MIT6.830-lab5-B+ Tree Index(数据库的索引B+树的搜索、插入、删除窃取、删除合并)
MIT6.830的lab5中,我们将实现 B+ 树索引以进行高效查找和范围扫描。项目已经提供实现树结构所需的所有低级代码。我们所要做的是实现搜索、拆分页面、在页面之间重新分配元组以及合并页面。实现B+树的搜索,根据给定的key查找适当的页节点;实现内部节点、页节点的拆分,当页面中key的数量大于n-1时,对页面进行拆分;实现节点的重新分配,当删除key后如果页面中key的数量小于m/2 时,从其兄
文章目录
任务介绍
MIT6.830的lab5中,我们将实现 B+ 树索引以进行高效查找和范围扫描。
项目已经提供实现树结构所需的所有低级代码。我们所要做的是实现搜索、拆分页面、在页面之间重新分配元组以及合并页面。
主要任务就是:
- 实现B+树的搜索,根据给定的key查找适当的页节点;
- 实现内部节点、页节点的拆分,当页面中key的数量大于n-1时,对页面进行拆分;
- 实现节点的重新分配,当删除key后如果页面中key的数量小于m/2 时,从其兄弟节点“窃取”一个key;
- 实现节点的合并,当删除key后如果页面中key的数量小于m/2 时,且兄弟节点也只有m/2个key,则将两个节点合并。
B+树
基本介绍
B+树是B-树的变体,也是一颗多路搜索树。一棵n阶的B+树主要有这些特点:
- 每个结点至多有n个子女;
- 非根节点关键值个数范围:n/2(取上界) <= k <= n-1
- 相邻叶子节点是通过指针连起来的,并且是关键字大小排序的。
一颗3阶的B+树如下:
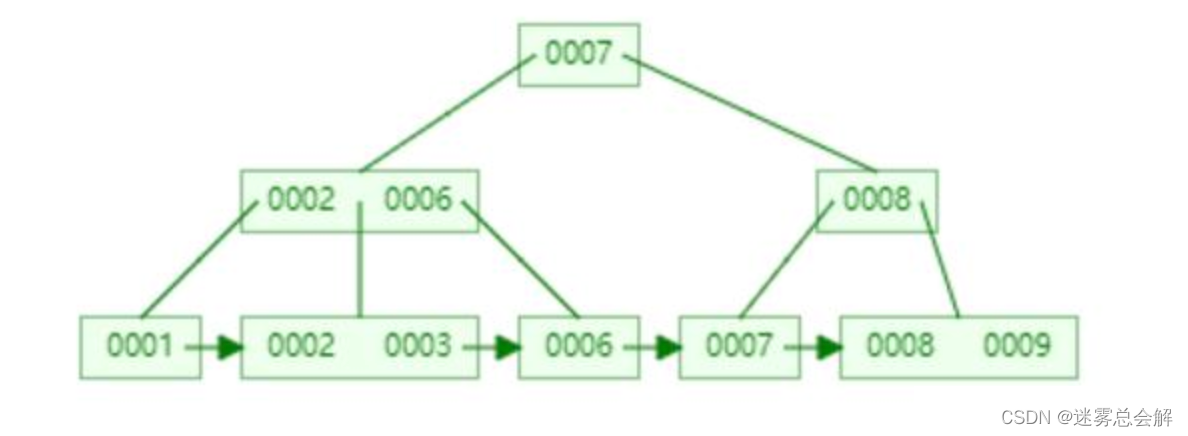
- B+树内部节点是不保存数据的,只作索引作用,它的叶子节点才保存数据;
- B+树相邻的叶子节点之间是通过链表指针连起来的;
- B+树中,内部节点与其父节点的key值不能重复,页节点与其父节点的key值可以重复。
查询
B+树的数据只存储在叶子节点,内部节点值存储索引,通过索引找到相应的叶子节点进行查询
(1)B+树的单值查询
当查询key=70的节点时,首先从读取根节点,判断得key<75;然后读取根节点的左孩子节点,将70依次与左孩子节点中的值进行比较,判断得key>66;则读取66的右孩子节点,key存储于该叶节点中,读取其中的数据。
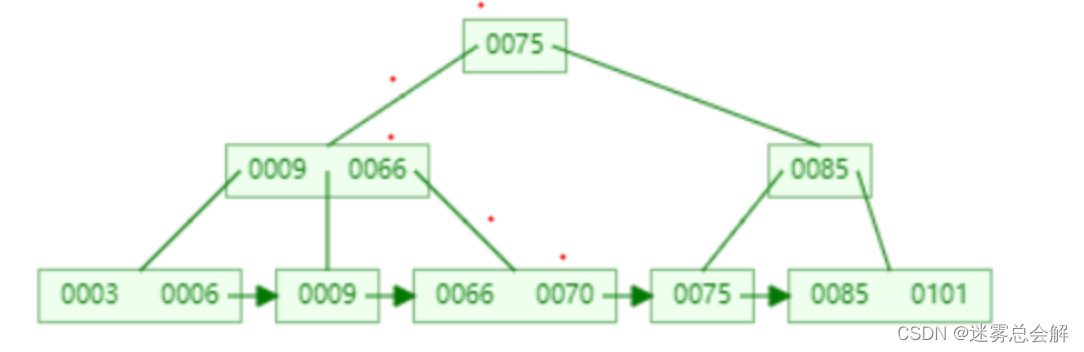
(2)B+树的范围查询
当要读取[68,100]范围内的数据时,首先找到第一个大于等于68的节点,然后在叶节点中向后遍历。
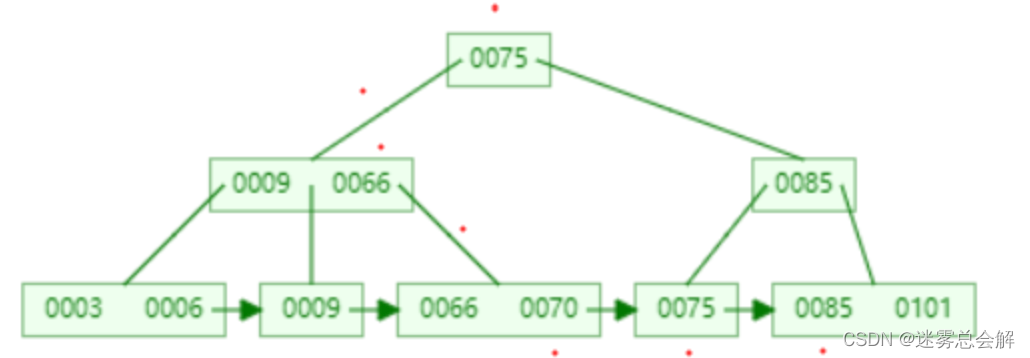
插入
B+树的插入是从叶子节点中进行的,找到要插入的叶子结点,将数据插入。然后根据插入后叶节点中key的数量进行不同的处理。
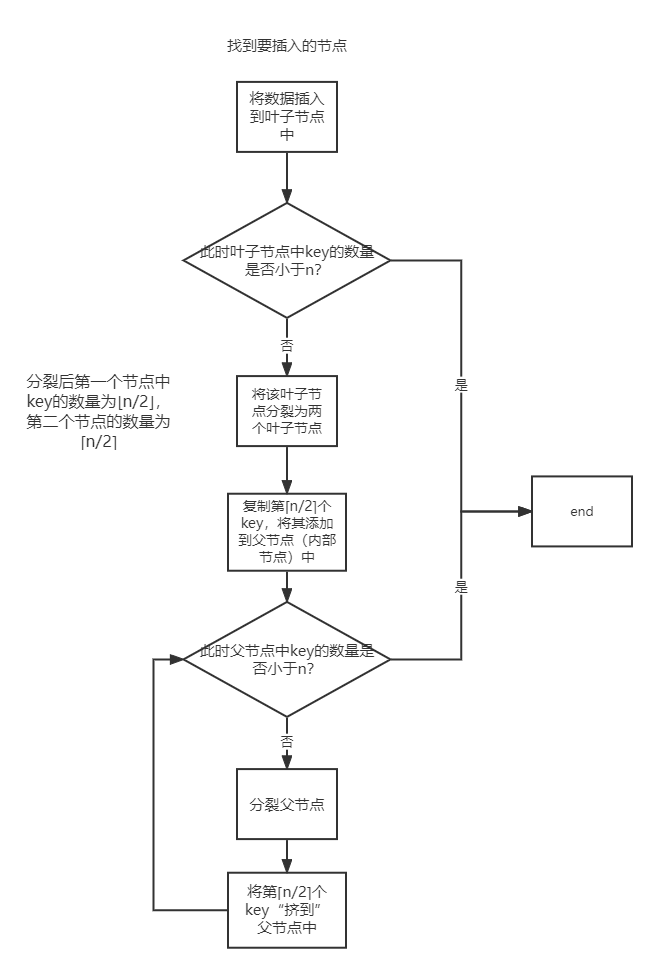
分裂叶节点和分裂内节点的情况是不同的。分裂叶节点时,节点中的key值复制到父节点中(即叶节点和内部节点可以有相同的值)
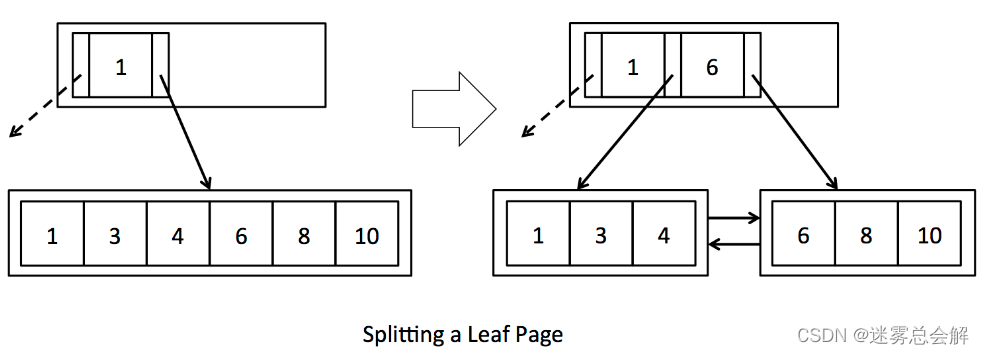
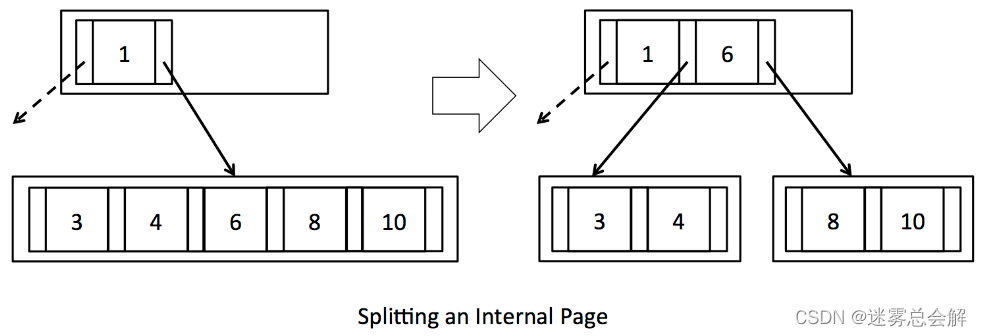
分裂内部节点时,是将节点中的key值“挤到”父节点中(即内部节点之间的key值不能重复)
删除
设:kyesNum = 节点中key的数量;min = ⌈n/2⌉-1 节点能容纳key的最小值,keysNum<min时该节点要进行合并或者“窃取”的操作;max = n-1
7阶B+树,min = 3
(1)叶子节点
keysNum < min ,兄弟节点的keys > min,从兄弟节点处“窃取”key:
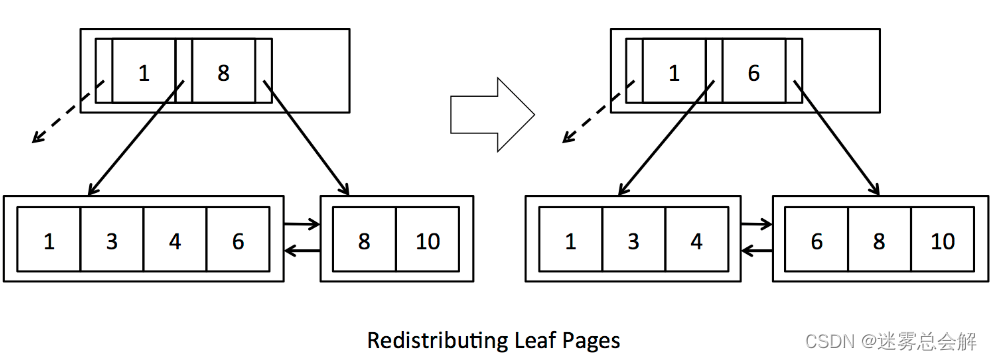
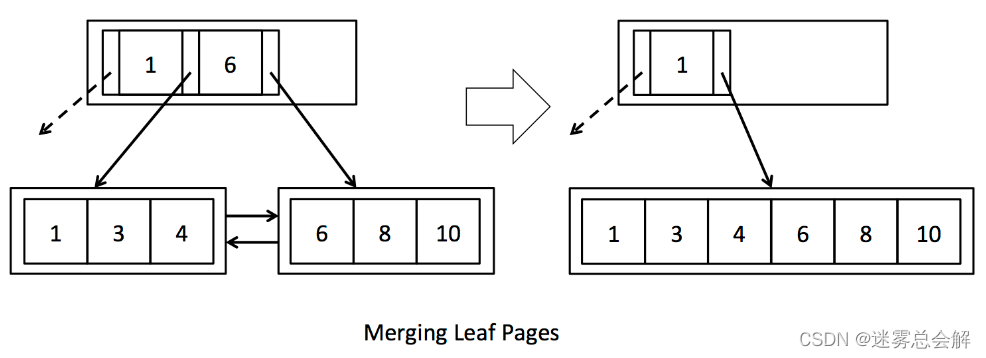
keysNum < min ,兄弟节点的keys = min,与兄弟节点合并:
