WPF之数据绑定基础
数据绑定是WPF(Windows Presentation Foundation)中最强大的特性之一,它实现了UI元素与数据源之间的自动同步。通过数据绑定,开发者可以将界面与业务逻辑分离,实现MVVM(Model-View-ViewModel)等设计模式,提高代码的可维护性和可测试性。数据绑定建立了目标对象(通常是UI元素)和源对象(数据源)之间的连接。当源对象发生变化时,目标对象会自动更新;反之
可以根据Github拉取示例程序运行
GitHub程序演示地址(点击直达)
也可以在本文资源中下载
数据绑定是WPF(Windows Presentation Foundation)中最强大的特性之一,它实现了UI元素与数据源之间的自动同步。通过数据绑定,开发者可以将界面与业务逻辑分离,实现MVVM(Model-View-ViewModel)等设计模式,提高代码的可维护性和可测试性。
1. 数据绑定的概念
数据绑定建立了目标对象(通常是UI元素)和源对象(数据源)之间的连接。当源对象发生变化时,目标对象会自动更新;反之亦然(取决于绑定模式)。
1.1 绑定的基本组成部分
一个完整的绑定表达式通常包含以下几个部分:
- 目标:接收数据的对象和属性(如TextBox.Text)
- 源:提供数据的对象(如ViewModel中的属性)
- 路径:指定源对象上的哪个属性被绑定
- 模式:指定数据如何在源和目标之间流动
- 更新触发器:确定何时将修改后的值从目标传回源
- 转换器:在源和目标之间转换数据(如果需要)
2. 绑定表达式
WPF中的绑定主要通过XAML中的{Binding}标记扩展来实现。基本语法如下:
<对象属性="{Binding [Path=]属性路径,
Source=绑定源,
Mode=绑定模式,
UpdateSourceTrigger=更新触发器,
Converter=转换器,
...其他参数}" />
2.1 简单绑定示例
<TextBox x:Name="txtName" Text="{Binding Name}" />
这里,TextBox的Text属性被绑定到数据上下文(DataContext)中的Name属性。
3. 绑定源和目标
3.1 绑定目标
绑定目标是接收数据的UI元素属性,例如TextBox的Text属性、Image的Source属性等。任何依赖属性都可以作为绑定目标。
3.2 绑定源
绑定源是提供数据的对象,可以通过以下几种方式指定:
- DataContext:最常用的方式,一个元素的DataContext会被其所有子元素继承
- ElementName:绑定到界面上另一个命名元素的属性
- RelativeSource:相对于目标元素的源(如Self、FindAncestor等)
- Source:直接指定绑定源对象
下面是几种指定绑定源的示例:
<!-- 使用DataContext (隐式) -->
<TextBox Text="{Binding Name}" />
<!-- 使用ElementName -->
<Slider x:Name="slider1" Maximum="100" />
<TextBox Text="{Binding Value, ElementName=slider1}" />
<!-- 使用RelativeSource -->
<Button Content="{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource Self}, Path=ActualWidth}" />
<!-- 使用静态资源作为Source -->
<TextBox Text="{Binding Path=AppName, Source={StaticResource AppSettings}}" />
4. 绑定路径
Path属性指定了在源对象上要绑定的属性路径。路径可以是:
4.1 简单属性
<TextBox Text="{Binding FirstName}" />
4.2 复合属性(属性链)
<TextBox Text="{Binding Address.City}" />
4.3 索引器
<TextBox Text="{Binding Items[0]}" />
4.4 附加属性
<Button Content="{Binding (Grid.Row)}" />
4.5 集合对象的当前项
<TextBox Text="{Binding Path=/}" />
4.6 使用点号表示当前对象
<TextBox Text="{Binding Path=.}" />
5. 绑定模式
绑定模式决定了数据如何在源和目标之间流动。WPF提供了五种绑定模式:
| 模式 | 描述 | 典型使用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| OneWay | 从源到目标的单向绑定 | 显示只读数据 |
| TwoWay | 源和目标之间的双向绑定 | 可编辑表单 |
| OneTime | 初始化时从源到目标绑定一次 | 静态数据显示 |
| OneWayToSource | 从目标到源的单向绑定 | 特殊场景,如只需将用户输入传递给源 |
| Default | 取决于目标属性的默认绑定模式 | 默认情况 |
<!-- 单向绑定 -->
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Status, Mode=OneWay}" />
<!-- 双向绑定 -->
<TextBox Text="{Binding UserInput, Mode=TwoWay}" />
<!-- 一次性绑定 -->
<TextBlock Text="{Binding StaticText, Mode=OneTime}" />
<!-- 单向绑定到源 -->
<Slider Value="{Binding Percentage, Mode=OneWayToSource}" />
不同控件属性有不同的默认绑定模式:
- 大多数读写属性(如TextBox.Text)默认为TwoWay
- 只读属性(如TextBlock.Text)默认为OneWay
- 其他属性通常默认为OneWay
6. 更新触发器
UpdateSourceTrigger属性指定了在双向绑定中,何时将更改从目标传回源。有四个选项:
| 触发器 | 描述 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| PropertyChanged | 属性值发生变化时立即更新源 | 即时反馈,如CheckBox |
| LostFocus | 控件失去焦点时更新源 | 表单字段完成输入后 |
| Explicit | 仅当调用BindingExpression.UpdateSource()时更新源 | 需要手动控制更新时机 |
| Default | 取决于目标属性的默认更新行为 | 默认情况 |
<!-- 属性变化时立即更新 -->
<TextBox Text="{Binding SearchTerm, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" />
<!-- 失去焦点时更新 -->
<TextBox Text="{Binding CustomerName, UpdateSourceTrigger=LostFocus}" />
