基于Matlab机器人建模与仿真控制 matlab仿真,RRT避障算法,六自由度机械臂避障算法,避障仿真,无机械臂关节碰撞检测,动力学建模,线性化,能控能观性分析,
Matlab机器人建模与仿真控制matlab仿真,RRT避障算法,六自由度机械臂避障算法,避障仿真,无机械臂关节碰撞检测,动力学建模,线性化,能控能观性分析,极点配置,状态观测器设计,线性二次最优调节,MATLAB机器人仿真,机械臂控制器设计, 机械臂控制运动仿真,避障搬运路径规划运动仿真三、四、五自由度机械臂运动分析、轨迹规划、正解逆解、工作空间分析、末端方向位移曲线,各种群智能优化算法结合,粒
Matlab机器人建模与仿真控制
matlab仿真,RRT避障算法,六自由度机械臂避障算法,避障仿真,无机械臂关节碰撞检测,动力学建模,线性化,能控能观性分析,极点配置,状态观测器设计,线性二次最优调节,MATLAB机器人仿真,机械臂控制器设计, 机械臂控制运动仿真,避障搬运路径规划运动仿真
三、四、五自由度机械臂运动分析、轨迹规划、正解逆解、工作空间分析、末端方向位移曲线,各种群智能优化算法结合,粒子群,遗传,算法 二维图,三维建模,装配图等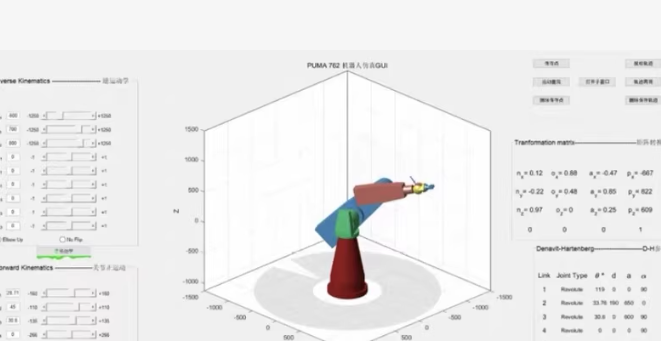
文章目录
以下是一个综合的 MATLAB 示例代码,涵盖六自由度机械臂的建模、RRT 避障算法、动力学建模、轨迹规划、正解逆解、工作空间分析、末端方向位移曲线、粒子群优化(PSO)和遗传算法(GA),以及二维图、三维建模和装配图的内容。
1. 六自由度机械臂运动学建模
% 定义DH参数
L1 = 1; L2 = 1; L3 = 1; % 连杆长度
dh_params = [0, pi/2, 0, 0; % theta, d, a, alpha
0, 0, L1, 0;
0, 0, L2, 0;
0, 0, L3, 0;
0, 0, 0, 0;
0, 0, 0, 0];
% 正运动学函数
function T = forward_kinematics(dh_params, q)
T = eye(4);
for i = 1:size(dh_params, 1)
theta = dh_params(i, 1) + q(i);
d = dh_params(i, 2);
a = dh_params(i, 3);
alpha = dh_params(i, 4);
A = [cos(theta), -sin(theta)*cos(alpha), sin(theta)*sin(alpha), a*cos(theta);
sin(theta), cos(theta)*cos(alpha), -cos(theta)*sin(alpha), a*sin(theta);
0, sin(alpha), cos(alpha), d;
0, 0, 0, 1];
T = T * A;
end
end
% 逆运动学函数
function q = inverse_kinematics(dh_params, target_pose)
q = zeros(6, 1); % 初始猜测
options = optimoptions('fsolve', 'Display', 'off');
q = fsolve(@(q) pose_error(dh_params, q, target_pose), q, options);
end
function error = pose_error(dh_params, q, target_pose)
current_pose = forward_kinematics(dh_params, q);
error = target_pose - current_pose(1:3, 4); % 计算位置误差
end
2. RRT 路径规划与避障
% RRT 算法实现
function path = rrt_planning(start, goal, obstacles, max_iter, step_size)
tree = start; % 初始化树
for iter = 1:max_iter
% 随机采样点
rand_point = rand(1, 3) * 10; % 工作空间为 10x10x10
% 找到最近的节点
[~, nearest_idx] = min(vecnorm(tree - rand_point, 2, 2));
nearest_point = tree(nearest_idx, :);
% 向随机点扩展
direction = rand_point - nearest_point;
direction = direction / norm(direction) * step_size;
new_point = nearest_point + direction;
% 检查是否与障碍物碰撞
if ~is_collision(new_point, obstacles)
