学习open62541 --- [13] 历史数据
当我们使用OPC UA时,有时想观察一个变量的变化情况,就需要记录其历史数据,最后呈现出一个随时间变化的趋势图,下面就讲述如何在open62541里历史数据功能。一 配置open62541在open62541源码目录下的CMakeLists.txt里找到下面2个option,把默认值改为ON,UA_ENABLE_AMALGAMATIONUA_ENABLE_HISTORIZING第2...
当我们使用OPC UA时,有时想观察一个变量的变化情况,这就需要记录其历史数据,并呈现出一个随时间变化的趋势图,下面就讲述如何在open62541里使用历史数据功能。
一 配置open62541
在open62541源码目录下的CMakeLists.txt里找到下面2个option,把默认值改为ON,
- UA_ENABLE_AMALGAMATION
- UA_ENABLE_HISTORIZING
第2个option就是开启历史数据功能。设置完毕后,按如下步骤操作,
- cd到open62541源码目录下,新建build目录并cd进入
- 执行
cmake .. && make - 把open62541.h和bin下的libopen62541.a拷贝出来,放到如下目录,也可以随便放在自己想要的目录
历史数据的具体代码实现是在以下2个目录,第一个存放源文件,第二个存放头文件
- open62541/plugins/historydata
- open62541/plugins/include/open62541/historydata
是作为一个插件存在。
二 代码
1. OPCUA Server端代码
代码是opcua自带的example代码,即tutorial_server_historicaldata.c,对其做了一点修改,
// filename: server.c
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "open62541.h"
static UA_Boolean running = true;
static void stopHandler(int sign)
{
UA_LOG_INFO(UA_Log_Stdout, UA_LOGCATEGORY_SERVER, "received ctrl-c");
running = false;
}
typedef struct {
UA_NodeId nodeId;
UA_Server *server;
} container_t;
// 本函数用来修改opcua server添加的变量值,每隔3s修改一次
void *ChangeValueFunc(void *arg)
{
static UA_UInt32 update = 1; // 这是静态变量
container_t *ptr = (container_t*)arg;
UA_Server *server = ptr->server;
UA_NodeId targetNodeId = ptr->nodeId;
while (1)
{
sleep(3);
UA_Variant myVar;
UA_Variant_init(&myVar);
UA_Variant_setScalar(&myVar, &update, &UA_TYPES[UA_TYPES_UINT32]);
UA_Server_writeValue(server, targetNodeId, myVar);
++update;
if (update == 100)
{
break;
}
}
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
// 当按下ctrl+c后会调用stophandler()
signal(SIGINT, stopHandler);
signal(SIGTERM, stopHandler);
UA_Server *server = UA_Server_new();
UA_ServerConfig *config = UA_Server_getConfig(server);
UA_ServerConfig_setDefault(config);
/* We need a gathering for the plugin to constuct.
* The UA_HistoryDataGathering is responsible to collect data and store it to the database.