注:TextBox.Text属性的默认UpdateSourceTrigger是LostFocus,而CheckBox.IsChecked是PropertyChanged。
7. 代码示例
7.1 基本的数据绑定
下面是一个简单的数据绑定示例,展示了ViewModel和View之间的绑定:
Person类 (Model)
public class Person
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
PersonViewModel类 (ViewModel)
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
public class PersonViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private Person _person;
// 实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
public PersonViewModel()
{
// 初始化模型数据
_person = new Person
{
FirstName = "张",
LastName = "三",
Age = 30
};
}
// 公开的属性,用于绑定
public string FirstName
{
get { return _person.FirstName; }
set
{
if (_person.FirstName != value)
{
_person.FirstName = value;
OnPropertyChanged(); // 通知UI该属性已变更
OnPropertyChanged(nameof(FullName)); // 关联属性也需要通知变更
}
}
}
public string LastName
{
get { return _person.LastName; }
set
{
if (_person.LastName != value)
{
_person.LastName = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
OnPropertyChanged(nameof(FullName));
}
}
}
public int Age
{
get { return _person.Age; }
set
{
if (_person.Age != value)
{
_person.Age = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
// 计算属性示例
public string FullName
{
get { return $"{FirstName} {LastName}"; }
}
}
MainWindow.xaml
<Window x:Class="WpfBindingDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="WPF绑定示例" Height="350" Width="500">
<Grid Margin="10">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<!-- 标题 -->
<TextBlock Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2"
Text="人员信息" FontSize="20" Margin="0,0,0,20"/>
<!-- 姓绑定 -->
<TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" Text="姓:" Margin="0,0,10,5"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBox Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1" Text="{Binding FirstName, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
Margin="0,0,0,5" Padding="3"/>
<!-- 名绑定 -->
<TextBlock Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="0" Text="名:" Margin="0,0,10,5"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBox Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="1" Text="{Binding LastName, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
Margin="0,0,0,5" Padding="3"/>
<!-- 年龄绑定 -->
<TextBlock Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="0" Text="年龄:" Margin="0,0,10,5"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBox Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="1" Text="{Binding Age, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
Margin="0,0,0,5" Padding="3"/>
<!-- 全名显示 (只读) -->
<TextBlock Grid.Row="4" Grid.Column="0" Text="全名:" Margin="0,0,10,5"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBlock Grid.Row="4" Grid.Column="1" Text="{Binding FullName}"
Margin="0,0,0,5" Padding="3" Background="LightGray"/>
</Grid>
</Window>
MainWindow.xaml.cs
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfBindingDemo
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 设置数据上下文为ViewModel实例
this.DataContext = new PersonViewModel();
}
}
}
7.2 ElementName绑定示例
绑定到其他UI元素的属性:
<Window x:Class="WpfBindingDemo.ElementNameDemo"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="ElementName绑定示例" Height="300" Width="400">
<StackPanel Margin="10">
