自动化、脚本技术、AI系统、智能体、知识库的概念关系与工作机制
摘要 本文系统阐述了自动化技术体系中的核心概念及其相互关系。首先明确定义了自动化、脚本技术、AI系统等7个关键概念,并通过UML类图展示其层级关系:自动化是广义概念,脚本技术是其实现手段,AI系统基于人工智能理论构建,智能体是AI系统的表现形式,机器人是物理载体,知识库则为智能系统提供知识支持。文章进一步剖析了自动化系统的四层架构(感知层、执行层、控制层、应用层)和AI系统的核心原理,包括机器学习
·
自动化、脚本技术、AI系统、机器人、人工智能、智能体、知识库的概念关系与工作机制
1. 概念定义与层级关系
1.1 核心概念定义
| 概念 | 定义 | 范畴 |
|---|---|---|
| 自动化 | 使用技术使流程、系统或设备在最少或无需人工干预下运行 | 广义概念 |
| 脚本技术 | 使用脚本语言编写程序,自动化执行特定任务 | 实现自动化的具体技术手段 |
| 人工智能 | 使机器模拟人类智能行为的技术科学 | 理论框架与技术领域 |
| AI系统 | 基于人工智能理论构建的完整技术系统 | 具体实现 |
| 智能体 | 能够感知环境并自主行动以实现目标的实体 | AI系统的具体表现形式 |
| 机器人 | 能够执行物理动作的自动化机器,可能包含AI系统 | 物理实现载体 |
| 知识库 | 结构化存储的知识集合,支持推理和决策 | 智能系统的核心组件 |
1.2 概念关系UML图
2. 核心工作机制与原理
2.1 自动化系统的分层架构
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 应用层 (Application) │
│ • 业务流程自动化 │
│ • 用户界面自动化 │
│ • 数据流程自动化 │
└─────────────────┬───────────────────────┘
│
┌─────────────────▼───────────────────────┐
│ 控制层 (Control) │
│ • 工作流引擎 │
│ • 调度器 │
│ • 决策逻辑 │
└─────────────────┬───────────────────────┘
│
┌─────────────────▼───────────────────────┐
│ 执行层 (Execution) │
│ • 脚本解释器 │
│ • API调用模块 │
│ • 设备控制接口 │
└─────────────────┬───────────────────────┘
│
┌─────────────────▼───────────────────────┐
│ 感知层 (Perception) │
│ • 数据采集 │
│ • 传感器接口 │
│ • 环境监测 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘
2.2 AI系统核心原理
2.2.1 机器学习工作流程
数据采集 → 数据预处理 → 特征工程 → 模型训练 → 模型评估 → 部署推理
│ │ │ │ │ │
▼ ▼ ▼ ▼ ▼ ▼
传感器 清洗/归一化 特征提取 反向传播 准确率/召回率 预测服务
│ │ │ │ │ │
数据库 数据增强 降维 优化器 交叉验证 实时推理
2.2.2 智能体架构(POMDP模型)
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 智能体(Agent) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 状态s_t ∈ S 策略π(a|s) 奖励R(s,a) │
├─────────────┬───────────────────────┬───────────────────┤
│ 信念更新 │ 行动选择 │ 价值评估 │
│ b' = τ(b,a,o) a ~ π(·|b) │ V(b) = E[Σγ^t r_t]│
└──────┬──────┴──────────┬────────────┴──────┬───────────┘
│ │ │
┌──────▼─────┐ ┌─────▼──────┐ ┌───────▼────────┐
│ 观察 │ │ 行动 │ │ 环境模型 │
│ o ∈ Ω │ │ a ∈ A │ │ T(s'|s,a) │
└──────┬─────┘ └─────┬──────┘ └───────┬────────┘
│ │ │
└─────────────────┼────────────────────┘
│
┌──────▼──────┐
│ 环境 │
│ Environment │
└──────────────┘
2.3 知识库系统架构
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 知识应用层 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ • 问答系统 • 推荐系统 • 决策支持 • 语义搜索 │
└──────────────────────────┬──────────────────────────────┘
│
┌──────────────────────────▼──────────────────────────────┐
│ 知识推理层 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ • 规则引擎 • 本体推理 • 逻辑推理 • 概率推理 │
└──────────────────────────┬──────────────────────────────┘
│
┌──────────────────────────▼──────────────────────────────┐
│ 知识表示层 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ • 本体(Ontology) • 知识图谱 • 规则库 │
│ • 框架(Frame) • 语义网络 • 案例库 │
└──────────────────────────┬──────────────────────────────┘
│
┌──────────────────────────▼──────────────────────────────┐
│ 知识存储层 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ • 图数据库(Neo4j) • RDF存储 • 关系数据库 │
│ • 文档数据库 • 向量数据库 • 缓存系统 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
3. 脚本语言技术详解
3.1 脚本语言分类与特性
3.2 典型脚本示例
3.2.1 Python自动化脚本示例
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
智能文件管理系统 - 结合AI和自动化的示例
"""
import os
import shutil
import hashlib
from datetime import datetime
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Dict, List
import json
from dataclasses import dataclass, asdict
from enum import Enum
import logging
# 配置日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class FileCategory(Enum):
"""文件分类枚举"""
DOCUMENT = "documents"
IMAGE = "images"
VIDEO = "videos"
CODE = "code"
DATA = "data"
ARCHIVE = "archives"
OTHER = "other"
@dataclass
class FileMetadata:
"""文件元数据类"""
filename: str
path: str
size: int
created: datetime
modified: datetime
category: FileCategory
hash_md5: str
tags: List[str] = None
def to_dict(self):
return asdict(self)
class IntelligentFileManager:
"""智能文件管理器"""
# 文件扩展名到分类的映射
FILE_EXTENSIONS = {
FileCategory.DOCUMENT: ['.pdf', '.doc', '.docx', '.txt', '.md', '.rtf'],
FileCategory.IMAGE: ['.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.gif', '.bmp', '.svg'],
FileCategory.VIDEO: ['.mp4', '.avi', '.mov', '.mkv', '.wmv'],
FileCategory.CODE: ['.py', '.js', '.java', '.cpp', '.html', '.css'],
FileCategory.DATA: ['.csv', '.json', '.xml', '.sql', '.db'],
FileCategory.ARCHIVE: ['.zip', '.tar', '.gz', '.rar', '.7z']
}
def __init__(self, knowledge_base_path: str = "knowledge_base.json"):
self.knowledge_base_path = knowledge_base_path
self.knowledge_base = self.load_knowledge_base()
self.file_index = {}
def load_knowledge_base(self) -> Dict:
"""加载知识库"""
try:
if os.path.exists(self.knowledge_base_path):
with open(self.knowledge_base_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
return json.load(f)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"加载知识库失败: {e}")
return {"file_patterns": {}, "user_preferences": {}, "organize_rules": {}}
def save_knowledge_base(self):
"""保存知识库"""
try:
with open(self.knowledge_base_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(self.knowledge_base, f, indent=2, default=str)
logger.info("知识库已保存")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"保存知识库失败: {e}")
def categorize_file(self, filepath: Path) -> FileCategory:
"""基于规则和知识库对文件进行分类"""
# 从知识库中获取用户偏好
user_prefs = self.knowledge_base.get("user_preferences", {})
# 检查文件扩展名
ext = filepath.suffix.lower()
# 首先检查知识库中的自定义规则
for pattern, category in self.knowledge_base.get("file_patterns", {}).items():
if pattern in filepath.name.lower():
try:
return FileCategory(category)
except ValueError:
continue
# 使用预定义规则
for category, extensions in self.FILE_EXTENSIONS.items():
if ext in extensions:
return category
# 使用AI增强分类(简化版)
return self._ai_enhanced_categorization(filepath)
def _ai_enhanced_categorization(self, filepath: Path) -> FileCategory:
"""AI增强的文件分类(简化实现)"""
# 在实际应用中,这里可以集成ML模型
# 此处使用基于文件内容的启发式方法
try:
# 读取文件头部进行内容分析
with open(filepath, 'rb') as f:
header = f.read(1024) # 读取前1KB
# 简单的魔法数字检测
magic_numbers = {
b'%PDF': FileCategory.DOCUMENT,
b'\x89PNG': FileCategory.IMAGE,
b'\xff\xd8\xff': FileCategory.IMAGE, # JPEG
b'<?xml': FileCategory.DATA,
}
for magic, category in magic_numbers.items():
if header.startswith(magic):
return category
# 文本内容分析
try:
text_sample = header.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore')
keywords = {
'import': FileCategory.CODE,
'function': FileCategory.CODE,
'class': FileCategory.CODE,
'<html': FileCategory.CODE,
'select': FileCategory.DATA,
}
for keyword, category in keywords.items():
if keyword in text_sample.lower():
return category
except:
pass
except Exception as e:
logger.debug(f"AI分类失败: {e}")
return FileCategory.OTHER
def calculate_file_hash(self, filepath: Path) -> str:
"""计算文件哈希值"""
hash_md5 = hashlib.md5()
try:
with open(filepath, "rb") as f:
for chunk in iter(lambda: f.read(4096), b""):
hash_md5.update(chunk)
return hash_md5.hexdigest()
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"计算文件哈希失败 {filepath}: {e}")
return ""
def scan_directory(self, directory: str) -> List[FileMetadata]:
"""扫描目录并收集文件元数据"""
files_metadata = []
dir_path = Path(directory)
if not dir_path.exists():
logger.error(f"目录不存在: {directory}")
return files_metadata
logger.info(f"开始扫描目录: {directory}")
for filepath in dir_path.rglob('*'):
if filepath.is_file():
try:
stat = filepath.stat()
metadata = FileMetadata(
filename=filepath.name,
path=str(filepath),
size=stat.st_size,
created=datetime.fromtimestamp(stat.st_ctime),
modified=datetime.fromtimestamp(stat.st_mtime),
category=self.categorize_file(filepath),
hash_md5=self.calculate_file_hash(filepath),
tags=[]
)
files_metadata.append(metadata)
self.file_index[metadata.hash_md5] = metadata
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"处理文件失败 {filepath}: {e}")
logger.info(f"扫描完成,发现 {len(files_metadata)} 个文件")
return files_metadata
def organize_files(self, source_dir: str, target_base: str,
strategy: str = "categorical") -> Dict:
"""
组织文件根据指定策略
Args:
source_dir: 源目录
target_base: 目标基础目录
strategy: 组织策略 (categorical, date_based, hybrid)
"""
files = self.scan_directory(source_dir)
report = {
"total_files": len(files),
"organized": 0,
"skipped": 0,
"errors": 0,
"details": []
}
target_base_path = Path(target_base)
target_base_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
for file_meta in files:
try:
source_path = Path(file_meta.path)
# 确定目标路径
if strategy == "categorical":
target_dir = target_base_path / file_meta.category.value
elif strategy == "date_based":
date_str = file_meta.created.strftime("%Y/%m/%d")
target_dir = target_base_path / date_str
elif strategy == "hybrid":
category_dir = file_meta.category.value
date_str = file_meta.created.strftime("%Y/%m")
target_dir = target_base_path / category_dir / date_str
else:
target_dir = target_base_path / "organized"
target_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
target_path = target_dir / source_path.name
# 检查是否已存在相同文件
if target_path.exists():
existing_hash = self.calculate_file_hash(target_path)
if existing_hash == file_meta.hash_md5:
logger.info(f"文件已存在: {target_path}")
report["skipped"] += 1