(2)内部节点
keysNum < min ,兄弟节点的keys > min,从兄弟节点处“窃取”key:
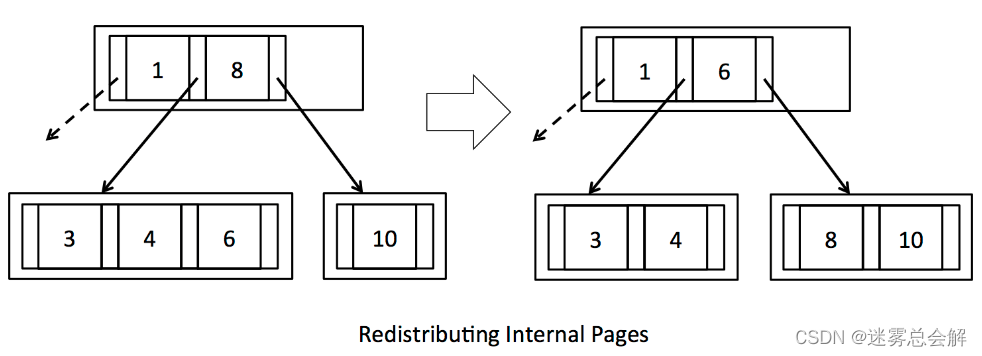
keysNum < min ,兄弟节点的keys = min,与兄弟节点合并:
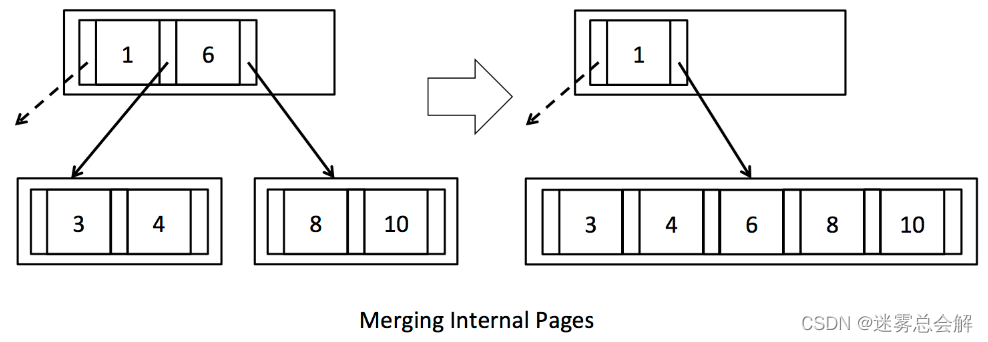
基本源码介绍
在本lab中,有些基本的类已经给出了,我们只需要调用即可,但这些类,我们也要搞清楚其中的关系。
为方便起见,我们在 BTreePage.java 中创建了一个抽象类,其中包含叶页和内部页共有的代码。此外,标题页在 BTreeHeaderPage.java 中实现,并跟踪文件中的哪些页面正在使用中。最后,每个 BTreeFile 的开头都有一个页面,它指向树的根页面和第一个标题页面。这个单例页面在 BTreeRootPtrPage.java 中实现。熟悉这些类的接口,尤其是BTreePage、BTreeInternalPage 和BTreeLeafPage。您将需要在 B+Tree 的实现中使用这些类。
除了我们要实现的BTreeFile之外,主要就是:BTreePageId、BTreePage、BTreeInternalPage、 BTreeLeafPage、 BTreeHeaderPage、BTreeRootPtrPage、BTreeEntry。
(1)BTreePageId
public final static int ROOT_PTR = 0;
public final static int INTERNAL = 1;
public final static int LEAF = 2;
public final static int HEADER = 3;
private final int tableId; //该page所在的的table id
private final int pgNo; //该page所在page的序号(table中的第几个页)
private final int pgcateg; //用于标识BTreePage的类型,也就是ROOT_PTR、INTERNAL、LEAF、HEADER这四种类型
和在前面lab中的HeapPage一样,每一个BTreePage也都会有一个BTreePageId。
注意下ROOT_PTR、INTERNAL、LEAF、HEADER这四种类型:
- ROOT_PTR是一个指向root节点的指针;
- INTERNAL和LEAF是一棵B+树中包含的节点;
- HEADER主要是标记页的使用情况。
(2)BTreePage
// 脏页标记和事务id
protected volatile boolean dirty = false;
protected volatile TransactionId dirtier = null;
// 索引的大小,也就是每一个指针的大小
// 以页节点为例,每一个页节点都有三个索引指针:left sibling pointer, right sibling pointer, parent pointer
protected final static int INDEX_SIZE = Type.INT_TYPE.getLen();
protected final BTreePageId pid; //当前节点的BTreePageId
protected final TupleDesc td; //当前节点的tuple元数据
protected final int keyField; //索引的关键字字段下标
//当前page的父page,如果是根节点那么就是0
protected int parent; // parent is always internal node or 0 for root node
// 存储旧的数据,oldDataLock是用于并发synchronized的锁
protected byte[] oldData;
