computed(() => {
if (username.value.length === 0) return '';
if (username.value.length < 3) return '用户名至少3个字符';
if (username.value.length > 20) return '用户名最多20个字符';
return '';
});
// 邮箱验证
const emailValid = computed(() => {
if (!email.value) return true; // 空值暂时视为有效,提交时再强制检查
const emailRegex = /^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/;
return emailRegex.test(email.value);
});
const emailError = computed(() => {
if (!email.value) return '';
return emailValid.value ? '' : '请输入有效的邮箱地址';
});
// 密码验证
const passwordValid = computed(() => {
if (!password.value) return true; // 空值暂时视为有效
return password.value.length >= 6 && /[A-Z]/.test(password.value) && /[0-9]/.test(password.value);
});
const passwordError = computed(() => {
if (!password.value) return '';
if (password.value.length < 6) return '密码至少6个字符';
if (!/[A-Z]/.test(password.value)) return '密码必须包含大写字母';
if (!/[0-9]/.test(password.value)) return '密码必须包含数字';
return '';
});
// 确认密码验证
const confirmPasswordValid = computed(() => {
return password.value ===

DAMO开发者矩阵,由阿里巴巴达摩院和中国互联网协会联合发起,致力于探讨最前沿的技术趋势与应用成果,搭建高质量的交流与分享平台,推动技术创新与产业应用链接,围绕“人工智能与新型计算”构建开放共享的开发者生态。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容





所有评论(0)