2025年睿抗机器人开发者CAIP-编程技能赛-本科组省赛题解
已全部补完。
·
已全部补完
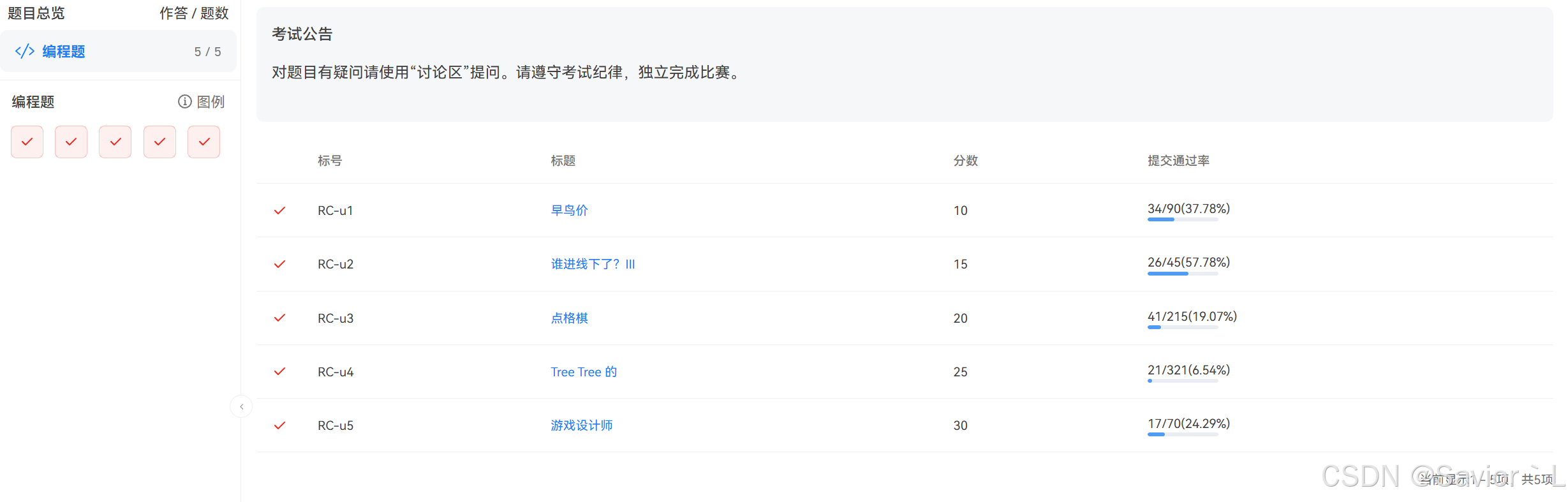
RC-u1 早鸟价
条件判断
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
void solve(){
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int m,d,c;
cin>>m>>d>>c;
if(m<6 || (m==6 && d<=20)){
if(c==1800){
cout<<"Ok!"<<'\n';
}else if(c>1800){
cout<<"^_^"<<'\n';
}else if(c<1800){
cout<<"Need more!"<<'\n';
}
}else if(m>7 || (m==7 && d>11)){
cout<<"Too late!"<<'\n';
}else{
if(c==2000){
cout<<"Ok!"<<'\n';
}else if(c>2000){
cout<<"^_^"<<'\n';
}else if(c<2000){
cout<<"Need more!"<<'\n';
}
}
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
// cin>>T;
while(T--) solve();
return 0;
}
RC-u2 谁进线下了?III
根据题意模拟
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
void solve(){
int n,s;
cin>>n>>s;
int cnt=0;
int sc=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int r,c;
cin>>r>>c;
if(r==1) cnt++;
sc+=c;
}
if(cnt*2>=n){
cout<<1;
}else{
cout<<0;
}
cout<<' '<<(sc-s>=50?1:0)<<'\n';
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--) solve();
return 0;
}
RC-u3 点格棋
很多坑
注意到题面:“完成每个 1×1 方框的最后一条边的玩家获得 1 分,且如当前回合获得了分数,则额外再进行另一回合。” 意思就是当前玩家操作获得了分数那么下一步还是由当前玩家操作。
我们需要注意所有有问题的步骤可能出现的情况:
- 小A必须是先手方,第一个操作者必须是0
- 玩家轮流操作,意味着0后就是1,1后就是0,除非出现当前玩家操作获得分数,这都需要判断,我是用一个变量记录当前操作是谁,每次开始前进行判断
- 给出的点可能不合法,例如(0,0)
- 给出的点连线重复出现
- 给出的点连线不是水平线或垂直线,或者距离不为1
此外我们第一行输出有问题的编号时,最后一个编号后不能有空格!