* We will use this gathering for one node, only. initialNodeIdStoreSize = 1
* The store will grow if you register more than one node, but this is expensive. */
UA_HistoryDataGathering gathering = UA_HistoryDataGathering_Default(1);
/* We set the responsible plugin in the configuration. UA_HistoryDatabase is
* the main plugin which handles the historical data service. */
config->historyDatabase = UA_HistoryDatabase_default(gathering);
/* Define the attribute of the uint32 variable node */
UA_VariableAttributes attr = UA_VariableAttributes_default;
UA_UInt32 myUint32 = 0;
UA_Variant_setScalar(&attr.value, &myUint32, &UA_TYPES[UA_TYPES_UINT32]);
attr.description = UA_LOCALIZEDTEXT("en-US","myUIntValue");
attr.displayName = UA_LOCALIZEDTEXT("en-US","myUIntValue");
attr.dataType = UA_TYPES[UA_TYPES_UINT32].typeId;
/* We set the access level to also support history read
* This is what will be reported to clients */
attr.accessLevel = UA_ACCESSLEVELMASK_READ | UA_ACCESSLEVELMASK_WRITE | UA_ACCESSLEVELMASK_HISTORYREAD;
/* We also set this node to historizing, so the server internals also know from it. */
attr.historizing = true;
/* Add the variable node to the information model */
UA_NodeId uint32NodeId = UA_NODEID_STRING(1, "myUIntValue");
UA_QualifiedName uint32Name = UA_QUALIFIEDNAME(1, "myUIntValue");
UA_NodeId parentNodeId = UA_NODEID_NUMERIC(0, UA_NS0ID_OBJECTSFOLDER);
UA_NodeId parentReferenceNodeId = UA_NODEID_NUMERIC(0, UA_NS0ID_ORGANIZES);
UA_NodeId outNodeId;
UA_NodeId_init(&outNodeId);
UA_StatusCode retval = UA_Server_addVariableNode(server,
uint32NodeId,
parentNodeId,
parentReferenceNodeId,
uint32Name,
UA_NODEID_NUMERIC(0, UA_NS0ID_BASEDATAVARIABLETYPE),
attr,
NULL,
&outNodeId);
UA_LOG_INFO(UA_Log_Stdout, UA_LOGCATEGORY_SERVER,
"UA_Server_addVariableNode %s", UA_StatusCode_name(retval));
/* Now we define the settings for our node */
UA_HistorizingNodeIdSettings setting;
/* There is a memory based database plugin. We will use that. We just
* reserve space for 3 nodes with 100 values each. This will also
* automaticaly grow if needed, but that is expensive, because all data must
* be copied. */
setting.historizingBackend = UA_HistoryDataBackend_Memory(3, 100);
/* We want the server to serve a maximum of 100 values per request. This
* value depend on the plattform you are running the server. A big server
* can serve more values, smaller ones less. */
setting.maxHistoryDataResponseSize = 100;
/* If we have a sensor which do not report updates
* and need to be polled we change the setting like that.
* The polling interval in ms.
*
setting.pollingInterval = 100;
*
* Set the update strategie to polling.
*
setting.historizingUpdateStrategy = UA_HISTORIZINGUPDATESTRATEGY_POLL;
*/
/* If you want to insert the values to the database yourself, we can set the user strategy here.
* This is useful if you for example want a value stored, if a defined delta is reached.
* Then you should use a local monitored item with a fuzziness and store the value in the callback.
*
setting.historizingUpdateStrategy = UA_HISTORIZINGUPDATESTRATEGY_USER;
*/
/* We want the values stored in the database, when the nodes value is
* set. */
setting.historizingUpdateStrategy = UA_HISTORIZINGUPDATESTRATEGY_VALUESET;
/* At the end we register the node for gathering data in the database. */
retval = gathering.registerNodeId(server, gathering.context, &outNodeId, setting);
UA_LOG_INFO(UA_Log_Stdout, UA_LOGCATEGORY_SERVER, "registerNodeId %s", UA_StatusCode_name(retval));
// -------------- 创建线程去修改opcua server添加的变量值 ---------------
pthread_t tid;
container_t container = {.nodeId = outNodeId, .server = server};
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, ChangeValueFunc, &container);
// --------------------------------------------------------------------
/* If you use UA_HISTORIZINGUPDATESTRATEGY_POLL, then start the polling.
*
retval = gathering.startPoll(server, gathering.context, &outNodeId);
UA_LOG_INFO(UA_Log_Stdout, UA_LOGCATEGORY_SERVER, "startPoll %s", UA_StatusCode_name(retval));
*/
retval = UA_Server_run(server, &running);
UA_LOG_INFO(UA_Log_Stdout, UA_LOGCATEGORY_SERVER, "UA_Server_run %s", UA_StatusCode_name(retval));
/*
* If you use UA_HISTORIZINGUPDATESTRATEGY_POLL, then stop the polling.