protected final Byte oldDataLock= (byte) 0;
这是一个抽象类,其中包含BTreeInternalPage和BTreeLeafPage共有的代码。
(3)BTreeInternalPage(继承BTreePage)
private final byte[] header; //记录slot的占用情况
private final Field[] keys; //存储key的数组
private final int[] children; //存储page的序号,用于获取左孩子、右孩子的BTreePageId
private final int numSlots; //不是key的数量,而是内部节点中能存储的指针的数量(即n,内部节点中最多能存储key的数量为n-1)
private int childCategory; //孩子节点的类型(内部节点或叶节点)
其实内部节点可以看成保存着一个个BTreeEntry,内部节点对key的查找、插入、删除、迭代,都是以entry为单位的。通过BTreeEntry可以获取key、LeftChild、RightChild这三种信息,然后存入相应数组中。
(4)BTreeLeafPage(继承BTreePage)
private final byte[] header; //记录slot的占用情况
private final Tuple[] tuples; //存储该page的所有tuple
private final int numSlots; //叶节点中能存储的tuple数量(即n-1)
// 页节点的双向链表结构
private int leftSibling; //左兄弟的pageNo,用于获取左兄弟的BTreePageId,为0则没有左兄弟
private int rightSibling; //右兄弟的pageNo,用于获取右兄弟的BTreePageId,为0则没有右兄弟
叶节点和内部节点不一样的地方在于,其保存的是一个个真正的数据,也就是保存着一个个Tuple。还有就是其的链表结构用于顺序查找。
(5)BTreeRootPtrPage
//这个page的大小
public final static int PAGE_SIZE = 9;
// 脏页标记和事务id
private boolean dirty = false;
private TransactionId dirtier = null;
// 当前节点的BTreePageId
private final BTreePageId pid;
private int root; //保存当前根节点的pageNo
private int rootCategory; //保存当前根节点的类型,INTERNAL或LEAF,当只有一个节点时,就是LEAF
private int header; //保存当前header页的pageNo
private byte[] oldData; //存储旧的数据
(6)BTreeHeaderPage
// 脏页标记和事务id
private volatile boolean dirty = false;
private volatile TransactionId dirtier = null;
// 索引的大小,也就是每一个指针的大小
final static int INDEX_SIZE = Type.INT_TYPE.getLen();
final BTreePageId pid; //当前节点的BTreePageId
final byte[] header; //记录每一个page的使用情况,对应一个个pageNo
final int numSlots; //记录能存储的page使用情况数量
private int nextPage; // 下一个header page的pageNo,如果是最后一个,就是0
private int prevPage; // 上一个header page的pageNo,如果是第一个,就是0