<TextBlock Text="拖动滑块来调整文本大小" Margin="0,0,0,10"/>
<!-- 滑块控件 -->
<Slider x:Name="fontSizeSlider"
Minimum="10" Maximum="50" Value="14"
TickFrequency="2" TickPlacement="BottomRight"
Margin="0,0,0,20"/>
<!-- 显示当前值 -->
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Value, ElementName=fontSizeSlider, StringFormat=当前字体大小: {0}}"
Margin="0,0,0,10"/>
<!-- 应用字体大小 -->
<TextBlock Text="这段文字的大小会随着滑块的值变化而变化"
FontSize="{Binding Value, ElementName=fontSizeSlider}"/>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
7.3 RelativeSource绑定示例
使用RelativeSource查找祖先元素:
<Window x:Class="WpfBindingDemo.RelativeSourceDemo"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="RelativeSource绑定示例" Height="300" Width="400">
<Grid>
<ListBox Margin="10">
<ListBoxItem>
<Border BorderBrush="Blue" BorderThickness="1" Padding="5">
<TextBlock>
<!-- 使用RelativeSource查找ListBoxItem,并绑定到其Content属性 -->
<Run>我的父级ListBoxItem的内容是: </Run>
<Run Text="{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource
FindAncestor, AncestorType={x:Type ListBoxItem}},
Path=Content}"/>
</TextBlock>
</Border>
</ListBoxItem>
<ListBoxItem>第二项</ListBoxItem>
<ListBoxItem>第三项</ListBoxItem>
</ListBox>
</Grid>
</Window>
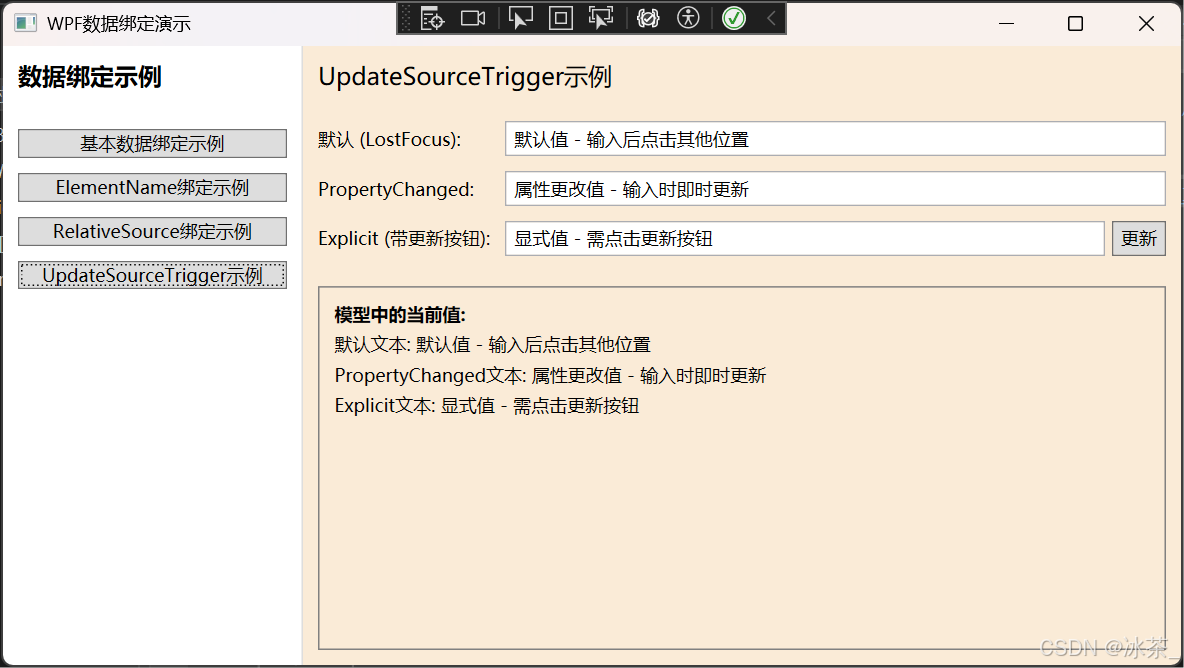
7.4 使用UpdateSourceTrigger示例
比较不同的UpdateSourceTrigger设置:
<Window x:Class="WpfBindingDemo.UpdateSourceTriggerDemo"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="UpdateSourceTrigger示例" Height="350" Width="500">
<Window.Resources>
<!-- 为演示创建一个简单的ViewModel -->
<local:UpdateSourceViewModel x:Key="ViewModel"/>
</Window.Resources>
<Grid DataContext="{StaticResource ViewModel}" Margin="10">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<TextBlock Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2"
Text="UpdateSourceTrigger示例" FontSize="16" Margin="0,0,0,20"/>
<!-- 默认行为 (LostFocus) -->
<TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" Text="默认 (LostFocus):"
VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="0,0,10,10"/>
<TextBox Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1"
Text="{Binding DefaultText}" Margin="0,0,0,10" Padding="3"/>
<!-- PropertyChanged -->
<TextBlock Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="0" Text="PropertyChanged:"
VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="0,0,10,10"/>
<TextBox Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="1"
Text="{Binding PropertyChangedText, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
Margin="0,0,0,10" Padding="3"/>
<!-- Explicit -->
<TextBlock Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="0" Text="Explicit (带更新按钮):"
VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="0,0,10,10"/>
<Grid Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="1" Margin="0,0,0,10">
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<TextBox x:Name="explicitTextBox" Grid.Column="0"
Text="{Binding ExplicitText, UpdateSourceTrigger=Explicit}"
Padding="3"/>
<Button Grid.Column="1" Content="更新" Margin="5,0,0,0" Padding="5,0"
Click="UpdateExplicit_Click"/>
</Grid>
<!-- 结果显示 -->
<Border Grid.Row="4" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2"
BorderBrush="Gray" BorderThickness="1" Margin="0,10,0,0" Padding="10">
<StackPanel>