详情看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N=110;
int a[N][N];
void solve() {
int n,m,s;
cin>>n>>m>>s;
map<array<int,4>,int> mp;
int c1=0,c2=0;
vector<int> err;
int lst=-1,f=0;
for(int i=1; i<=s; i++) {
int op;
cin>>op;
int sx,sy,ex,ey;
cin>>sx>>sy>>ex>>ey;
if(mp.count({sx,sy,ex,ey}) || op!=f) {
err.push_back(i);
continue;
}
if(sx>=1 && sx<=n && sy>=1 && sy<=m && ex>=1 && ex<=n && ey>=1 && ey<=m && !(sx==ex && sy==ey)) {
if(!op) {
if(sx==ex) {
if(abs(sy-ey)==1) {
bool ok=0;
if(sx-1>=1 && mp.count({sx,sy,sx-1,sy}) && mp.count({sx-1,sy,ex-1,ey}) && mp.count({ex,ey,ex-1,ey})) c1++,lst=0,ok=1;
if(sx+1<=n && mp.count({sx,sy,sx+1,sy}) && mp.count({sx+1,sy,ex+1,ey}) && mp.count({ex,ey,ex+1,ey})) c1++,lst=0,ok=1;
if(!ok) lst=-1;
} else {
err.push_back(i);
continue;
}
} else if(sy==ey) {
if(abs(sx-ex)==1) {
bool ok=0;
if(sy-1>=1 && mp.count({sx,sy-1,sx,sy}) && mp.count({sx,sy-1,ex,ey-1}) && mp.count({ex,ey-1,ex,ey})) c1++,lst=0,ok=1;
if(sy+1<=m && mp.count({sx,sy+1,sx,sy}) && mp.count({sx,sy+1,ex,ey+1}) && mp.count({ex,ey+1,ex,ey})) c1++,lst=0,ok=1;
if(!ok) lst=-1;
} else {
err.push_back(i);
continue;
}
} else {
err.push_back(i);
continue;
}
} else {
if(sx==ex) {
if(abs(sy-ey)==1) {
bool ok=0;
if(sx-1>=1 && mp.count({sx,sy,sx-1,sy}) && mp.count({sx-1,sy,ex-1,ey}) && mp.count({ex,ey,ex-1,ey})) c2++,lst=1,ok=1;
if(sx+1<=n && mp.count({sx,sy,sx+1,sy}) && mp.count({sx+1,sy,ex+1,ey}) && mp.count({ex,ey,ex+1,ey})) c2++,lst=1,ok=1;
if(!ok) lst=-1;
} else {
err.push_back(i);
continue;
}
} else if(sy==ey) {
if(abs(sx-ex)==1) {
bool ok=0;
if(sy-1>=1 && mp.count({sx,sy-1,sx,sy}) && mp.count({sx,sy-1,ex,ey-1}) && mp.count({ex,ey-1,ex,ey})) c2++,lst=1,ok=1;
if(sy+1<=m && mp.count({sx,sy+1,sx,sy}) && mp.count({sx,sy+1,ex,ey+1}) && mp.count({ex,ey+1,ex,ey})) c2++,lst=1,ok=1;
if(!ok) lst=-1;
} else {
err.push_back(i);
continue;
}
} else {
err.push_back(i);
continue;
}
}
mp[ {sx,sy,ex,ey}]=1;
mp[ {ex,ey,sx,sy}]=1;
if(lst==-1) f=1-f;
} else {
err.push_back(i);
}
}
if(err.size()==0) {
cout<<-1<<'\n';
} else {
for(int i=0;i<err.size();i++){
cout<<err[i];
if(i!=err.size()-1) cout<<' ';
}
cout<<'\n';
}
if(c1>c2) {
cout<<0<<' '<<c1<<'\n';
} else {
cout<<1<<' '<<c2<<'\n';
}
}
/*
(sx-1,sy) (ex-1,ey)
(sx,sy) (ex,ey)
(sx+1,sy) (ex+1,ey)
(sx,sy-1) (sx,sy) (sx,sy+1)
(ex,ey-1) (ex,ey) (ex,ey+1)
*/
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
// cin>>T;
while(T--) solve();
return 0;
}
RC-u4 Tree Tree 的
题中子图要求原本联通的情况下删除任一节点后仍然联通,且构成一棵树。
显然只有环才能满足,暴力找出每个环即可。
注意:题目要求最大环与次大环大小不一样,还有就是一个点也是满足的。
详情看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N=11;
vector<int> g[N];
int n,m,vis[N];
int S,ans1,ans2;
void dfs(int u,int cnt){
for(auto v:g[u]){
if(vis[v]) continue;
if(v==S){
if(cnt>ans1){
ans2=ans1;
ans1=cnt;
}else if(cnt!=ans1 && cnt>ans2){
ans2=cnt;