// 存储旧的数据,oldDataLock是用于并发synchronized的锁
byte[] oldData;
private final Byte oldDataLock= (byte) 0;
这个page其实就和INTERNAL和LEAF中的byte[] header作用类似,就是当做一种标记记录,来记录每一个pageNo的使用情况,当删除一页时,就可以调用BTreeFile.setEmptyPage()函数,进而调用BTreeHeaderPage.markSlotUsed()函数将header中指定的pageNo设置为unused。
(7)BTreeEntry
/**
* The key of this entry
* */
private Field key; //内部节点中的key
/**
* The left child page id
* */
private BTreePageId leftChild; //左孩子的BTreePageId
/**
* The right child page id
* */
private BTreePageId rightChild; //右孩子的BTreePageId
/**
* The record id of this entry
* */
private RecordId rid; // 标识该entry所在的位置。(即该entry是哪个page中的)
内部节点中的entry,内部节点对key的查找、插入、删除、迭代,都是以entry为单位的。
来张图来直观的看一下:
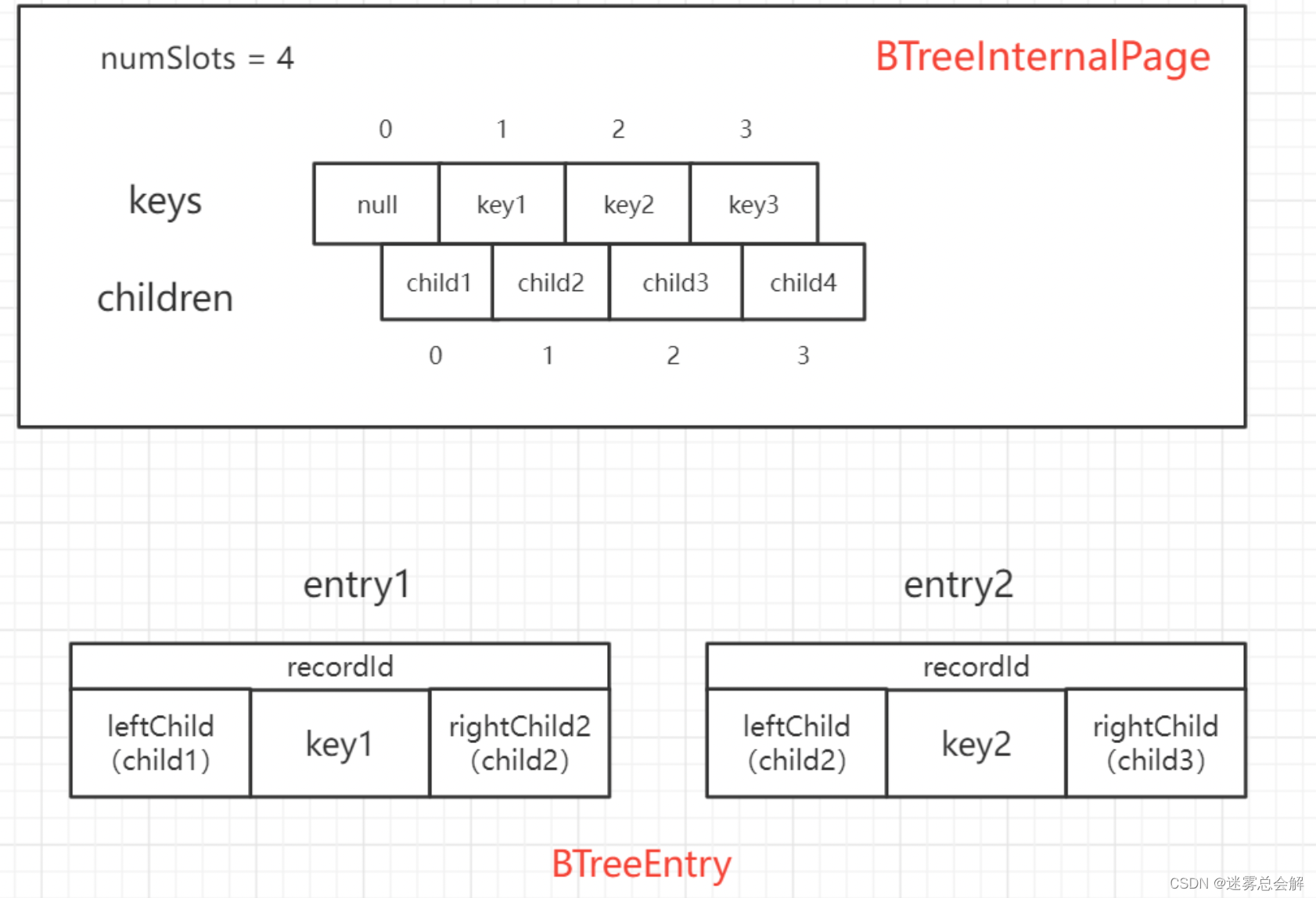
BTreeInternalPage底层页面并不存储BTreeEntry,而是存储n-1个key和n个指向子节点的指针(子页的pageNo,父页与子页同处一个table中,知道子页的pageNo就能获取到子页)。
exercise 1 - Search(BTreeFile.findLeafPage())
这个exercise主要就是实现BTreeFile中的findLeafPage()方法,实现B+树的查询。
注意这是一个递归函数,在B+树中查找可能包含字段 f 的叶节点。它使用只读权限锁定叶节点路径上的所有内部节点,并使用权限perm锁定叶节点。如果f为null,它将查找最左边的叶节点,用于迭代器。
private BTreeLeafPage findLeafPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages, BTreePageId pid, Permissions perm,
Field f)
throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
//1. 如果是叶子节点,直接返回
if(pid.pgcateg() == BTreePageId.LEAF){
return (BTreeLeafPage) getPage(tid,dirtypages,pid,perm);
}
BTreeInternalPage page = (BTreeInternalPage) getPage(tid,dirtypages,pid,perm);
Iterator<BTreeEntry> iterator = page.iterator();
//2. 如果filed为空,找到最左边的节点
if(f==null){
if(iterator.hasNext()){
return findLeafPage(tid,dirtypages,iterator.next().getLeftChild(),perm,f);
}
return null;
}
BTreeEntry next = null;
//3. 否则,内部节点查找符合条件的entry,并递归查找
while(iterator.hasNext()){
next = iterator.next();
Field key = next.getKey();