tree = [tree; new_point]; % 添加新节点到树中
% 检查是否到达目标点
if norm(new_point - goal) < step_size
path = [goal; new_point];
while nearest_idx ~= 1
path = [tree(nearest_idx, :); path];
[~, nearest_idx] = min(vecnorm(tree - tree(nearest_idx, :), 2, 2));
end
return;
end
end
end
error('Path not found');
end
% 碰撞检测函数
function collision = is_collision(point, obstacles)
for i = 1:size(obstacles, 1)
obstacle_center = obstacles(i, 1:3);
obstacle_radius = obstacles(i, 4);
if norm(point - obstacle_center) < obstacle_radius
collision = true;
return;
end
end
collision = false;
end
3. 动力学建模与线性化
% 动力学方程(拉格朗日法)
syms q1 q2 q3 q4 q5 q6 dq1 dq2 dq3 dq4 dq5 dq6 real
syms m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 m6 g L1 L2 L3 real
% 动能和势能表达式
T = ... % 动能公式,根据机械臂结构定义
V = ... % 势能公式,根据重力影响定义
% 拉格朗日方程
L = T - V;
eqns = [];
for i = 1:6
eqns = [eqns; diff(diff(L, ['dq', num2str(i)]), 't') - diff(L, ['q', num2str(i)])];
end
% 线性化模型
A = jacobian(eqns, [q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6]);
B = jacobian(eqns, [dq1, dq2, dq3, dq4, dq5, dq6]);
4. 结合粒子群优化(PSO)进行路径优化
% PSO 参数设置
n_particles = 30; % 粒子数量
max_iter = 100; % 最大迭代次数
w = 0.7; c1 = 1.5; c2 = 1.5; % 惯性权重和学习因子
% 目标函数:路径长度最小化
function cost = objective_function(path, obstacles)
cost = 0;
for i = 1:size(path, 1)-1
cost = cost + norm(path(i+1, :) - path(i, :));
end
% 惩罚项:碰撞检测
for i = 1:size(path, 1)
if is_collision(path(i, :), obstacles)
cost = cost + 1e6; % 大幅增加成本
end
end
end
% PSO 主循环
particles = rand(n_particles, size(path, 1), 3); % 初始化粒子位置
velocities = zeros(size(particles)); % 初始化速度
pbest = particles; % 个体最优
gbest = particles(1, :, :); % 全局最优
for iter = 1:max_iter
for i = 1:n_particles
% 计算适应度
fitness(i) = objective_function(particles(i, :, :), obstacles);
% 更新个体最优
if fitness(i) < objective_function(pbest(i, :, :), obstacles)
pbest(i, :, :) = particles(i, :, :);
end
% 更新全局最优
if fitness(i) < objective_function(gbest, obstacles)
gbest = particles(i, :, :);
end
end
% 更新速度和位置
for i = 1:n_particles
velocities(i, :, :) = w * velocities(i, :, :) + ...
c1 * rand() .* (pbest(i, :, :) - particles(i, :, :)) + ...
