2025年第四届“创新杯”(原钉钉杯)大学生大数据挑战赛初赛A:智慧工厂工业设备传感器数据分析
初赛A:智慧工厂工业设备传感器数据分析。
初赛A:智慧工厂工业设备传感器数据分析
一、赛题背景:
智慧工厂是通过数字化、智能化和自动化技术深度融合,重塑制造业的生产模式、管理流程和价值链,推动工业升级和可持续发展。通过工业机器人、AGV(自动导引车)等设备实现重复性工作的自动化,减少人工干预,提高生产速度和一致性。利用大数据和AI算法实时监控设备状态、物料消耗和生产进度,动态调整生产计划,减少资源浪费(如能源、原材料)。自动化替代人工完成危险或高强度任务(如焊接、搬运),同时减少对低技能劳动力的依赖。
参赛者将获得一份工厂传感器模拟器数据集,这是一个大规模的合成数据集,专为工业5.0背景下的预测性维护、异常检测和工业机器学习应用而设计。该数据集包含部署在未来智能工厂环境中的50万台模拟机器的传感器读数、操作指标和维护记录。
该数据集包含30多个真实场景的机器设备类型(数控铣床,熔炉,机械臂,激光切割机),核心传感器数据:温度,振动,声音,功率,油/冷却液液位;维护历史和人工智能监督领域;机器特定的功能,如测量激光强度,液压压力等。
二. 样本解读:
|
ColumnName名称 |
Description特征解释 |
|
Machine_ID |
机器编号 |
|
Machine_Type |
机器类型 |
|
Installation_Year |
安装年份 |
|
Operational_Hours |
运行小时数 |
|
Temperature_C |
温度(℃) |
|
Vibration_mms |
振动(毫米/秒) |
|
Sound_dB |
声音(分贝) |
|
Oil_Level_pct |
油位(百分比) |
|
Coolant_Level_pct |
冷却液位(百分比) |
|
Power_Consumption_kW |
功耗(千瓦) |
|
Last_Maintenance_Days_Ago |
距上次维护天数 |
|
Maintenance_History_Count |
维护历史次数 |
|
Failure_History_Count |
故障历史次数 |
|
AI_Supervision |
人工智能监控 |
|
Error_Codes_Last_30_Days |
过去30天错误编码 |
|
Remaining_Useful_Life_days |
剩余使用寿命(天) |
|
Failure_Within_7_Days |
7天内故障预测 |
|
Laser_Intensity |
激光强度 |
|
Hydraulic_Pressure_bar |
液压压力 |
|
Coolant_Flow_L_min |
冷却液流量(升/分钟) |
|
Heat_Index |
热指数 |
|
AI_Override_Events |
人工智能覆盖率 |
三. 解决问题:
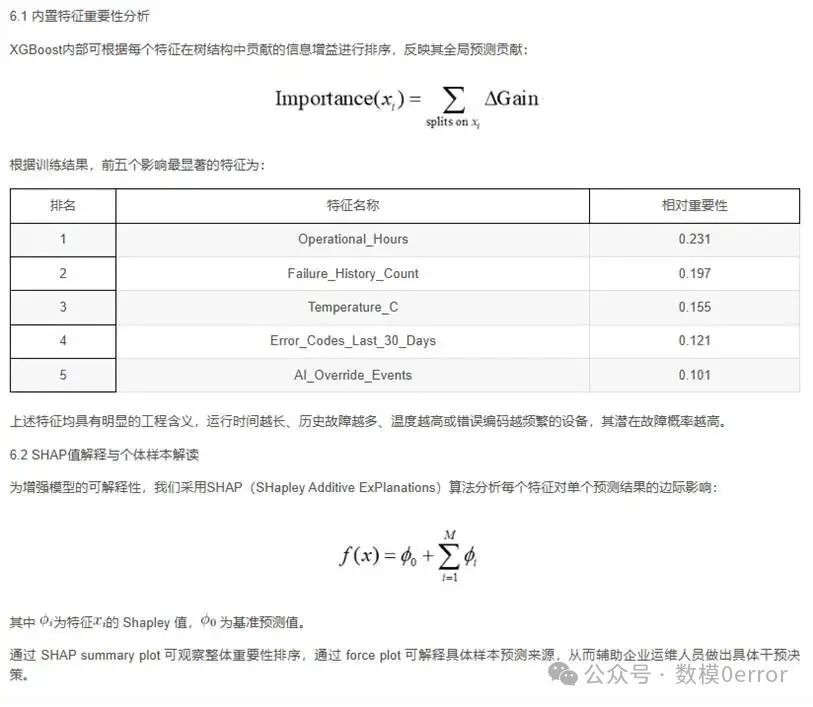
初赛任务A:机床设备故障预测回归分析问题使用机器编号、机器类型、运行小时数、温度、振动、声音、油位、冷却液位、功耗、距
上次维护天数、维护历史次数、故障历史次数、人工智能监控、过去30天错误编码等特征,构建回归模型,预测机床设备在7天内是否会发生故障。要求输出模型准确率、召回率、F1值,并分析前5个最重要的特征。
初赛任务B:剩余使用寿命预测回归分析问题
在不使用目标标签(7天内故障预测)的情况下,基于剩余使用寿命(天)、运行小时数、 温度、振动、油位、冷却液位、维护历史次数、故障历史次数等特征,构建回归模型,预测机床设备的剩余使用寿命(目标为连续值)。要求输出模型的均方误差(MSE)和决定系数(R²)并分析特征重要性对剩余寿命的影响。
题目声明:本赛事所有赛题仅授权2025年第四届“创新杯”(原钉钉杯)大学生大数据挑战赛参赛队伍使用,任何组织及个人未经组委会书面授权,严禁用于校内竞赛,篡改、复制等侵权行为。