<TextBlock Text="模型中的当前值:" FontWeight="Bold"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding DefaultText, StringFormat=默认文本: {0}}" Margin="0,5,0,0"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding PropertyChangedText, StringFormat=PropertyChanged文本: {0}}" Margin="0,5,0,0"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding ExplicitText, StringFormat=Explicit文本: {0}}" Margin="0,5,0,0"/>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
</Grid>
</Window>
UpdateSourceViewModel.cs
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
namespace WpfBindingDemo
{
public class UpdateSourceViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
// 实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
// 三种不同绑定方式的文本属性
private string _defaultText = "默认值 - 输入后点击其他位置";
public string DefaultText
{
get { return _defaultText; }
set
{
if (_defaultText != value)
{
_defaultText = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
private string _propertyChangedText = "属性更改值 - 输入时即时更新";
public string PropertyChangedText
{
get { return _propertyChangedText; }
set
{
if (_propertyChangedText != value)
{
_propertyChangedText = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
private string _explicitText = "显式值 - 需点击更新按钮";
public string ExplicitText
{
get { return _explicitText; }
set
{
if (_explicitText != value)
{
_explicitText = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
}
}
UpdateSourceTriggerDemo.xaml.cs
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Data;
namespace WpfBindingDemo
{
public partial class UpdateSourceTriggerDemo : Window
{
public UpdateSourceTriggerDemo()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// 显式更新绑定源
private void UpdateExplicit_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// 获取TextBox的绑定表达式并手动更新源
BindingExpression binding = explicitTextBox.GetBindingExpression(TextBox.TextProperty);
binding.UpdateSource();
}
}
}
8. 绑定调试
调试数据绑定时的常见问题及解决方法:
8.1 启用绑定调试
在App.xaml.cs中添加以下代码可以启用绑定调试输出:
public partial class App : Application
{
public App()
{
// 开启绑定调试跟踪
PresentationTraceSources.DataBindingSource.Switch.Level = SourceLevels.Warning;
}
}
8.2 常见绑定问题
-
未设置DataContext
- 检查DataContext是否正确设置
- 验证继承的DataContext是否符合预期
-
路径错误
- 确保Path拼写正确
- 确保绑定源包含该属性
-
未实现INotifyPropertyChanged
- 确保源对象实现并正确触发PropertyChanged事件
-
绑定模式不正确
- 检查是否需要双向绑定(TwoWay)
-
转换器问题
- 验证转换器逻辑是否正确
- 确保转换器已注册为资源
8.3 使用PresentationTraceSources
可以为单个绑定设置调试级别:
<TextBox Text="{Binding Name,
PresentationTraceSources.TraceLevel=High}" />
9. 高级绑定功能
WPF还提供了一些高级的绑定功能,如:
9.1 MultiBinding(多重绑定)
将多个值组合成单一结果:
<TextBlock>
<TextBlock.Text>
<MultiBinding Converter="{StaticResource NameCombiner}">
<Binding Path="FirstName"/>
<Binding Path="LastName"/>
</MultiBinding>
</TextBlock.Text>
</TextBlock>
9.2 PriorityBinding(优先级绑定)
按优先级尝试多个绑定,使用第一个成功的绑定:
<TextBlock>
<TextBlock.Text>
<PriorityBinding>
<Binding Path="FastProperty" IsAsync="False"/>
<Binding Path="SlowProperty" IsAsync="True"/>
</PriorityBinding>
</TextBlock.Text>
</TextBlock>
10. 总结
WPF的数据绑定是一个强大的特性,可以将UI和数据分离,实现松耦合的应用架构。理解绑定的基本概念和机制对于构建可维护的WPF应用至关重要。通过掌握绑定表达式、绑定模式、更新触发器等知识,开发者可以充分利用WPF的声明式编程模型,创建响应式和易于维护的用户界面。
相关学习资源

DAMO开发者矩阵,由阿里巴巴达摩院和中国互联网协会联合发起,致力于探讨最前沿的技术趋势与应用成果,搭建高质量的交流与分享平台,推动技术创新与产业应用链接,围绕“人工智能与新型计算”构建开放共享的开发者生态。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容








所有评论(0)