*
retval = gathering.stopPoll(server, gathering.context, &outNodeId);
UA_LOG_INFO(UA_Log_Stdout, UA_LOGCATEGORY_SERVER, "stopPoll %s", UA_StatusCode_name(retval));
*/
UA_Server_delete(server);
return retval == UA_STATUSCODE_GOOD ? EXIT_SUCCESS : EXIT_FAILURE;
}
代码注意点:
- 创建变量的attribute时,其accessLevel属性要或上UA_ACCESSLEVELMASK_HISTORYREAD,其historizing属性设置为true
- UA_Server_addVariableNode()关于节点自身的id有2个参数,第2个和最后一个,即uint32NodeId和outNodeId,uint32NodeId是期望的id,outNodeId是server给出的id,一般来说2个id是一样的
- UA_HistoryDataGathering_Default()创建UA_HistoryDataGathering类型的变量,这个变量用于highlevel的数据库操作,如收集历史数据并存放到数据库里,并提供数据库的增删改查操作,具体可以参考其源码
- UA_HistorizingNodeIdSettings用于对node进行历史数据功能设置,UA_HistoryDataBackend_Memory()的返回值赋给historizingBackend属性,这个属性是用于创建实际的数据库,并且执行lowlevel的数据库操作 ;historizingUpdateStrategy值为UA_HISTORIZINGUPDATESTRATEGY_VALUESET,表示历史数据的更新策略是当变量值发生变化就会把数据写到数据库里
- 调用gathering.registerNodeId()把目标node注册进去
- 创建线程去每隔3s修改节点的值,这样就会触发历史数据的写入
剩余的内容可以看代码里的注释,或者去看源码,总体来说,还是有点小复杂的。
2. OPC UA Client端代码
代码是opcua自带的example代码,即client_historical.c,对其做了一点修改,
// filename: client.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "open62541.h"
static void printTimestamp(char *name, UA_DateTime date)
{
UA_DateTimeStruct dts = UA_DateTime_toStruct(date);
if (name)
printf("%s: %02u-%02u-%04u %02u:%02u:%02u.%03u, ", name,
dts.day, dts.month, dts.year, dts.hour, dts.min, dts.sec, dts.milliSec);
else
printf("%02u-%02u-%04u %02u:%02u:%02u.%03u, ",
dts.day, dts.month, dts.year, dts.hour, dts.min, dts.sec, dts.milliSec);
}
static void printDataValue(UA_DataValue *value)
{
// Print status and timestamps
if (value->hasServerTimestamp)
printTimestamp("ServerTime", value->serverTimestamp);
if (value->hasSourceTimestamp)
printTimestamp("SourceTime", value->sourceTimestamp);
if (value->hasStatus)
printf("Status 0x%08x, ", value->status);
if (value->value.type == &UA_TYPES[UA_TYPES_UINT32]) {
UA_UInt32 hrValue = *(UA_UInt32 *)value->value.data;
printf("Uint32Value %u\n", hrValue);
}
if (value->value.type == &UA_TYPES[UA_TYPES_DOUBLE]) {
UA_Double hrValue = *(UA_Double *)value->value.data;
printf("DoubleValue %f\n", hrValue);
}
}
static UA_Boolean readRaw(const UA_HistoryData *data)
{
printf("readRaw Value count: %lu\n", (long unsigned)data->dataValuesSize);
// Iterate over all values
for (UA_UInt32 i = 0; i < data->dataValuesSize; ++i)
{
printDataValue(&data->dataValues[i]);
}
// We want more data!