//当有重复值的时候 节点分裂有可能一半在左边一半在右边,所以是小于等于
if(f.compare(Op.LESS_THAN_OR_EQ,key)){
return findLeafPage(tid,dirtypages,next.getLeftChild(),perm,f);
}
}
//最后一个entry的右子节点
if(next!=null){
return findLeafPage(tid,dirtypages,next.getRightChild(),perm,f);
}
return null;
}
注意一下dirtypages:当创建新page或更改page中的数据、指针时,需要将其添加到dirtypages中。
主要判断步骤如下:
- 如果当前的节点就是叶节点了,那么直接返回,这里的叶节点要么是只有一个根节点,要么是进行递归所找到的叶节点;
- 如果filed为空,则递归找到最左边的节点,用于迭代器;
- 否则,就在当前这个内部节点进行查找,判断关键字的大小,从而进行下一步的递归。
getPage:调用getPage()获取page时,将检查页面是否已经存储在本地缓存dirtypage中,如果不再,则调用BufferPool.getPage去获取。getPage()如果使用读写权限获取页面,也会将页面添加到dirtypages缓存中,因为它们可能很快就会被弄脏。这种方法的一个优点是,如果在一个元组插入或删除过程中多次访问相同的页面,它可以防止更新丢失。
exercise 2 - Insert(Splitting Pages)
当我们进行插入Tuple时,可能会将数据插入到一个已经存满了Tuple的叶节点中,这就需要将该叶节点进行拆分,并将所有Tuple平均分配到两个page中(一半留在该page,一半放入另一个page)。
每次叶节点分裂时,都需要将第一页的最后一个元组对应的新条目添加到父节点。有时,内部节点也可能已满,无法接受新条目。在这种情况下,父级应该拆分并向其父级添加一个新条目。这可能会导致递归拆分并最终创建新的根节点。
而基于上诉思想,insertTuple并不需要我们完成,我们要做的任务是完成两个分裂函数:
- splitLeafPage():进行叶节点的拆分;
- splitInternalPage():进行内部节点的拆分。
(1)splitLeafPage
当页节点中元组数量等于n时,将其拆分成两个页节点。返回插入tuple所在的page。
public BTreeLeafPage splitLeafPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages, BTreeLeafPage page, Field field)
throws DbException, IOException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
//
// Split the leaf page by adding a new page on the right of the existing
// page and moving half of the tuples to the new page. Copy the middle key up
// into the parent page, and recursively split the parent as needed to accommodate
// the new entry. getParentWithEmtpySlots() will be useful here. Don't forget to update
// the sibling pointers of all the affected leaf pages. Return the page into which a
// tuple with the given key field should be inserted.