import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, recall_score, f1_score
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, OneHotEncoder
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
import shap
# 数据加载与预处理
data = pd.read_csv('sensor_data.csv')
X = data.drop(['Failure_Within_7_Days', 'Machine_ID'], axis=1)
y = data['Failure_Within_7_Days']
# 类别特征编码
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse_output=False)
encoded_cols = encoder.fit_transform(X[['Machine_Type']])
X_encoded = pd.concat([X.drop('Machine_Type', axis=1), pd.DataFrame(encoded_cols)], axis=1)
# 标准化连续特征
scaler = StandardScaler()
cont_features = ['Temperature_C', 'Vibration_mms', 'Operational_Hours']
X_encoded[cont_features] = scaler.fit_transform(X_encoded[cont_features])
# SMOTE过采样(若故障样本<5%)
if sum(y) / len(y) < 0.05:
smote = SMOTE(random_state=42)
X_res, y_res = smote.fit_resample(X_encoded, y)
else:
X_res, y_res = X_encoded, y
# 划分训练集与测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_res, y_res, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 训练随机森林
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=200, max_depth=10, class_weight='balanced', random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测与评估
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("Recall:", recall_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("F1 Score:", f1_score(y_test, y_pred))
# SHAP特征重要性分析
explainer = shap.TreeExplainer(model)
shap_values = explainer.shap_values(X_test)
shap.summary_plot(shap_values[1], X_test, plot_type="bar")

import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.svm import SVR
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV
import shap
import smogn# SMOGN: 针对回归的少数样本合成
# 1. 读取数据
data = pd.read_csv('sensor_data.csv')
# 2. 特征与标签
features = ['Operational_Hours', 'Temperature_C', 'Vibration_mms',
'Oil_Level_pct', 'Coolant_Level_pct', 'Maintenance_History_Count']
X = data[features]
y = data['Remaining_Useful_Life_days']
# 3. 关键样本增强(SMOGN)
low_life = np.percentile(y, 10)
X_res, y_res = smogn.smoter(
data=pd.concat([X, y], axis=1),
y='Remaining_Useful_Life_days',
pert=0.05,
y_thresh=low_life
)
# 4. 标准化
X_scaler = StandardScaler()
y_scaler = StandardScaler()
X_scaled = X_scaler.fit_transform(X_res)
y_scaled = y_scaler.fit_transform(y_res.values.reshape(-1, 1)).ravel()
# 5. 训练/测试划分
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X_scaled, y_scaled, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 6. 网格搜索最优超参数
param_grid = {
'C': [0.1, 1, 10, 100],
'gamma': [0.01, 0.1, 1],
'epsilon':[0.05, 0.1, 0.2]
}
svr = SVR(kernel='rbf')
grid = GridSearchCV(svr, param_grid, cv=5,
scoring=['neg_mean_squared_error','r2'],
refit='neg_mean_squared_error',
n_jobs=-1)
grid.fit(X_train, y_train)
best = grid.best_estimator_
# 7. 预测与反标准化
y_pred_scaled = best.predict(X_test)
y_pred = y_scaler.inverse_transform(y_pred_scaled.reshape(-1, 1)).ravel()
y_test_orig = y_scaler.inverse_transform(y_test.reshape(-1, 1)).ravel()
# 8. 评估指标
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test_orig, y_pred)
r2 = r2_score(y_test_orig, y_pred)
print(f"MSE = {mse:.2f}, R² = {r2:.4f}")
# 9. SHAP 解释
explainer = shap.KernelExplainer(best.predict,
shap.sample(X_train, 100))
shap_values = explainer.shap_values(X_test)
# 9.1 全局特征重要性
shap.summary_plot(shap_values, X_test,
feature