report["details"].append({
"file": file_meta.filename,
"status": "skipped_duplicate",
"target": str(target_path)
})
continue
# 移动文件
shutil.move(str(source_path), str(target_path))
logger.info(f"已移动: {source_path} -> {target_path}")
# 更新知识库
self._update_knowledge_base(file_meta, target_path)
report["organized"] += 1
report["details"].append({
"file": file_meta.filename,
"status": "organized",
"target": str(target_path),
"category": file_meta.category.value
})
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"组织文件失败 {file_meta.filename}: {e}")
report["errors"] += 1
report["details"].append({
"file": file_meta.filename,
"status": "error",
"error": str(e)
})
# 保存知识库更新
self.save_knowledge_base()
logger.info(f"组织完成: {report}")
return report
def _update_knowledge_base(self, file_meta: FileMetadata, target_path: Path):
"""更新知识库基于文件组织行为"""
# 更新文件模式知识
pattern_key = file_meta.filename.lower()
if pattern_key not in self.knowledge_base.get("file_patterns", {}):
self.knowledge_base.setdefault("file_patterns", {})[pattern_key] = file_meta.category.value
# 更新组织规则
org_rule = {
"source_pattern": file_meta.filename,
"category": file_meta.category.value,
"target_pattern": str(target_path.parent),
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()
}
self.knowledge_base.setdefault("organize_rules", []).append(org_rule)
# 限制规则数量
if len(self.knowledge_base["organize_rules"]) > 1000:
self.knowledge_base["organize_rules"] = self.knowledge_base["organize_rules"][-1000:]
def find_duplicates(self, directory: str) -> Dict[str, List[str]]:
"""查找重复文件"""
files = self.scan_directory(directory)
hash_groups = {}
for file_meta in files:
if file_meta.hash_md5:
hash_groups.setdefault(file_meta.hash_md5, []).append(file_meta.path)
# 过滤出重复组
duplicates = {hash_val: paths for hash_val, paths in hash_groups.items()
if len(paths) > 1}
return duplicates
def generate_report(self, directory: str) -> Dict:
"""生成目录分析报告"""
files = self.scan_directory(directory)
report = {
"summary": {
"total_files": len(files),
"total_size": sum(f.size for f in files),
"categories": {}
},
"largest_files": [],
"recent_files": [],
"category_distribution": {}
}
# 分类统计
category_stats = {}
for file_meta in files:
cat = file_meta.category.value
category_stats.setdefault(cat, {"count": 0, "size": 0})
category_stats[cat]["count"] += 1
category_stats[cat]["size"] += file_meta.size
report["summary"]["categories"] = category_stats
# 最大的文件
largest_files = sorted(files, key=lambda x: x.size, reverse=True)[:10]
report["largest_files"] = [
{"file": f.filename, "size": f.size, "category": f.category.value}
for f in largest_files
]
# 最近修改的文件
recent_files = sorted(files, key=lambda x: x.modified, reverse=True)[:10]
report["recent_files"] = [
{"file": f.filename, "modified": f.modified.isoformat(),
"category": f.category.value}
for f in recent_files
]
return report
def main():
"""主函数"""
# 初始化智能文件管理器
manager = IntelligentFileManager()
# 示例使用
source_directory = "~/Downloads" # 示例目录
target_directory = "~/Documents/OrganizedFiles"
# 1. 扫描并分析目录
print("=== 目录分析 ===")
analysis_report = manager.generate_report(source_directory)
print(f"总文件数: {analysis_report['summary']['total_files']}")
print(f"总大小: {analysis_report['summary']['total_size'] / (1024*1024):.2f} MB")
# 2. 查找重复文件
print("\n=== 重复文件检测 ===")
duplicates = manager.find_duplicates(source_directory)
print(f"发现 {len(duplicates)} 组重复文件")
# 3. 智能组织文件
print("\n=== 文件组织 ===")
organize_report = manager.organize_files(
source_directory,
target_directory,
strategy="hybrid" # 使用混合策略
)
print(f"已组织 {organize_report['organized']} 个文件")
print(f"跳过 {organize_report['skipped']} 个重复文件")
# 4. 保存知识库供未来使用
manager.save_knowledge_base()
print("\n=== 知识库已更新 ===")
print(f"知识库文件: {manager.knowledge_base_path}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
3.2.2 Bash自动化脚本示例
#!/bin/bash
# 智能系统监控与自动化维护脚本
set -euo pipefail
IFS=$'\n\t'
# 配置
LOG_DIR="/var/log/automation"
BACKUP_DIR="/backup"
REPORT_EMAIL="admin@example.com"
THRESHOLD_DISK_USAGE=80
THRESHOLD_MEMORY_USAGE=90
THRESHOLD_LOAD_AVERAGE=5.0
# 初始化目录
init_directories() {
mkdir -p "$LOG_DIR"
mkdir -p "$BACKUP_DIR"
local timestamp=$(date +"%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
LOG_FILE="$LOG_DIR/automation_${timestamp}.log"
exec 1> >(tee -a "$LOG_FILE")
exec 2>&1
}
# 日志函数
log() {
local level=$1
shift
echo "[$(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')] [$level] $@" | tee -a "$LOG_FILE"
}
# 系统健康检查
check_system_health() {
log "INFO" "开始系统健康检查"