//1. 将当前page的后半部分放入新page
int half = page.getNumTuples() / 2;
BTreeLeafPage newPage = (BTreeLeafPage) getEmptyPage(tid, dirtypages, BTreePageId.LEAF);
Iterator<Tuple> iterator = page.reverseIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext() && half > 0) {
Tuple next = iterator.next();
//这里要先删除在插入,就很坑
page.deleteTuple(next);
newPage.insertTuple(next);
half--;
}
//2. 获取当前要插入的父节点,并插入新节点
Tuple up = iterator.next();
BTreeInternalPage parentPage = getParentWithEmptySlots(tid, dirtypages, page.getParentId(), field);
BTreeEntry insetEntry = new BTreeEntry(up.getField(keyField), page.getId(), newPage.getId());
parentPage.insertEntry(insetEntry);
//3. 设置节点间的关系
// page newPage rightSibling
if (page.getRightSiblingId() != null) {
BTreeLeafPage right = (BTreeLeafPage) getPage(tid, dirtypages, page.getRightSiblingId(), Permissions.READ_WRITE);
right.setLeftSiblingId(newPage.getId());
dirtypages.put(right.getId(),right);
}
newPage.setRightSiblingId(page.getRightSiblingId());
newPage.setLeftSiblingId(page.getId());
page.setRightSiblingId(newPage.getId());
//4. 增加脏页
dirtypages.put(parentPage.getId(),parentPage);
dirtypages.put(page.getId(),page);
dirtypages.put(newPage.getId(),newPage);
//5. 返回要插入field的页
if (field.compare(Op.GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ, up.getField(keyField))) {
return newPage;
}
return page;
}
- 将当前page的后半部分放入新page。通过getEmptyPage创建一个newPage,将当前page中后一半的tuple插入到newPage中。插入时应该先从page中删除tuple,然后再插入到newPage。(newRightPage插入tuple后会给其赋值新的recordId,page删除tuple时根据其recordId进行查找然后删除,而page无法定位到被赋值了新recordId的tuple,则无法将其删除);
- 获取当前要插入的父节点,并插入新节点。也就是将分裂后的page的最后一个tuple关键字形成一个entry并插入到父结点中。
- 设置节点间的关系。
- 如果当前page有右兄弟right,将right左兄弟的指针指向newPage,并将right添加到dirtypages中;
- 将newPage的左兄弟指针指向page,newPage的右兄弟指针指向page的右兄弟,将page的右兄弟指针指向newPage;
- 设置page和newPage的父节点;
- 将page、newPage、parentPage添加到dirtypages中。
- 返回field所在的页(page或newPage)。
getParentWithEmptySlots() 函数是获取一个父结点,并且这个父结点能够插入一个entry。因此这个函数中,可能会涉及内部节点的分裂。
(2)BTreeInternalPage
实现与splitLeafPage类似,区别是分裂之后要将中间的key“挤到” 父节点中去。
public BTreeInternalPage splitInternalPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages,
BTreeInternalPage page, Field field)
throws DbException, IOException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
//
// Split the internal page by adding a new page on the right of the existing
// page and moving half of the entries to the new page. Push the middle key up
// into the parent page, and recursively split the parent as needed to accommodate
// the new entry. getParentWithEmtpySlots() will be useful here. Don't forget to update
// the parent pointers of all the children moving to the new page. updateParentPointers()
// will be useful here. Return the page into which an entry with the given key field
// should be inserted.
//1. 将当前page的后半部分放入新page
int half = page.getNumEntries()/2;
BTreeInternalPage newPage = (BTreeInternalPage) getEmptyPage(tid, dirtypages, BTreePageId.INTERNAL);
Iterator<BTreeEntry> iterator = page.reverseIterator();
while(iterator.hasNext() && half>0){
BTreeEntry next = iterator.next();
page.deleteKeyAndRightChild(next);
newPage.insertEntry(next);
half--;
}
//2. 分裂完,中间的entry插入父节点。注意up节点要在原page中删除,并设置左右子节点。
BTreeEntry up = iterator.next();
page.deleteKeyAndRightChild(up);
up.setLeftChild(page.getId());
up.setRightChild(newPage.getId());
//这里父节点可能还会分裂获取
BTreeInternalPage parentPage = getParentWithEmptySlots(tid, dirtypages, page.getParentId(), field);
parentPage.insertEntry(up);
page.setParentId(parentPage.getId());
newPage.setParentId(parentPage.getId());
//3. 设置newPage子节点的父节点指向
updateParentPointers(tid,dirtypages,newPage);
//4. 增加脏页
dirtypages.put(parentPage.getId(),parentPage);
dirtypages.put(newPage.getId(),newPage);
dirtypages.put(page.getId(),page);
//5. 返回要插入field的页
if (field.compare(Op.GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ, up.getKey())) {
return newPage;
}
return page;
}
- 将当前page的后半部分放入新page;
- 分配完entry后,选出page中最大的entry,将其从page中删除,并将该entry的左孩子指针指向page,右孩子指针指向newPage,获取父节点parent,将该entry添加到父节点中(实现将中间的key“挤到”父节点中);
- 将父节点parent、page、newPage添加到dirtypages中,并更新它们孩子节点的父指针;
- 返回field所在的页(page或newPage)。
exercise 3 - Delete(Redistributing pages)
删除又是B+树的一个难点,核心在于一个节点被删到小于半满的时候,要么从(丰满的)兄弟那窃取一个元素,要么和另一个也小于半满的(苗条的)兄弟合并。而合并又会导致父节点中的划分元素被删除,运气好的时候父节点又会因为划分元素被删除了,而变成小于半满的苗条状态,然后又是要么从兄弟那窃取一个,要么和不够丰满的兄弟合并。而合并又导致他(父节点)的父节点的划分元素被删除……然后就这么在树上递归了,运气好的话能把Root节点给删了,也就是整个B+树的层数减一。
而在exercise 3中主要是实现三个和窃取有关的函数:
- stealFromLeafPage():叶节点从左/右节点窃取tuple;
- stealFromLeftInternalPage():内部节点从左内部节点窃取entry;
- stealFromRightInternalPage():内部节点从右内部节点窃取entry。
(1)stealFromLeafPage
public void stealFromLeafPage(BTreeLeafPage page, BTreeLeafPage sibling,
BTreeInternalPage parent, BTreeEntry entry, boolean isRightSibling) throws DbException {
// some code goes here
//
// Move some of the tuples from the sibling to the page so
// that the tuples are evenly distributed. Be sure to update
// the corresponding parent entry.