return true;
}
static UA_Boolean readHist(UA_Client *client, const UA_NodeId *nodeId,
UA_Boolean moreDataAvailable,
const UA_ExtensionObject *data, void *unused)
{
printf("\nRead historical callback:\n");
printf("\tHas more data:\t%d\n\n", moreDataAvailable);
if (data->content.decoded.type == &UA_TYPES[UA_TYPES_HISTORYDATA])
{
return readRaw((UA_HistoryData*)data->content.decoded.data);
}
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
UA_Client *client = UA_Client_new();
UA_ClientConfig_setDefault(UA_Client_getConfig(client));
// Connect to OPC UA server
UA_StatusCode retval = UA_Client_connect(client, "opc.tcp://localhost:4840");
if(retval != UA_STATUSCODE_GOOD) {
UA_Client_delete(client);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Read historical values (uint32)
printf("\nStart historical read (1, \"myUIntValue\"):\n");
UA_NodeId node = UA_NODEID_STRING(1, "myUIntValue");
retval = UA_Client_HistoryRead_raw(client, &node, readHist,
UA_DateTime_fromUnixTime(0), UA_DateTime_now(),
UA_STRING_NULL, false, 10,
UA_TIMESTAMPSTORETURN_BOTH, NULL);
if (retval != UA_STATUSCODE_GOOD) {