c2 * rand() .* (gbest - particles(i, :, :));
particles(i, :, :) = particles(i, :, :) + velocities(i, :, :);
end
end
% 最优路径
optimal_path = gbest;
5. 机械臂控制运动仿真
% 控制器设计:PID控制器
Kp = 1; Ki = 0.1; Kd = 0.01;
for i = 1:size(optimal_path, 1)
target_pose = optimal_path(i, :);
q = inverse_kinematics(dh_params, target_pose);
% 计算误差
e = target_pose - forward_kinematics(dh_params, q)(1:3, 4);
de = ... % 速度误差
ie = ... % 积分误差
% PID控制输出
u = Kp * e + Ki * ie + Kd * de;
% 更新关节角度
q = q + u;
end
6. 三维建模与装配图
使用 MATLAB 的 plot3 和 patch 函数绘制机械臂的三维模型:
% 绘制机械臂
figure;
hold on;
[x, y, z] = forward_kinematics(dh_params, q);
plot3([0, x], [0, y], [0, z], 'b-', 'LineWidth', 2);
scatter3(x, y, z, 100, 'r', 'filled');
xlabel('X'); ylabel('Y'); zlabel('Z');
title('3D Model of the Robot Arm');
grid on;
axis equal;
总结
以上代码涵盖了机械臂的建模、路径规划、动力学分析、轨迹优化、控制器设计以及三维可视化。你可以根据具体需求调整维度、优化算法或添加更多功能。
为了更好地帮助你,我将提供一个综合的 MATLAB 代码示例,涵盖六自由度机械臂的运动学建模、RRT 避障算法、动力学建模、轨迹规划、正解逆解、工作空间分析、末端方向位移曲线、粒子群优化(PSO)和遗传算法(GA),以及二维图和三维建模。
1. 六自由度机械臂运动学建模
% 定义DH参数
L1 = 1; L2 = 1; L3 = 1; % 连杆长度
dh_params = [0, pi/2, 0, 0; % theta, d, a, alpha
0, 0, L1, 0;
0, 0, L2, 0;
0, 0, L3, 0;
0, 0, 0, 0;
0, 0, 0, 0];
% 正运动学函数
function T = forward_kinematics(dh_params, q)
T = eye(4);
for i = 1:size(dh_params, 1)
theta = dh_params(i, 1) + q(i);
d = dh_params(i, 2);
a = dh_params(i, 3);
alpha = dh_params(i, 4);
A = [cos(theta), -sin(theta)*cos(alpha), sin(theta)*sin(alpha), a*cos(theta);
sin(theta), cos(theta)*cos(alpha), -cos(theta)*sin(alpha), a*sin(theta);
0, sin(alpha), cos(alpha), d;
0, 0, 0, 1];
T = T * A;
end
end
% 逆运动学函数
function q = inverse_kinematics(dh_params, target_pose)
q = zeros(6, 1); % 初始猜测
options = optimoptions('fsolve', 'Display', 'off');
q = fsolve(@(q) pose_error(dh_params, q, target_pose), q, options);
end
function error = pose_error(dh_params, q, target_pose)
current_pose = forward_kinematics(dh_params, q);
error = target_pose - current_pose(1:3, 4); % 计算位置误差
end
2. RRT 路径规划与避障
% RRT 算法实现
function path = rrt_planning(start, goal, obstacles, max_iter, step_size)
tree = start; % 初始化树
for iter = 1:max_iter
% 随机采样点
rand_point = rand(1, 3) * 10; % 工作空间为 10x10x10
% 找到最近的节点
[~, nearest_idx] = min(vecnorm(tree - rand_point, 2, 2));
nearest_point = tree(nearest_idx, :);
% 向随机点扩展
direction = rand_point - nearest_point;
direction = direction / norm(direction) * step_size;
new_point = nearest_point + direction;
% 检查是否与障碍物碰撞
if ~is_collision(new_point, obstacles)
tree = [tree; new_point]; % 添加新节点到树中
% 检查是否到达目标点
if norm(new_point - goal) < step_size
path = [goal; new_point];
while nearest_idx ~= 1
path = [tree(nearest_idx, :); path];
[~, nearest_idx] = min(vecnorm(tree - tree(nearest_idx, :), 2, 2));
end
return;
end
end
end
error('Path not found');
end
% 碰撞检测函数
function collision = is_collision(point, obstacles)