//1. 获取要窃取的tuple个数
int stealNum = ((page.getNumTuples()+sibling.getNumTuples())/2) - page.getNumTuples();
if(stealNum<=0){
return;
}
//2. 判断是从左还是右节点窃取,并获取迭代器
Iterator<Tuple> tupleIterator;
if(isRightSibling){
tupleIterator = sibling.iterator();
}else{
tupleIterator = sibling.reverseIterator();
}
//3. 进行窃取
Tuple next = null;
while(stealNum>0){
next = tupleIterator.next();
sibling.deleteTuple(next);
page.insertTuple(next);
stealNum--;
}
//4. 新建一个entry插入父节点
if(isRightSibling){
entry.setKey(tupleIterator.next().getField(keyField));
}else{
entry.setKey(next.getField(keyField));
}
parent.updateEntry(entry);
}
- 计算要窃取的tuple数量;
- 根据传入的参数
isRightSibling确定是从左兄弟中“窃取”,还是从右兄弟中“窃取”; - 进行tuple窃取,主要就是将兄弟节点的tuple删除,然后插入该节点;
- 参数
entry是父节点中指向page和其兄弟节点的entry,将entry的key更改为两个中右方节点的第一个tuple的关键字。
(2)stealFromLeftInternalPage
public void stealFromLeftInternalPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages,
BTreeInternalPage page, BTreeInternalPage leftSibling, BTreeInternalPage parent,
BTreeEntry parentEntry) throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
// Move some of the entries from the left sibling to the page so
// that the entries are evenly distributed. Be sure to update
// the corresponding parent entry. Be sure to update the parent
// pointers of all children in the entries that were moved.
//1. 获取要窃取的tuple个数
int stealNum = (page.getNumEntries()+leftSibling.getNumEntries())/2 - page.getNumEntries();
if(stealNum<=0){
return;
}
//2. 获取迭代器和节点
Iterator<BTreeEntry> leftIterator = leftSibling.reverseIterator();
Iterator<BTreeEntry> pageIterator = page.iterator();
BTreeEntry leftLastEntry = leftIterator.next();
BTreeEntry pageFirstEntry = pageIterator.next();
//3. 先将父节点中的中间entry插入page
BTreeEntry midEntry = new BTreeEntry(parentEntry.getKey(), leftLastEntry.getRightChild(), pageFirstEntry.getLeftChild());
page.insertEntry(midEntry);
stealNum--;
//4. 再插入左节点中的entry
while(stealNum>0){
leftSibling.deleteKeyAndRightChild(leftLastEntry);
page.insertEntry(leftLastEntry);
stealNum--;
leftLastEntry = leftIterator.next();
}
//5. 将左节点最大的entry插入到父节点
leftSibling.deleteKeyAndRightChild(leftLastEntry);
parentEntry.setKey(leftLastEntry.getKey());
parent.updateEntry(parentEntry);
//6. 设置newPage子节点的父节点指向
updateParentPointers(tid,dirtypages,page);
//7. 增加脏页
dirtypages.put(leftSibling.getId(),leftSibling);
dirtypages.put(page.getId(),page);
dirtypages.put(parent.getId(),parent);
}
- 根据page及其左兄弟中key的数量,确定从其做兄弟中“窃取”几个key;
- 因为内部节点与其父节点中的key值没有重复,迁移key的时候也需要将父节点中的key移动到page中。
- 将page左兄弟节点中的key平均分配给page;
- 分配之后,将page左兄弟节点中最大的key“挤到”父节点中;
- 更新newPage子节点的父节点指向;
- 增加脏页。
(3)stealFromRightInternalPage
public void stealFromRightInternalPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages,
BTreeInternalPage page, BTreeInternalPage rightSibling, BTreeInternalPage parent,
BTreeEntry parentEntry) throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
// Move some of the entries from the right sibling to the page so
// that the entries are evenly distributed. Be sure to update
// the corresponding parent entry. Be sure to update the parent
// pointers of all children in the entries that were moved.