# 磁盘使用率检查
local disk_usage=$(df -h / | awk 'NR==2 {print $5}' | tr -d '%')
if [ "$disk_usage" -gt "$THRESHOLD_DISK_USAGE" ]; then
log "WARNING" "磁盘使用率过高: ${disk_usage}%"
send_alert "磁盘使用率过高" "当前使用率: ${disk_usage}%"
fi
# 内存使用率检查
local memory_usage=$(free | awk '/Mem:/ {printf("%.0f"), $3/$2 * 100}')
if [ "$memory_usage" -gt "$THRESHOLD_MEMORY_USAGE" ]; then
log "WARNING" "内存使用率过高: ${memory_usage}%"
send_alert "内存使用率过高" "当前使用率: ${memory_usage}%"
fi
# 负载平均值检查
local load_average=$(uptime | awk -F'load average:' '{print $2}' | awk -F, '{print $1}' | tr -d ' ')
if (( $(echo "$load_average > $THRESHOLD_LOAD_AVERAGE" | bc -l) )); then
log "WARNING" "系统负载过高: ${load_average}"
send_alert "系统负载过高" "当前负载: ${load_average}"
fi
log "INFO" "系统健康检查完成"
}
# 自动备份
perform_backup() {
local backup_type=$1
local timestamp=$(date +"%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
local backup_name="backup_${backup_type}_${timestamp}.tar.gz"
log "INFO" "开始${backup_type}备份"
case $backup_type in
"system")
tar -czf "$BACKUP_DIR/$backup_name" \
--exclude="$BACKUP_DIR" \
--exclude="/tmp" \
--exclude="/proc" \
--exclude="/sys" \
--exclude="/dev" \
--exclude="/run" \
/
;;
"web")
tar -czf "$BACKUP_DIR/$backup_name" \
/var/www/html \
/etc/nginx \
/etc/apache2
;;
"database")
perform_database_backup "$backup_name"
;;
*)
log "ERROR" "未知的备份类型: $backup_type"
return 1
;;
esac
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
log "INFO" "${backup_type}备份完成: $backup_name"
# 清理旧备份(保留最近30天)
find "$BACKUP_DIR" -name "backup_${backup_type}_*.tar.gz" \
-mtime +30 -delete
else
log "ERROR" "${backup_type}备份失败"
send_alert "备份失败" "${backup_type}备份过程出错"
fi
}
# 数据库备份
perform_database_backup() {
local backup_name=$1
# 检测数据库类型
if systemctl is-active --quiet mysql; then
# MySQL备份
mysqldump --all-databases --single-transaction \
--routines --triggers \
> "/tmp/db_dump.sql"
tar -czf "$BACKUP_DIR/$backup_name" -C /tmp "db_dump.sql"
rm -f "/tmp/db_dump.sql"
elif systemctl is-active --quiet postgresql; then
# PostgreSQL备份
sudo -u postgres pg_dumpall > "/tmp/pg_dump.sql"
tar -czf "$BACKUP_DIR/$backup_name" -C /tmp "pg_dump.sql"
rm -f "/tmp/pg_dump.sql"
else
log "ERROR" "未找到活动的数据库服务"
return 1
fi
}
# 安全扫描
security_scan() {
log "INFO" "开始安全扫描"
# 检查可疑进程
local suspicious_procs=$(ps aux | grep -E "(miner|backdoor|malware)" | grep -v grep)
if [ -n "$suspicious_procs" ]; then
log "WARNING" "发现可疑进程"
echo "$suspicious_procs" >> "$LOG_FILE"
send_alert "发现可疑进程" "$suspicious_procs"
fi
# 检查异常网络连接
local unusual_connections=$(netstat -tunap | grep -E "(0.0.0.0:|:::)" | grep -v LISTEN)
if [ -n "$unusual_connections" ]; then
log "INFO" "检查网络连接"
echo "$unusual_connections" >> "$LOG_FILE"
fi
# 检查文件权限
check_file_permissions
log "INFO" "安全扫描完成"
}
# 文件权限检查
check_file_permissions() {
local critical_files=(
"/etc/passwd"
"/etc/shadow"
"/etc/sudoers"
"/etc/ssh/sshd_config"
)
for file in "${critical_files[@]}"; do
if [ -e "$file" ]; then
local perms=$(stat -c "%a" "$file")
local owner=$(stat -c "%U" "$file")
case "$file" in
"/etc/shadow")
if [ "$perms" != "640" ] || [ "$owner" != "root" ]; then
log "WARNING" "$file 权限/所有者异常: $perms/$owner"
fi
;;
"/etc/passwd"|"/etc/sudoers")
if [ "$perms" != "644" ] || [ "$owner" != "root" ]; then
log "WARNING" "$file 权限/所有者异常: $perms/$owner"
fi
;;
esac
fi
done
}
# 发送警报
send_alert() {
local subject=$1
local message=$2
# 如果有邮件配置,发送邮件
if command -v mail &> /dev/null; then
echo "$message" | mail -s "系统警报: $subject" "$REPORT_EMAIL"
fi
# 也可以集成到其他通知系统
# send_slack_notification "$subject" "$message"
# send_telegram_notification "$subject" "$message"
}
# 性能优化
optimize_performance() {
log "INFO" "开始性能优化"
# 清理临时文件
clean_temporary_files
# 优化数据库
optimize_databases
# 重启服务(如果需要)
restart_stale_services
log "INFO" "性能优化完成"
}
# 清理临时文件
clean_temporary_files() {
local temp_dirs=(
"/tmp"
"/var/tmp"
"$HOME/.cache"
)
for dir in "${temp_dirs[@]}"; do
if [ -d "$dir" ]; then
find "$dir" -type f -atime +7 -delete 2>/dev/null || true
log "INFO" "已清理 $dir 中的旧文件"
fi
done
}
# 优化数据库
optimize_databases() {
if systemctl is-active --quiet mysql; then
mysqlcheck --all-databases --optimize --silent
log "INFO" "MySQL数据库已优化"
fi
if systemctl is-active --quiet postgresql; then
sudo -u postgres vacuumdb --all --analyze
log "INFO" "PostgreSQL数据库已优化"
fi
}
# 重启停滞的服务
restart_stale_services() {
local services=("nginx" "apache2" "mysql" "postgresql")
for service in "${services[@]}"; do
if systemctl is-active --quiet "$service"; then
# 检查服务状态
local status=$(systemctl status "$service" | grep -E "(active|failed)")