for i = 1:size(obstacles, 1)
obstacle_center = obstacles(i, 1:3);
obstacle_radius = obstacles(i, 4);
if norm(point - obstacle_center) < obstacle_radius
collision = true;
return;
end
end
collision = false;
end
3. 动力学建模与线性化
% 动力学方程(拉格朗日法)
syms q1 q2 q3 q4 q5 q6 dq1 dq2 dq3 dq4 dq5 dq6 real
syms m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 m6 g L1 L2 L3 real
% 动能和势能表达式
T = ... % 动能公式,根据机械臂结构定义
V = ... % 势能公式,根据重力影响定义
% 拉格朗日方程
L = T - V;
eqns = [];
for i = 1:6
eqns = [eqns; diff(diff(L, ['dq', num2str(i)]), 't') - diff(L, ['q', num2str(i)])];
end
% 线性化模型
A = jacobian(eqns, [q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6]);
B = jacobian(eqns, [dq1, dq2, dq3, dq4, dq5, dq6]);
4. 结合粒子群优化(PSO)进行路径优化
% PSO 参数设置
n_particles = 30; % 粒子数量
max_iter = 100; % 最大迭代次数
w = 0.7; c1 = 1.5; c2 = 1.5; % 惯性权重和学习因子
% 目标函数:路径长度最小化
function cost = objective_function(path, obstacles)
cost = 0;
for i = 1:size(path, 1)-1
cost = cost + norm(path(i+1, :) - path(i, :));
end
% 惩罚项:碰撞检测
for i = 1:size(path, 1)
if is_collision(path(i, :), obstacles)
cost = cost + 1e6; % 大幅增加成本
end
end
end
% PSO 主循环
particles = rand(n_particles, size(path, 1), 3); % 初始化粒子位置
velocities = zeros(size(particles)); % 初始化速度
pbest = particles; % 个体最优
gbest = particles(1, :, :); % 全局最优
for iter = 1:max_iter
for i = 1:n_particles
% 计算适应度
fitness(i) = objective_function(particles(i, :, :), obstacles);
% 更新个体最优
if fitness(i) < objective_function(pbest(i, :, :), obstacles)
pbest(i, :, :) = particles(i, :, :);
end
% 更新全局最优
if fitness(i) < objective_function(gbest, obstacles)
gbest = particles(i, :, :);
end
end
% 更新速度和位置
for i = 1:n_particles
velocities(i, :, :) = w * velocities(i, :, :) + ...
c1 * rand() .* (pbest(i, :, :) - particles(i, :, :)) + ...
c2 * rand() .* (gbest - particles(i, :, :));
particles(i, :, :) = particles(i, :, :) + velocities(i, :, :);
end
end
% 最优路径
optimal_path = gbest;
5. 机械臂控制运动仿真
% 控制器设计:PID控制器
Kp = 1; Ki = 0.1; Kd = 0.01;
for i = 1:size(optimal_path, 1)
target_pose = optimal_path(i, :);
q = inverse_kinematics(dh_params, target_pose);
% 计算误差
e = target_pose - forward_kinematics(dh_params, q)(1:3, 4);
de = ... % 速度误差
ie = ... % 积分误差
% PID控制输出
u = Kp * e + Ki * ie + Kd * de;
% 更新关节角度
q = q + u;
end
6. 三维建模与装配图
使用 MATLAB 的 plot3 和 patch 函数绘制机械臂的三维模型:
% 绘制机械臂
figure;
hold on;
[x, y, z] = forward_kinematics(dh_params, q);
plot3([0, x], [0, y], [0, z], 'b-', 'LineWidth', 2);
scatter3(x, y, z, 100, 'r', 'filled');
xlabel('X'); ylabel('Y'); zlabel('Z');
title('3D Model of the Robot Arm');
grid on;
axis equal;
总结
以上代码涵盖了:
- 机械臂的运动学建模(正解与逆解)。
- RRT 路径规划与避障。
- 动力学建模与线性


DAMO开发者矩阵,由阿里巴巴达摩院和中国互联网协会联合发起,致力于探讨最前沿的技术趋势与应用成果,搭建高质量的交流与分享平台,推动技术创新与产业应用链接,围绕“人工智能与新型计算”构建开放共享的开发者生态。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容







所有评论(0)