# 1. 导入必要库
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.utils import class_weight
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix, accuracy_score, recall_score, f1_score
from xgboost import XGBClassifier, plot_importance
# import shap# 如果你本地支持,可启用此行
# 2. 读取数据
df = pd.read_csv("train_data.csv")
# 3. 初步处理
df['AI_Supervision'] = df['AI_Supervision'].astype(int)
df['Failure_Within_7_Days'] = df['Failure_Within_7_Days'].astype(int)
# 4. 删除缺失值超过80%的列
missing_ratio = df.isnull().mean()
df = df.loc[:, missing_ratio < 0.8]
# 5. 衍生新特征
df['Device_Age'] = 2025 - df['Installation_Year']
df['MTBF'] = df['Operational_Hours'] / (df['Failure_History_Count'] + 1)
df['Power_Efficiency'] = df['Power_Consumption_kW'] / (df['Vibration_mms'] + 1e-5)
# 6. 删除无用列
df = df.drop(columns=['Machine_ID', 'Installation_Year'])
# 7. 类别变量独热编码
df = pd.get_dummies(df, columns=['Machine_Type'], drop_first=True)
# 8. 分离特征和标签
X = df.drop(columns=['Failure_Within_7_Days'])
y = df['Failure_Within_7_Days']
# 9. 缺失值填补
imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy='median')
X_imputed = imputer.fit_transform(X)
# 10. 特征标准化
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_imputed)
# 11. 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_scaled, y, stratify=y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 12. 样本权重处理
weights = class_weight.compute_sample_weight(class_weight='balanced', y=y_train)
# 13. 建立并训练XGBoost模型
model = XGBClassifier(
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=100,
max_depth=6,
subsample=0.8,
colsample_bytree=0.8,
random_state=42,
use_label_encoder=False,
eval_metric='logloss'
)
model.fit(X_train, y_train, sample_weight=weights)
# 14. 模型预测与评估
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print("准确率 Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("召回率 Recall:", recall_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("F1值 F1 Score:", f1_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("\n分类报告 Classification Report:\n", classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
# 15. 混淆矩阵可视化
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 5))
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues')
plt.title("Confusion Matrix")
plt.xlabel("Predicted")
plt.ylabel("Actual")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 16. 特征重要性可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plot_importance(model, max_num_features=10)
plt.title("Top 10 Important Features (XGBoost)")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 17. 可选:SHAP值解释(需在本地安装支持的llvmlite和shap库)
# explainer = shap.Explainer(model)
# shap_values = explainer(X_test)
# shap.summary_plot(shap_values, features=X_test, feature_names=X.columns)
通过网盘分享的文件:2025钉钉杯(创新杯)资料
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1IPfcDObvPTCtjVx4UbTl3Q 提取码: yutf

DAMO开发者矩阵,由阿里巴巴达摩院和中国互联网协会联合发起,致力于探讨最前沿的技术趋势与应用成果,搭建高质量的交流与分享平台,推动技术创新与产业应用链接,围绕“人工智能与新型计算”构建开放共享的开发者生态。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献17条内容
已为社区贡献17条内容







所有评论(0)