if echo "$status" | grep -q "failed"; then
log "WARNING" "服务 $service 失败,尝试重启"
systemctl restart "$service"
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
log "INFO" "服务 $service 重启成功"
else
log "ERROR" "服务 $service 重启失败"
fi
fi
fi
done
}
# 生成报告
generate_report() {
local timestamp=$(date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
local report_file="$LOG_DIR/report_$(date +%Y%m%d).html"
cat > "$report_file" << EOF
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>系统自动化报告 - $timestamp</title>
<style>
body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; margin: 20px; }
h1 { color: #333; }
.section { margin-bottom: 30px; }
.success { color: green; }
.warning { color: orange; }
.error { color: red; }
pre { background: #f5f5f5; padding: 10px; border-radius: 5px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>系统自动化报告</h1>
<p>生成时间: $timestamp</p>
<div class="section">
<h2>系统状态</h2>
<pre>
$(uptime)
$(free -h)
$(df -h)
</pre>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>安全检查</h2>
<pre>
$(ps aux | head -20)
$(netstat -tulpn | head -20)
</pre>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>备份状态</h2>
<p>最新备份:</p>
<pre>
$(ls -la "$BACKUP_DIR" | tail -10)
</pre>
</div>
</body>
</html>
EOF
log "INFO" "报告已生成: $report_file"
}
# 主函数
main() {
init_directories
log "INFO" "自动化脚本开始执行"
# 执行各项任务
check_system_health
# 根据星期执行不同的备份
local day_of_week=$(date +%u)
case $day_of_week in
1) perform_backup "database" ;; # 周一:数据库备份
2) perform_backup "web" ;; # 周三:Web备份
3) perform_backup "system" ;; # 周五:系统备份
esac
security_scan
# 每月1号执行性能优化
if [ "$(date +%d)" = "01" ]; then
optimize_performance
fi
generate_report
log "INFO" "自动化脚本执行完成"
}
# 错误处理
trap 'log "ERROR" "脚本异常退出"; exit 1' ERR
trap 'log "INFO" "脚本被用户中断"; exit 0' INT TERM
# 执行主函数
main "$@"
4. 集成系统架构设计
4.1 智能自动化系统整体架构
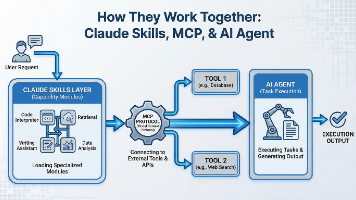
4.2 智能体系统详细设计
# 智能体系统配置示例
agent_system:
name: "enterprise_automation_agent"
version: "1.0.0"
components:
perception_module:
sensors:
- type: "file_system"
config:
watch_paths: ["/data/inbound", "/var/log"]
events: ["create", "modify", "delete"]
- type: "api_monitor"
config:
endpoints: ["/api/v1/health", "/api/v1/metrics"]
interval: "30s"
- type: "database_monitor"
config:
connection_string: "${DB_URL}"
queries:
- "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM jobs WHERE status='pending'"
- "SELECT AVG(response_time) FROM api_logs"
decision_module:
planner_type: "hierarchical_task_network"
policies:
- name: "resource_optimization"
conditions:
- "memory_usage > 80%"
- "cpu_usage > 75%"
actions:
- "scale_down_non_critical_services"
- "trigger_garbage_collection"
- "notify_administrator"
- name: "security_incident"
conditions:
- "failed_login_attempts > 10"
- "unusual_network_traffic detected"
actions:
- "block_ip_address"
- "increase_logging_level"
- "initiate_forensic_analysis"
action_module:
executors:
- type: "script_executor"
languages: ["python", "bash", "powershell"]
timeout: "300s"
- type: "api_caller"
config:
retry_policy:
max_attempts: 3
backoff: "exponential"
timeout: "30s"
- type: "infrastructure_orchestrator"
supported_providers: ["aws", "azure", "kubernetes"]
learning_module:
algorithm: "reinforcement_learning"
config:
state_space:
- "system_metrics"
- "workload_patterns"
- "user_behavior"
action_space:
- "scale_resources"
- "adjust_configurations"
- "execute_remediation"
reward_function: "weighted_composite_of_qos_and_cost"
knowledge_base:
storage:
primary: "graph_database"
secondary: "vector_database"
cache: "redis"
schemas:
- name: "system_topology"
type: "ontology"
file: "schemas/topology.ttl"
- name: "incident_patterns"
type: "knowledge_graph"
file: "schemas/incidents.neo4j"
- name: "best_practices"
type: "document_store"
file: "knowledge/best_practices.json"
communication:
internal:
protocol: "gRPC"
message_format: "protobuf"
external:
apis:
- type: "rest"
authentication: "jwt"
rate_limit: "1000/hour"
- type: "websocket"
events: ["status_update", "alert", "completion"]
monitoring:
metrics:
- "agent_decision_latency"
- "action_success_rate"
- "knowledge_base_hit_rate"
- "learning_progress"
logging:
level: "INFO"
format: "json"
retention: "30d"
alerting:
channels: ["slack", "email", "pagerduty"]
thresholds:
error_rate: "5%"
latency_p95: "1000ms"
5. 知识库系统实现方案
5.1 知识图谱构建流程
"""
知识图谱构建与管理系统
"""
from typing import Dict, List, Set, Tuple, Optional
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
from datetime import datetime
import networkx as nx
from enum import Enum