printf("Failed. %s\n", UA_StatusCode_name(retval));
}
UA_Client_disconnect(client);
UA_Client_delete(client);
return retval == UA_STATUSCODE_GOOD ? EXIT_SUCCESS : EXIT_FAILURE;
}
主要是使用了函数UA_Client_HistoryRead_raw(),其原型如下,
UA_StatusCode
UA_Client_HistoryRead_raw(UA_Client *client, const UA_NodeId *nodeId,
const UA_HistoricalIteratorCallback callback,
UA_DateTime startTime, UA_DateTime endTime,
UA_String indexRange, UA_Boolean returnBounds, UA_UInt32 numValuesPerNode,
UA_TimestampsToReturn timestampsToReturn, void *callbackContext)
关键参数解释:
- nodeId:目标节点id
- callback:读取到历史数据后的回调函数,用来处理历史数据
- startTime:读取一段时间内的历史数据,这段时间的起点
- endTime:读取一段时间内的历史数据,这段时间的终点
- numValuesPerNode:一次最多读取的历史数据个数,注意,这里的一次不是指函数调用一次,而是从数据库读取一次,如果在规定时间段内有100个数据,本参数设置为10,那么一次函数调用就会读取10次
- timestampsToReturn:期望返回的历史数据的时间类型
代码中调用UA_Client_HistoryRead_raw()期望读取1970年0点0分到函数调用这段时间内的目标节点的所有历史数据并打印出来,UA_DateTime_fromUnixTime(0)返回的时间是1970年0点0分。
这里的callbck参数使用的是readHist(),这里只做了打印,也可以在里面添加代码把数据绘成趋势图,如使用gnuplot或者python。
3. 编译运行
整体工程结构如下,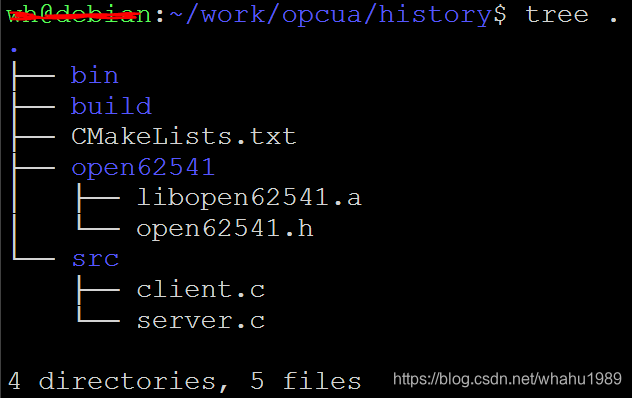
CMakeLists.txt如下,
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)