//1. 获取要窃取的tuple个数
int stealNum = (page.getNumEntries()+rightSibling.getNumEntries())/2 - page.getNumEntries();
if(stealNum<=0){
return;
}
//2. 获取迭代器和节点
Iterator<BTreeEntry> rightIterator = rightSibling.iterator();
Iterator<BTreeEntry> pageIterator = page.reverseIterator();
BTreeEntry rightFirstEntry = rightIterator.next();
BTreeEntry pageLastEntry = pageIterator.next();
//3. 先将父节点中的中间entry插入page
BTreeEntry midEntry = new BTreeEntry(parentEntry.getKey(), pageLastEntry.getRightChild(), rightFirstEntry.getLeftChild());
page.insertEntry(midEntry);
stealNum--;
//4. 再插入右节点中的entry
while(stealNum>0){
rightSibling.deleteKeyAndRightChild(rightFirstEntry);
page.insertEntry(pageLastEntry);
stealNum--;
rightFirstEntry = rightIterator.next();
}
//5. 将右节点最小的entry插入到父节点
rightSibling.deleteKeyAndRightChild(rightFirstEntry);
parentEntry.setKey(rightFirstEntry.getKey());
parent.updateEntry(parentEntry);
//6. 设置newPage子节点的父节点指向
updateParentPointers(tid,dirtypages,page);
//7. 增加脏页
dirtypages.put(rightSibling.getId(),rightSibling);
dirtypages.put(page.getId(),page);
dirtypages.put(parent.getId(),parent);
}
- 根据page及其右兄弟中key的数量,确定从其做兄弟中“窃取”几个key;
- 因为内部节点与其父节点中的key值没有重复,迁移key的时候也需要将父节点中的key移动到page中。
- 将page右兄弟节点中的key平均分配给page;
- 分配之后,将page右兄弟节点中最大的key“挤到”父节点中;
- 更新newPage子节点的父节点指向;
- 增加脏页。
exercise 4 - Delete(Merging pages)
在exercise 4中主要是实现两个和page合并有关的函数:
- mergeLeafPages:删除元组时如果同级也处于最小占用率,则两个叶子节点合并,并从父级中删除指向两个page的entry,因此父结点可能也会合并;
- mergeInternalPages:叶子节点进行合并时,会删除内部节点的entry,而这可能会造成内部节点的合并
(1)mergeLeafPages
public void mergeLeafPages(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages,
BTreeLeafPage leftPage, BTreeLeafPage rightPage, BTreeInternalPage parent, BTreeEntry parentEntry)
throws DbException, IOException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
//
// Move all the tuples from the right page to the left page, update
// the sibling pointers, and make the right page available for reuse.
// Delete the entry in the parent corresponding to the two pages that are merging -
// deleteParentEntry() will be useful here
//1. 设置右兄弟节点
leftPage.setRightSiblingId(rightPage.getRightSiblingId());
//2. 如果右节点有右兄弟节点,就设置其左节点指向
if(rightPage.getRightSiblingId()!=null){
BTreeLeafPage rightSiblingPage= (BTreeLeafPage) getPage(tid, dirtypages, rightPage.getRightSiblingId(), Permissions.READ_WRITE);
rightSiblingPage.setLeftSiblingId(leftPage.getId());
dirtypages.put(rightSiblingPage.getId(),rightSiblingPage);
}
//3. 进行合并
Iterator<Tuple> iterator = rightPage.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Tuple next = iterator.next();
rightPage.deleteTuple(next);
leftPage.insertTuple(next);
}
//4. 设置空page并删除父结点的entry
setEmptyPage(tid,dirtypages,rightPage.getId().getPageNumber());
deleteParentEntry(tid,dirtypages,leftPage,parent,parentEntry);
//5. 增加脏页
dirtypages.remove(rightPage.getId());
dirtypages.put(leftPage.getId(),leftPage);
dirtypages.put(parent.getId(),parent);
}
- 设置右兄弟节点;
- 判断右节点是否有右兄弟节点,如果有,就设置其左节点指向;
- 进行节点的合并;
- 调用setEmptyPage方法将rightPage在header标记为空,调用deleteParentEntry方法,从父级中删除左右孩子指针指向leftPage和rightPage的entry;
- 将leftPage、rightPage、parent添加到dirtypages中。
(2)mergeInternalPages
public void mergeInternalPages(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages,
BTreeInternalPage leftPage, BTreeInternalPage rightPage, BTreeInternalPage parent, BTreeEntry parentEntry)
throws DbException, IOException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
//
// Move all the entries from the right page to the left page, update
// the parent pointers of the children in the entries that were moved,
// and make the right page available for reuse
// Delete the entry in the parent corresponding to the two pages that are merging -
// deleteParentEntry() will be useful here
//1. 获取两个节点的迭代器
Iterator<BTreeEntry> leftIterator = leftPage.reverseIterator();
Iterator<BTreeEntry> rightIterator = rightPage.iterator();
BTreeEntry leftLastEntry = leftIterator.next();
BTreeEntry rightFirstEntry = rightIterator.next();
//2. 将两节点中间的父节点entry插入到左节点,并将其删除
BTreeEntry midEntry = new BTreeEntry(parentEntry.getKey(), leftLastEntry.getRightChild(), rightFirstEntry.getLeftChild());
leftPage.insertEntry(midEntry);
deleteParentEntry(tid,dirtypages,leftPage,parent,parentEntry);
//3. 插入右节点的第一个entry
rightPage.deleteKeyAndLeftChild(rightFirstEntry);
leftPage.insertEntry(rightFirstEntry);
//4. 循环插入右节点的entry
while(rightIterator.hasNext()){
rightFirstEntry = rightIterator.next();
rightPage.deleteKeyAndLeftChild(rightFirstEntry);
leftPage.insertEntry(rightFirstEntry);
}
//5. 更新左节点的子节点的父节点指向
updateParentPointers(tid,dirtypages,leftPage);
//6. 设置空page
setEmptyPage(tid,dirtypages,rightPage.getId().getPageNumber());
//7. 增加脏页
dirtypages.remove(rightPage.getId());
dirtypages.put(leftPage.getId(),leftPage);
dirtypages.put(parent.getId(),parent);
}
- 先将父节点中的指向leftPage和rightPage的entry添加到leftPage中,并将其删除;
- 将rightPage中的entry添加到leftPage中;
- 更新左节点的子节点的父节点指向;
- 设置空page;
- 增加脏页。

DAMO开发者矩阵,由阿里巴巴达摩院和中国互联网协会联合发起,致力于探讨最前沿的技术趋势与应用成果,搭建高质量的交流与分享平台,推动技术创新与产业应用链接,围绕“人工智能与新型计算”构建开放共享的开发者生态。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献11条内容
已为社区贡献11条内容





所有评论(0)