import json
import hashlib
class RelationType(Enum):
"""关系类型枚举"""
IS_A = "is_a" # 父子类关系
PART_OF = "part_of" # 部分关系
USES = "uses" # 使用关系
DEPENDS_ON = "depends_on" # 依赖关系
CREATES = "creates" # 创建关系
MANAGES = "manages" # 管理关系
RELATED_TO = "related_to" # 相关关系
@dataclass
class Entity:
"""知识实体"""
id: str
name: str
type: str
properties: Dict[str, any] = field(default_factory=dict)
attributes: Dict[str, any] = field(default_factory=dict)
created_at: datetime = field(default_factory=datetime.now)
updated_at: datetime = field(default_factory=datetime.now)
def to_dict(self):
return {
"id": self.id,
"name": self.name,
"type": self.type,
"properties": self.properties,
"attributes": self.attributes,
"created_at": self.created_at.isoformat(),
"updated_at": self.updated_at.isoformat()
}
@classmethod
def from_dict(cls, data: Dict):
entity = cls(
id=data["id"],
name=data["name"],
type=data["type"],
properties=data.get("properties", {}),
attributes=data.get("attributes", {})
)
entity.created_at = datetime.fromisoformat(data["created_at"])
entity.updated_at = datetime.fromisoformat(data["updated_at"])
return entity
@dataclass
class Relation:
"""实体关系"""
id: str
source_id: str
target_id: str
type: RelationType
properties: Dict[str, any] = field(default_factory=dict)
confidence: float = 1.0
created_at: datetime = field(default_factory=datetime.now)
def to_dict(self):
return {
"id": self.id,
"source_id": self.source_id,
"target_id": self.target_id,
"type": self.type.value,
"properties": self.properties,
"confidence": self.confidence,
"created_at": self.created_at.isoformat()
}
class KnowledgeGraph:
"""知识图谱"""
def __init__(self, name: str):
self.name = name
self.graph = nx.MultiDiGraph()
self.entities: Dict[str, Entity] = {}
self.relations: Dict[str, Relation] = {}
self.index = {} # 反向索引
def add_entity(self, entity: Entity) -> bool:
"""添加实体"""
if entity.id in self.entities:
return False
self.entities[entity.id] = entity
self.graph.add_node(entity.id, **entity.to_dict())
# 更新索引
for key, value in entity.properties.items():
index_key = f"{key}:{value}"
self.index.setdefault(index_key, set()).add(entity.id)
return True
def add_relation(self, relation: Relation) -> bool:
"""添加关系"""
if relation.id in self.relations:
return False
if relation.source_id not in self.entities:
raise ValueError(f"源实体不存在: {relation.source_id}")
if relation.target_id not in self.entities:
raise ValueError(f"目标实体不存在: {relation.target_id}")
self.relations[relation.id] = relation
self.graph.add_edge(
relation.source_id,
relation.target_id,
key=relation.id,
**relation.to_dict()
)
return True
def query(self, pattern: Dict) -> List[Dict]:
"""图模式查询"""
results = []
# 根据属性查询实体
if "properties" in pattern:
for key, value in pattern["properties"].items():
index_key = f"{key}:{value}"
if index_key in self.index:
for entity_id in self.index[index_key]:
entity = self.entities[entity_id]
if self._matches_pattern(entity, pattern):
results.append(entity.to_dict())
return results
def _matches_pattern(self, entity: Entity, pattern: Dict) -> bool:
"""检查实体是否匹配模式"""
for key, expected in pattern.items():
if key == "properties":
for prop_key, prop_value in expected.items():
if entity.properties.get(prop_key) != prop_value:
return False
elif key == "type":
if entity.type != expected:
return False
elif key == "name":
if expected not in entity.name:
return False
return True
def infer_relations(self, entity_id: str, depth: int = 2) -> List[Dict]:
"""推理相关关系"""
if entity_id not in self.entities:
return []
inferred = []
visited = set()
def dfs(current_id: str, current_depth: int, path: List):
if current_depth > depth or current_id in visited:
return
visited.add(current_id)
# 获取所有出边和入边
for _, target, data in self.graph.out_edges(current_id, data=True):
relation_info = {
"source": current_id,
"target": target,
"relation": data,
"path": path + [current_id]
}
inferred.append(relation_info)
dfs(target, current_depth + 1, path + [current_id])
for source, _, data in self.graph.in_edges(current_id, data=True):
relation_info = {
"source": source,
"target": current_id,
"relation": data,
"path": path + [current_id]
}
inferred.append(relation_info)
dfs(source, current_depth + 1, path + [current_id])
dfs(entity_id, 0, [])
return inferred
def save(self, filepath: str):
"""保存知识图谱"""
data = {
"name": self.name,
"entities": [e.to_dict() for e in self.entities.values()],
"relations": [r.to_dict() for r in self.relations.values()]
}
with open(filepath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(data, f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)