project(history)
set (EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin)
add_definitions(-std=c99)
include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/open62541)
link_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/open62541)
add_executable(server ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/server.c)
target_link_libraries(server libopen62541.a pthread)
add_executable(client ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/client.c)
target_link_libraries(client libopen62541.a)
编译过程如下,
- cd到build目录下,执行
cmake .. && make - 在bin目录下先执行server,等个十几秒后再执行client,client运行效果如下,
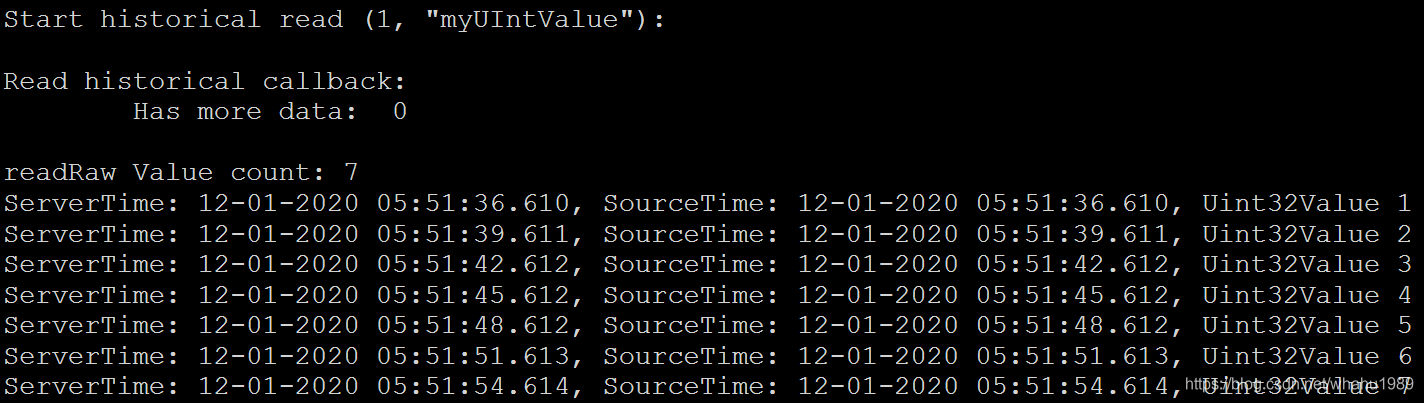
可以看到相邻数据值的时间间隔是3s,而且其值变化率也是和我们在server代码里的逻辑是一样的。
四 使用UAExpert查看
UAExpert也可以查看历史数据,并绘图。先运行server,然后使用UAExpert进行连接,连接ok后如下,
右击Project下的Documents,点击Add,在弹出的界面里选择History Trend View,然后点击Add,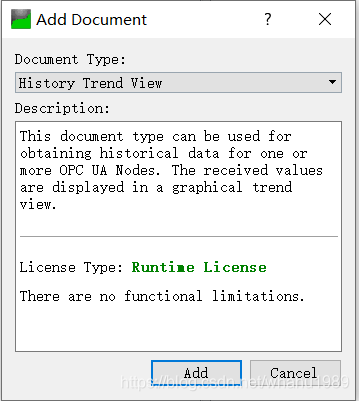
接着出现History Trend View,下面又个Configuration窗口,可以直接把目标节点拖拽到Configuration窗口里,或者,
在History Trend View的Configuration窗口里右击,然后点击Add custom node,
PS:在下图的History Data窗口中有三个曲线图,这些是样例,用来表示可以画出啥样的图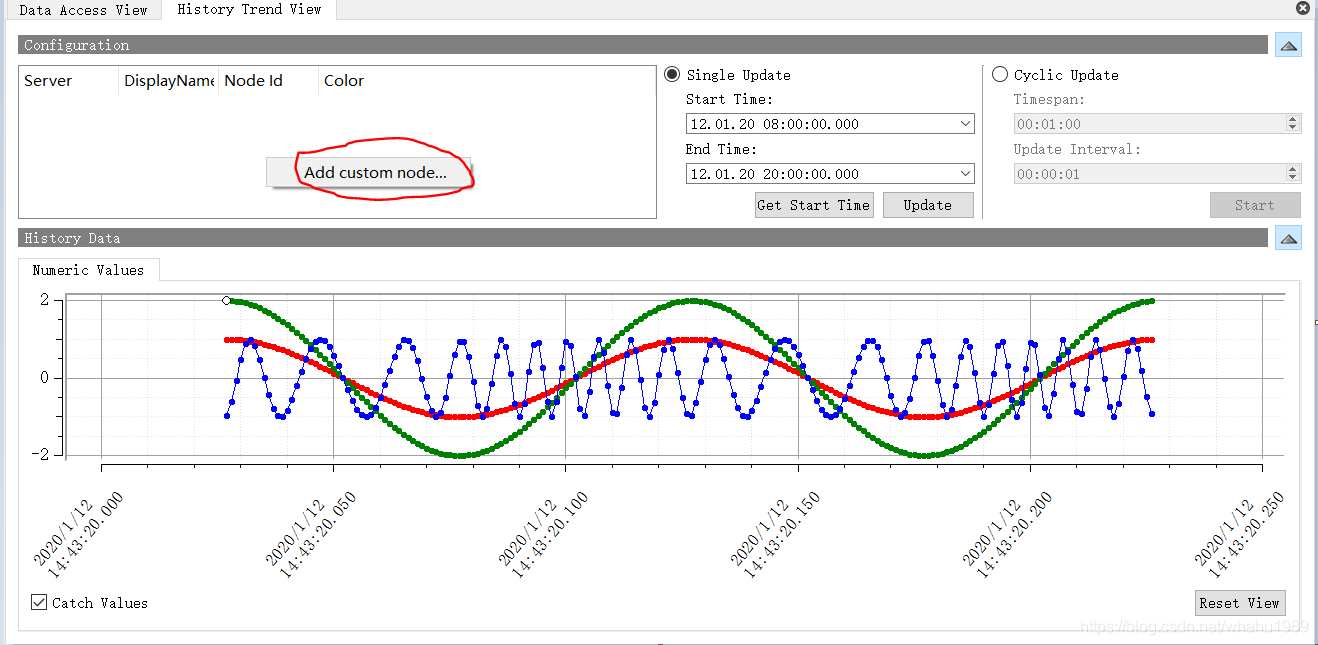