}
}
vis[v]=1;
dfs(v,cnt+1);
vis[v]=0;
}
}
void solve() {
cin>>n>>m;
ans1=1,ans2=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
g[i].clear();
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
S=i;
dfs(i,1);
}
cout<<ans1<<' '<<ans2<<'\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
cin>>T;
while(T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
RC-u5 游戏设计师
倒着很容易就想到从终点处开始bfs求最短距离
对于题目的翻滚操作可以大致分为三类:
图中标记为1表示长方块是立着的,占了一个方格,为0则表示长方块是躺着的,占了两个方格。
打三角标记表示以这个点为基准,在代码中我记录为x1,y2,基准点旁边的点我记录为x2,y2
对于立着的长方块,x1=x2,y1=y2
长方块总共就是三种放法,每种放法对应四种操作,操作均有差异,我是使用了多个dir数组记录(x,y)的改变情况
注意:直接用map记录距离会mle,还可能tle,用数组记录每个点作为基准点时的三种放法的距离
详情看代码,还是比较清晰的。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N=1010;
int n,m,g[N][N];
const int dir11[][2]= {{0,-1},{0,1},{-1,0},{1,0}};
const int dir12[][2]= {{0,-2},{0,2},{-2,0},{2,0}};
const int dir21[][2]= {{-1,0},{0,-1},{0,2},{1,0}};
const int dir22[][2]= {{-1,0},{0,-2},{0,1},{1,0}};
const int dir31[][2]= {{0,-1},{0,1},{-1,0},{2,0}};
const int dir32[][2]= {{0,-1},{0,1},{-2,0},{1,0}};
int dis[N][N][3];
void solve() {
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=m;j++){
for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
dis[i][j][k]=1e9;
}
}
}
int sx=-1,sy=-1;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++) {
char c;
cin>>c;
g[i][j]=c-'0';
if(g[i][j]==3) {
sx=i,sy=j;
}
}
}
dis[sx][sy][0]=0;
queue<array<int,3>> q;
q.push({sx,sy,0});
while(!q.empty()) {
auto [x1,y1,op]=q.front();
q.pop();
int d=dis[x1][y1][op];
int x2,y2;
if(!op) {
x2=x1,y2=y1;
} else if(op==1) {
x2=x1,y2=y1+1;
} else {
x2=x1+1,y2=y1;
}
for(int k=0; k<4; k++) {
int xx1,xx2,yy1,yy2;
if(x1==x2 && y1==y2) {
xx1=x1+dir11[k][0];
yy1=y1+dir11[k][1];
xx2=x2+dir12[k][0];
yy2=y2+dir12[k][1];
} else if(x1==x2) {
xx1=x1+dir21[k][0];
yy1=y1+dir21[k][1];
xx2=x2+dir22[k][0];
yy2=y2+dir22[k][1];
} else if(y1==y2) {
xx1=x1+dir31[k][0];
yy1=y1+dir31[k][1];
xx2=x2+dir32[k][0];
yy2=y2+dir32[k][1];
}
int f=0;
if(xx1==xx2 && yy1!=yy2) {
f=1;
if(yy1>yy2) swap(yy1,yy2);
}
if(yy1==yy2 && xx1!=xx2) {
f=2;
if(xx1>xx2) swap(xx1,xx2);
}
if(xx1>=1 && xx1<=n && yy1>=1 && yy1<=m && xx2>=1 && xx2<=n && yy2>=1 && yy2<=m) {
if(xx1==xx2 && yy1==yy2) {
if(g[xx1][yy1]==0 || g[xx1][yy1]==2) continue;
} else {
if(g[xx1][yy1]==0 || g[xx2][yy2]==0) continue;
}
if(dis[xx1][yy1][f]!=1e9) continue;
dis[xx1][yy1][f]=d+1;
q.push({xx1,yy1,f});
}
}
}
int cnt;
cin>>cnt;
for(int i=1; i<=cnt; i++) {
int x,y,op;
cin>>x>>y>>op;
if(dis[x][y][op]==1e9) cout<<-1<<'\n';
else cout<<dis[x][y][op]<<'\n';
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int T=1;
// cin>>T;
while(T--) solve();
return 0;
}

DAMO开发者矩阵,由阿里巴巴达摩院和中国互联网协会联合发起,致力于探讨最前沿的技术趋势与应用成果,搭建高质量的交流与分享平台,推动技术创新与产业应用链接,围绕“人工智能与新型计算”构建开放共享的开发者生态。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)