@classmethod
def load(cls, filepath: str):
"""加载知识图谱"""
with open(filepath, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
kg = cls(data["name"])
# 加载实体
for entity_data in data["entities"]:
entity = Entity.from_dict(entity_data)
kg.add_entity(entity)
# 加载关系
for relation_data in data["relations"]:
relation = Relation(
id=relation_data["id"],
source_id=relation_data["source_id"],
target_id=relation_data["target_id"],
type=RelationType(relation_data["type"]),
properties=relation_data.get("properties", {}),
confidence=relation_data.get("confidence", 1.0),
created_at=datetime.fromisoformat(relation_data["created_at"])
)
kg.add_relation(relation)
return kg
class KnowledgeBaseSystem:
"""知识库系统"""
def __init__(self):
self.graphs: Dict[str, KnowledgeGraph] = {}
self.inference_rules = []
self.extractors = []
def create_graph(self, name: str) -> KnowledgeGraph:
"""创建知识图谱"""
if name in self.graphs:
raise ValueError(f"图谱已存在: {name}")
kg = KnowledgeGraph(name)
self.graphs[name] = kg
return kg
def register_extractor(self, extractor):
"""注册知识提取器"""
self.extractors.append(extractor)
def extract_from_text(self, text: str, graph_name: str):
"""从文本中提取知识"""
if graph_name not in self.graphs:
self.create_graph(graph_name)
kg = self.graphs[graph_name]
for extractor in self.extractors:
entities, relations = extractor.extract(text)
for entity in entities:
kg.add_entity(entity)
for relation in relations:
kg.add_relation(relation)
def query_across_graphs(self, query: Dict) -> List[Dict]:
"""跨图谱查询"""
results = []
for graph_name, kg in self.graphs.items():
graph_results = kg.query(query)
for result in graph_results:
result["graph"] = graph_name
results.append(result)
return results
def infer_new_knowledge(self):
"""推理新知识"""
for kg in self.graphs.values():
# 应用推理规则
for rule in self.inference_rules:
new_relations = rule.apply(kg)
for relation in new_relations:
kg.add_relation(relation)
# 示例使用
def main():
# 创建知识库系统
kbs = KnowledgeBaseSystem()
# 创建自动化知识图谱
automation_kg = kbs.create_graph("automation_concepts")
# 定义实体
automation = Entity(
id="ent_001",
name="自动化",
type="概念",
properties={"level": "抽象", "domain": "通用"}
)
script = Entity(
id="ent_002",
name="脚本技术",
type="技术",
properties={"type": "实现手段", "language": "多种"}
)
ai = Entity(
id="ent_003",
name="人工智能",
type="领域",
properties={"level": "理论", "complexity": "高"}
)
# 添加实体
automation_kg.add_entity(automation)
automation_kg.add_entity(script)
automation_kg.add_entity(ai)
# 定义关系
uses_relation = Relation(
id="rel_001",
source_id="ent_001", # 自动化
target_id="ent_002", # 脚本技术
type=RelationType.USES,
properties={"strength": "强", "frequency": "高"}
)
is_a_relation = Relation(
id="rel_002",
source_id="ent_002", # 脚本技术
target_id="ent_003", # 人工智能
type=RelationType.RELATED_TO,
properties={"direction": "subset", "nature": "implementation"}
)
# 添加关系
automation_kg.add_relation(uses_relation)
automation_kg.add_relation(is_a_relation)
# 查询示例
print("=== 知识图谱查询 ===")
results = automation_kg.query({
"properties": {"level": "抽象"}
})
for result in results:
print(f"找到实体: {result['name']}")
# 推理关系
print("\n=== 关系推理 ===")
inferred = automation_kg.infer_relations("ent_001", depth=2)
for rel in inferred:
print(f"关系: {rel['relation']['type']}")
print(f" 从: {rel['source']}")
print(f" 到: {rel['target']}")
# 保存知识图谱
automation_kg.save("automation_knowledge_graph.json")
print("\n=== 知识图谱已保存 ===")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
6. 现代自动化技术栈
6.1 技术栈架构
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 自动化技术栈 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 领域 技术栈 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 基础设施自动化 Terraform, Ansible, Kubernetes, Docker │
│ 持续集成/部署 Jenkins, GitLab CI, GitHub Actions, ArgoCD │
│ 测试自动化 Selenium, Cypress, Jest, Pytest │
│ 监控与告警 Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack, Datadog │
│ AI/ML自动化 Kubeflow, MLflow, Airflow, TensorFlow │
│ 业务流程自动化 UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Power Automate│
│ 数据管道自动化 Apache Airflow, Dagster, Prefect, dbt │
│ 安全自动化 SOAR平台, 漏洞扫描, 合规检查 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
6.2 容器化自动化部署示例
# docker-compose.yml - 自动化系统容器化部署
version: '3.8'
services:
# AI推理服务
ai-engine:
image: tensorflow/serving:latest
container_name: ai-inference
ports:
- "8500:8500"
- "8501:8501"
volumes:
- ./models:/models
environment:
- MODEL_NAME=automation_model
deploy:
resources:
limits:
cpus: '2'
memory: 4G
reservations:
cpus: '1'
memory: 2G