弹出如下界面,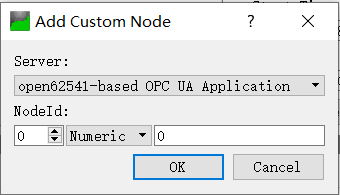
我们的目标节点的id定义如下,是string格式
UA_NodeId node = UA_NODEID_STRING(1, "myUIntValue");
所以按如下填入,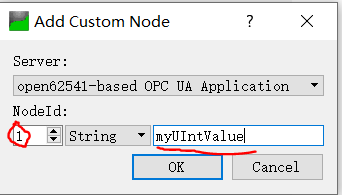
然后点击OK,这样节点就添加好了,如下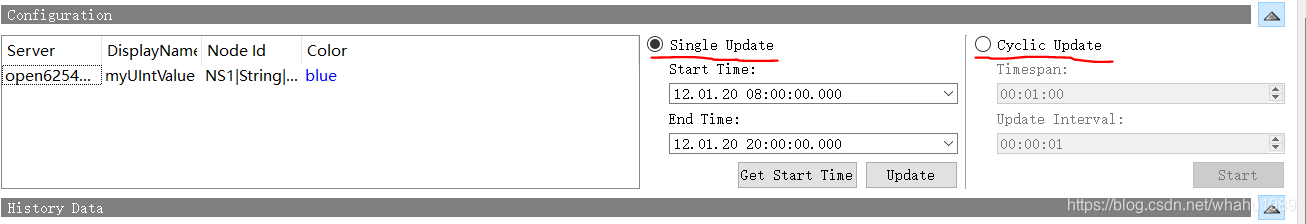
关于更新数据,有2个类型,Single Update和Cyclic Update,默认选的是Single Update,然后点击Update按钮就可以在History Data窗口中绘图了,显示在Numeric Values栏下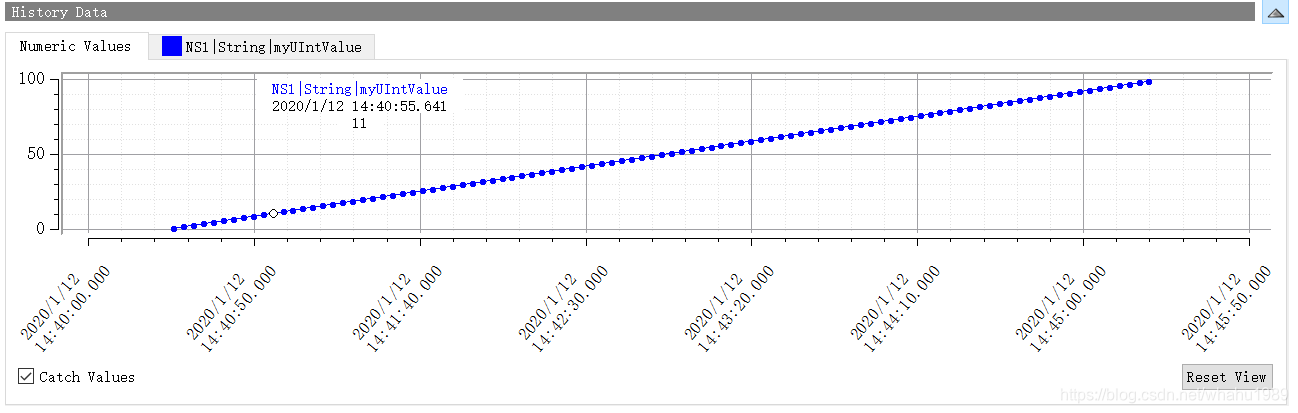
NS1|String|myUIntValue栏下则是使用打印的方式显示各个时间点的数据,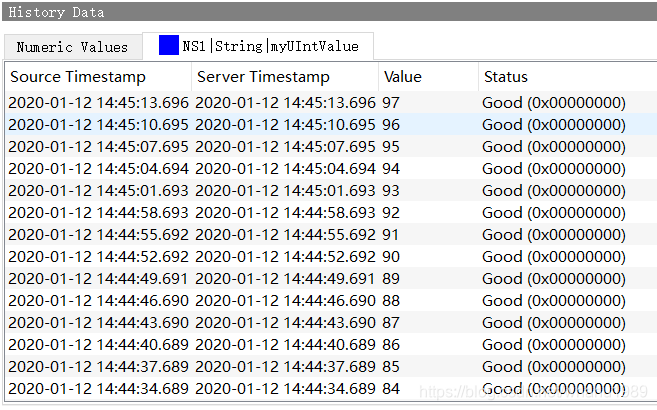
Single Update需要手动点击Update去主动进行更新,Cyclic Update可以自动更新并刷新趋势图,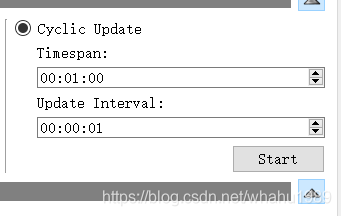
Cyclic Update有2个参数需要设置:Timespan和Update Interval,Timespan表示只显示该时间跨度内内的值,图片中设置的是1分钟,表示只显示1分钟的历史数据;Update Interval表示更新频率,图片中设置的是1秒,即每隔1s去更新一次。
这个类似于一个ringbuffer(环形buffer),当读取的数据超过了1分钟,就把最旧的数据丢弃,保持最新数据和最旧数据的时间差值在1分钟以内。
五 总结
本文主要讲述了如何设置节点的历史数据功能以及如何读取历史数据,该功能是以插件形式存在,用户可以自己修改源码或者添加自己的插件,另外,读者可以去阅读源码,来彻底搞懂内部是如何运行的。
如果有写的不对的地方,希望能留言指正,谢谢阅读。

DAMO开发者矩阵,由阿里巴巴达摩院和中国互联网协会联合发起,致力于探讨最前沿的技术趋势与应用成果,搭建高质量的交流与分享平台,推动技术创新与产业应用链接,围绕“人工智能与新型计算”构建开放共享的开发者生态。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容








所有评论(0)