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://localhost:8501/v1/models/automation_model"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
# 知识图谱服务
knowledge-graph:
image: neo4j:4.4
container_name: knowledge-graph-db
ports:
- "7474:7474" # HTTP
- "7687:7687" # Bolt
volumes:
- neo4j_data:/data
- neo4j_logs:/logs
- neo4j_import:/var/lib/neo4j/import
environment:
- NEO4J_AUTH=neo4j/automation123
- NEO4J_dbms_memory_pagecache_size=1G
- NEO4J_dbms_memory_heap_max__size=2G
restart: unless-stopped
# 工作流引擎
workflow-engine:
build: ./workflow-engine
container_name: workflow-orchestrator
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
- DB_HOST=postgres
- DB_PORT=5432
- DB_NAME=workflows
- DB_USER=automation
- DB_PASSWORD=securepass
- REDIS_HOST=redis
- REDIS_PORT=6379
- AI_ENGINE_URL=http://ai-engine:8501
- KNOWLEDGE_GRAPH_URL=bolt://knowledge-graph:7687
depends_on:
- postgres
- redis
- ai-engine
- knowledge-graph
volumes:
- ./workflows:/app/workflows
deploy:
replicas: 2
# 脚本执行器
script-executor:
build: ./script-executor
container_name: script-runner
environment:
- PYTHONPATH=/app
- EXECUTION_TIMEOUT=300
- MAX_CONCURRENT_SCRIPTS=10
volumes:
- ./scripts:/app/scripts
- ./shared:/app/shared
depends_on:
- redis
security_opt:
- no-new-privileges:true
cap_drop:
- ALL
cap_add:
- CHOWN
- SETGID
- SETUID
- DAC_OVERRIDE
# 消息队列
redis:
image: redis:7-alpine
container_name: message-broker
ports:
- "6379:6379"
command: redis-server --appendonly yes --requirepass redissecret
volumes:
- redis_data:/data
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "redis-cli", "ping"]
interval: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 3
# 数据库
postgres:
image: postgres:14-alpine
container_name: automation-db
ports:
- "5432:5432"
environment:
- POSTGRES_DB=automation
- POSTGRES_USER=automation
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=dbpassword123
volumes:
- postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
- ./init-db.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/init.sql
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD-SHELL", "pg_isready -U automation"]
interval: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 5
# 监控系统
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus:latest
container_name: metrics-collector
ports:
- "9090:9090"
volumes:
- ./prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
- prometheus_data:/prometheus
command:
- '--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml'
- '--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus'
- '--web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries'
- '--web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles'
- '--storage.tsdb.retention.time=200h'
- '--web.enable-lifecycle'
depends_on:
- workflow-engine
- script-executor
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:latest
container_name: monitoring-dashboard
ports:
- "3000:3000"
environment:
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=grafanaadmin
volumes:
- grafana_data:/var/lib/grafana
- ./grafana/provisioning:/etc/grafana/provisioning
depends_on:
- prometheus
# 前端界面
web-ui:
build: ./web-ui
container_name: automation-portal
ports:
- "80:80"
- "443:443"
volumes:
- ./nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- ./ssl:/etc/nginx/ssl
depends_on:
- workflow-engine
- script-executor
volumes:
neo4j_data:
neo4j_logs:
neo4j_import:
redis_data:
postgres_data:
prometheus_data:
grafana_data:
networks:
default:
name: automation-network
driver: bridge
ipam:
config:
- subnet: 172.20.0.0/16
7. 总结与未来展望
7.1 概念关系思维导图
7.2 核心洞察与趋势
-
技术融合趋势
- 脚本技术与AI系统深度融合,形成智能自动化
- 知识库为AI系统提供可解释性和领域知识
- 机器人作为物理世界的执行载体
-
架构演进方向
- 从集中式控制向分布式智能体架构演进
- 从规则驱动向数据驱动和模型驱动结合
- 从静态脚本向自适应学习系统发展
-
关键技术挑战
- 异构系统集成与互操作性
- 实时决策与资源约束平衡
- 安全性与可靠性保障
- 伦理与法规合规性
7.3 实用建议
-
实施路线图
阶段1: 基础自动化 → 脚本标准化 → 简单工作流自动化 → 基础监控告警 阶段2: 智能增强 → 引入机器学习组件 → 构建知识图谱 → 实现预测性维护 阶段3: 自主系统 → 强化学习优化 → 多智能体协作 → 自适应调整 -
技术选型建议
- 中小规模:Python + Airflow + PostgreSQL + Redis
- 企业级:Kubernetes + Kubeflow + Neo4j + Kafka
- 云端方案:AWS Step Functions + SageMaker + Neptune
-
人才培养策略
- 交叉学科团队:软件工程 + 数据科学 + 领域专家
- 持续学习计划:关注AI、自动化、DevOps最新进展
- 实践导向:通过实际项目积累经验
7.4 未来展望
随着技术的不断发展,自动化、脚本技术、AI系统、机器人、智能体和知识库将更加深度融合,形成真正意义上的自主智能系统。这些系统将具备更强的自适应能力、推理能力和协作能力,能够在复杂动态环境中完成各种任务,为人类社会带来前所未有的效率和价值。
同时,我们也需要关注这些技术带来的伦理、安全和社会影响,确保技术的发展符合人类价值观和利益,实现技术向善的目标。

DAMO开发者矩阵,由阿里巴巴达摩院和中国互联网协会联合发起,致力于探讨最前沿的技术趋势与应用成果,搭建高质量的交流与分享平台,推动技术创新与产业应用链接,围绕“人工智能与新型计算”构建开放共享的开发者生态。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)